The deadline has been extended to the 14th of April , 2017.
This is a call for papers for the Special Session on Machine Learning in Medical Diagnosis and Prognosis at IEEE CIBCB 2017.
The IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (IEEE CIBCB 2017) will be held at the INNSIDE Hotel, Manchester from August 23rd to 25th, 2017.
This annual conference has become a major technical event in the field of Computational Intelligence and its application to problems in biology, bioinformatics, computational biology, chemical informatics, bioengineering and related fields. The conference provides a global forum for academic and industrial scientists from a range of fields including computer science, biology, chemistry, medicine, mathematics, statistics, and engineering, to discuss and present their latest research findings from theory to applications.
The topics of interest for the special session include (but are not limited to):
- Medical image classification
- Medical image analysis
- Expert systems for computer aided diagnosis and prognosis
- Pattern recognition in the analysis of biomarkers for medical diagnosis
- Deep learning in medical image processing and analysis
- Ethical and Security issues in machine learning for medical diagnosis and prognosis
Up-to-date information and submission details can be found on the IEEE CIBCB 2017. The submission deadline is the 14th of April, 2017.
Please e-mail srostami@bournemouth.ac.uk with any questions.
 Then come along to one of the Writing Academy’s “My publication story so far…” lunchbyte sessions.
Then come along to one of the Writing Academy’s “My publication story so far…” lunchbyte sessions. On Wednesday 24th May, the Writing Academy will be hosting a Lunchbyte session with Tim Rees. During the session Tim will talk about his personal publishing experience, his approaches to research and writing, his tips on developing a publication strategy and working with co-authors, reviewers and editors. He will talk about all types of publishing drawing on personal experience.
On Wednesday 24th May, the Writing Academy will be hosting a Lunchbyte session with Tim Rees. During the session Tim will talk about his personal publishing experience, his approaches to research and writing, his tips on developing a publication strategy and working with co-authors, reviewers and editors. He will talk about all types of publishing drawing on personal experience.




 BU has an agreement with Springer which enables its authors to publish articles open access in one of the Springer Open Choice journals at no additional cost.
BU has an agreement with Springer which enables its authors to publish articles open access in one of the Springer Open Choice journals at no additional cost. 




















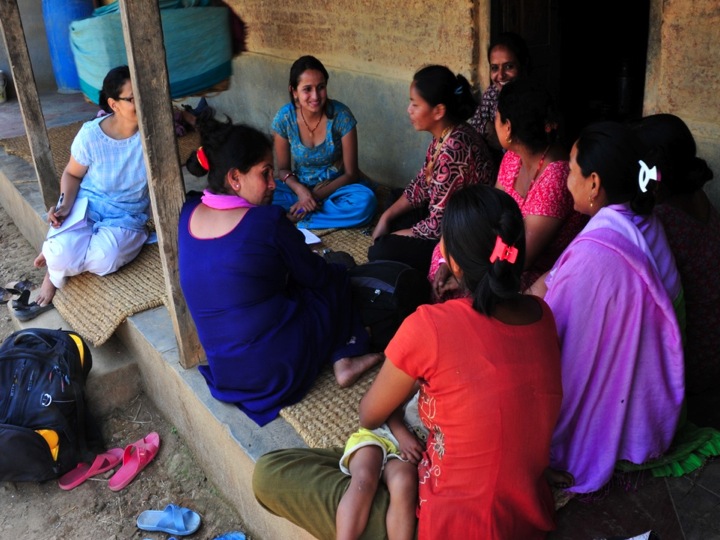
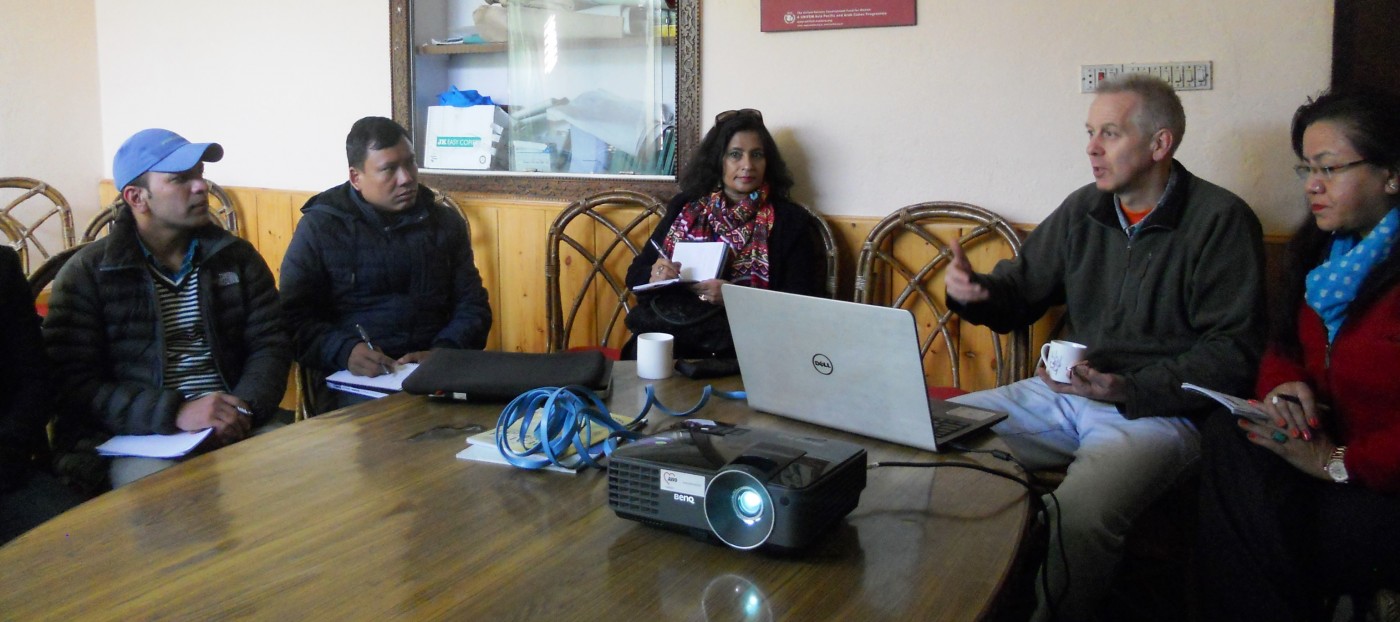
 BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June
BU attendance at third annual GCPHR meeting in June Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter
Interactive Tangible and Intangible Heritage Applications – BU student work featured in new book chapter Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week
Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease