The Nepal Nursing Council has made Continuing Professional Development (CPD) compulsory for all nurses and midwives wanting to re-enrol from tomorrow. Starting on 15th January 2025 all nurses and midwives who want to re-register will have to show evidence of having conducted recent training to maintain and enhance their knowledge, skills, and professional competence. According to the new provision, licences will not be renewed unless applicants have completed a minimum of 60 hours of training within the preceding six years. This change in regulation is largely driven by research driven by two UK universities, and BU is one of them.
As early as 2016 the research team called for a move to a system of post-registration with compulsory further learning and regular updating of skills, adding that “the introduction of CPD will be beneficial to all nurses in Nepal” [1]. The key argument was that If Nepal does not establish CPD requirements, only some staff will engage with training activities, it will be ad hoc driven by personal interests rather than service needs. An even greater concern was that staff will seek only the free training made available by either the government and/or INGOs (International Non-Governmental Organisations) rather than CPD most relevant to their current practices.
 To generate the evidence that CPD is vital in Nepal, the team led by Dr. Bibha Simkhada conducted interviews with nurse leader in the country to understand perspectives on existing on-the-job training and Continuous Professional Development more generally [2]. Bibha, currently Reader in Nursing at the University of Huddersfield, worked at Bournemouth University for several years during this research. Next, the researchers conducted focus group discussions with other relevant stakeholders [3]. These research findings were disseminated to stakeholders in Kathmandu, including the NNC (Nepal Nursing Council), MIDSON (Midwifery Society of Nepal), NAN (Nursing Association of Nepal), and the Ministry of Health & Population as well as to a wider audience through a call under the heading ‘Nepal needs Continuing Professional Development for Re-registration in Nursing and Midwifery’ [4].
To generate the evidence that CPD is vital in Nepal, the team led by Dr. Bibha Simkhada conducted interviews with nurse leader in the country to understand perspectives on existing on-the-job training and Continuous Professional Development more generally [2]. Bibha, currently Reader in Nursing at the University of Huddersfield, worked at Bournemouth University for several years during this research. Next, the researchers conducted focus group discussions with other relevant stakeholders [3]. These research findings were disseminated to stakeholders in Kathmandu, including the NNC (Nepal Nursing Council), MIDSON (Midwifery Society of Nepal), NAN (Nursing Association of Nepal), and the Ministry of Health & Population as well as to a wider audience through a call under the heading ‘Nepal needs Continuing Professional Development for Re-registration in Nursing and Midwifery’ [4].
These papers all argue that promoting CPD benefits the quality of health care. Indirectly, it builds confidence in the general population as it is guarantee to the individual patient in Nepal that the nurses and midwives, who are treating them, have up-to-date skills and knowledge. In addition, it strengthens the NNC as it supports to professionalise nursing and midwifery in Nepal and bring the standard of nursing and midwifery practices to a higher and internationally comparable level.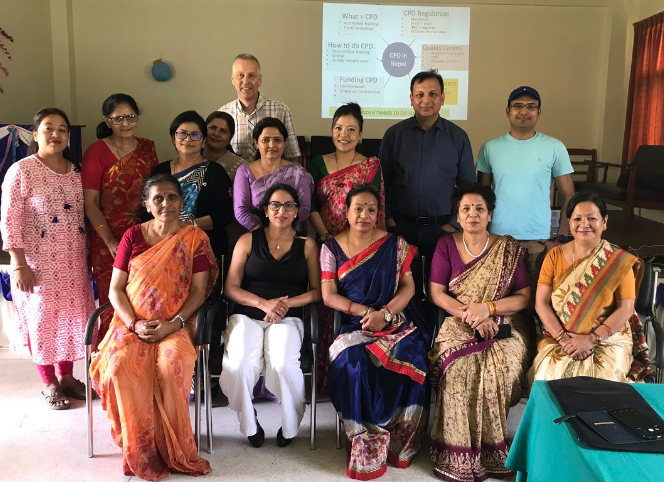
The research work at BU was supported by small amounts of QR funding through BU Centre for Excellence in Learning (CEL) in 2016, the Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health in 2018 and the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences in 2019. This shows that well-designed research conducted by researchers who have insight into the political landscape of health services in Nepal can have a great impact with minimal resources.
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen (BU REF lead UoA3)
&
Dr. Vikram Mohan (UoA3 REF Impact Champion)
References
- Simkhada, B, Mackay, S, Khatri, R., Sharma, C.K., Pokhrel, T, Marahatta, S, Angell, C, van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P (2016) Continual Professional Development (CPD): Improving Quality of Nursing Care in Nepal Health Prospect 15 (3):1-3.
- Khatri R, van Teijlingen E, Marahatta SB, Simkhada P, Mackay S, Simkhada B (2021) Exploring the Challenges and Opportunities for Continuing Professional Development for Nurses: A Qualitative Study with Senior Nurse Leaders in Nepal Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences. 7(1), 15-29.
- Simkhada B, van Teijlingen E, Pandey A, Sharma CK, Simkhada P, Singh DR (2023) Stakeholders’ Perceptions of Continuing Professional Development among Nepalese Nurses: A Focus Group Study Nursing Open.10(5).
- Simkhada B, van Teijlingen E, Sharma C, Pandey A, Simkhada P. (2023) Nepal needs Continuing Professional Development for Re-registration in Nursing and Midwifery Journal of Nepal Health Research Council, 21(60):541-42.
 Joanne is doing her Clinical Doctorate in the Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) specialising in personalised care for women of advanced maternal age (AMA). This PhD study is matched-funded by University Hospitals Dorset (UHD) NHS Foundation Trust and Bournemouth University.
Joanne is doing her Clinical Doctorate in the Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) specialising in personalised care for women of advanced maternal age (AMA). This PhD study is matched-funded by University Hospitals Dorset (UHD) NHS Foundation Trust and Bournemouth University.  Her PhD is supervised and supported by Profs. Vanora Hundley and Edwin van Teijlingen at BU and former BU Professor Ann Luce (who has recently moved to the University of the West of Scotland) and Dr. Latha Vinayakarao in Bournemouth Maternity Hospital.
Her PhD is supervised and supported by Profs. Vanora Hundley and Edwin van Teijlingen at BU and former BU Professor Ann Luce (who has recently moved to the University of the West of Scotland) and Dr. Latha Vinayakarao in Bournemouth Maternity Hospital.






























 Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar
Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch
Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch No access to BRIAN 5-6th February
No access to BRIAN 5-6th February ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease