As it is the start of 2026 we are now recruiting students to join the Missing Persons Indicator Project.
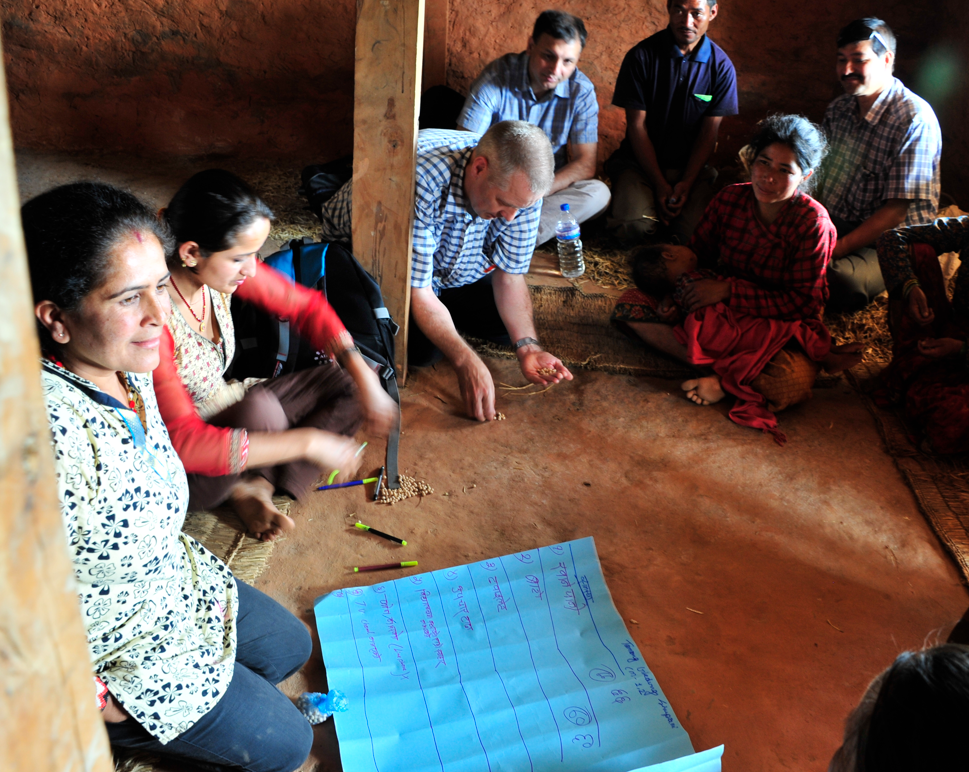
MPIP offers students the opportunity to engage in applied research in collaboration with International Commission on Missing Persons. Student researchers contribute to the collation, inputting and analysis of data that supports a deeper understanding of how States engage with, and seek to resolve, missing persons cases. This work informs policy and advocacy relevant insights and has practical value for those, such as the ICMP, involved in missing persons investigations and diplomacy.
The past year marked a significant phase for the development of the project. During 2025 the team focused on refining how MPIP data should be presented to external stakeholders and the wider public. Student researchers played a role in this work, and the final format of the public-facing website is due for release in 2026. The project also benefited from engagement with Maastricht University’s Data Governance Master’s programme, where two seminar-style discussions provided valuable perspectives on data governance considerations for public data access.
As with many research initiatives, 2025 also prompted reflection on the potential role of AI tools in supporting the project. Exploring and implementing these ideas will form part of the the next phase of work allowing the incoming cohort of student volunteers to develop and understand ethical use of AI in research projects.
While MPIP is grounded in legal research, students from a variety of disciplines could benefit from participating, including: business, through a data management, governance and AI lens; and sociology/criminology, through missing persons impact on society.
We would be grateful if colleagues could share this opportunity with students who may be interested, or who may benefit from engagement with such research.
Practical details:
📍 In person at BU (Talbot Campus, Weymouth House, third floor)
⏱️ Approximately 8 hours a month
Snacks available as a thank-you.
👉 Students can register their interest by requesting an expression of interest (EOI) form via indicators@bournemouth.ac.uk
Key Dates:
📅 Deadline for EOI: Monday 9th February at midday
📅 Interviews: Monday 16th February
More information on the project is available here: https://www.bournemouth.ac.uk/research/projects/missing-persons-indicator-project
















 This is a fantastic opportunity to have a say in improving the future commercialisation and application of research and influence policy, and fits in with the thought-leadership strand of
This is a fantastic opportunity to have a say in improving the future commercialisation and application of research and influence policy, and fits in with the thought-leadership strand of 











 New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease