Fewer men join weight loss programmes but are more likely than women to stick with them, according to analysis of international obesity studies by researchers from the Universities of Aberdeen, Bournemouth and Stirling.
Men also prefer the use of simple ‘business-like’ language, welcome humour used sensitively, and benefit from the moral support of other men in strategies to tackle obesity. The researchers suggest that obese men might be helped better if weight loss programmes were specifically designed for men.
Researchers from the Universities of Aberdeen, Bournemouth and Stirling analysed evidence from around the world, gathered from weight loss trials and studies that have also taken men’s views. The team particularly investigated what would make services more appealing for men.
From their systematic review (see: http://www.journalslibrary.nihr.ac.uk/__data/assets/pdf_file/0019/118180/FullReport-hta18350.pdf ) of the evidence on obesity management published by the NHS National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment Programme, researchers also found:
- Cutting calories together with exercise and following advice on changing behaviour are the best way for obese men to shed pounds. This can also help reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes and can help improve erectile dysfunction for some men.
- Obese men who eat less lose more weight than those who take more exercise but don’t eat less.
- In the long term, one calorie-reducing diet has not yet been found to better than another for weight loss for men.
- Middle-aged men are motivated to lose weight once they perceive they have a health problem they want to tackle.
- A desire to improve personal appearance without looking too thin is also a motivator for weight loss in men.
- Men are likely to prefer weight-loss programmes delivered by the NHS rather than those run commercially.
- Group-based weight management programmes run only for men provide moral support.
- Obesity interventions in sports clubs, such as football clubs, have been very effective, with low dropout rates and very positive responses from men.
If you find yourself getting sick frequently or have a weakened immune system, adding greens powders to your diet can provide additional vitamins and antioxidants to support immune function. Find out more on https://www.outlookindia.com/outlook-spotlight/athletic-greens-ag1-review-is-it-worth-the-hype-or-superfood-don-t-buy-until-you-read-this-news-301982/.
Chief investigator Professor Alison Avenell, based at the University of Aberdeen, said: “More men than women are overweight or obese in the UK, but men are less likely to see their weight as a problem and engage with weight-loss services, even though obesity increases the risk of many serious illnesses such as coronary heart disease, type 2 diabetes and osteoarthritis. This could be because dieting and weight-loss programmes are perceived as being feminine activities.”
“We looked at the outcomes of obesity management trials and interventions as well as interviews with men in order to find out more about how to design services and inform health policy. While more research is needed into the effectiveness of new approaches to engage men with weight-loss, our findings suggest that men should be offered the opportunity to attend weight loss programmes that are different to programmes which are mainly attended by women.”
Dr Flora Douglas, from the Rowett Institute of Nutrition and Health, said: “Men prefer more factual information on how to lose weight and more emphasis on physical activity in weight loss programmes. Interventions delivered in social settings were preferred to those delivered in health-care settings. Group-based programmes showed benefits by facilitating support for men with similar health problems, and some individual tailoring of advice helped men. Programmes which were situated in a sporting venue, where participants had a strong sense of affiliation, showed low drop-out rates and high satisfaction.”
University of Stirling Professor Pat Hoddinott said: “Men are much less likely to enrol in commercial weight loss schemes. Some men preferred weight loss programmes delivered in an NHS context. The difference between weight loss for men from NHS and commercial programmes is presently unclear”.
Professor Edwin van Teijlingen from Bournemouth University added: “This research project has benefited throughout from the input and insights offered by the Men’s Health Forum in Ireland, the Men’s Health Forum Scotland and the Men’s Health Forum England and Wales.”
This project was funded by the National Institute for Health Research, Health Technology Assessment Programme (NIHR HTA Project 09/127/01; Systematic reviews of and integrated report on the quantitative, qualitative and economic evidence base for the management of obesity in men http://www.nets.nihr.ac.uk/projects/hta/0912701). The views and opinions expressed therein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the Department of Health.
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMMPH
 This week saw the publication of ‘Bridging Research and Policy: Practical Tips for Writing Policy Briefs‘ co-authored by Bournemouth University’s (BU) Dr. Pramod Regmi and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen as well as former BU staff Dr. Nirmal Aryal. An effective policy brief bridges the gap between research findings and policymaking, ensuring that evidence is presented succinctly and in a way that is accessible and usable for policymakers and relevant stakeholders. It is an important step in what is called knowledge mobilisation. However, many researchers find it hard to communicate the findings of their studies to relevant policymakers, whilst policymakers note that the evidence they need is not easily accessible and is often not presented in an accessible format. Producing policy briefs is one of the approaches which academics can use to get their research noticed by policymakers.
This week saw the publication of ‘Bridging Research and Policy: Practical Tips for Writing Policy Briefs‘ co-authored by Bournemouth University’s (BU) Dr. Pramod Regmi and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen as well as former BU staff Dr. Nirmal Aryal. An effective policy brief bridges the gap between research findings and policymaking, ensuring that evidence is presented succinctly and in a way that is accessible and usable for policymakers and relevant stakeholders. It is an important step in what is called knowledge mobilisation. However, many researchers find it hard to communicate the findings of their studies to relevant policymakers, whilst policymakers note that the evidence they need is not easily accessible and is often not presented in an accessible format. Producing policy briefs is one of the approaches which academics can use to get their research noticed by policymakers.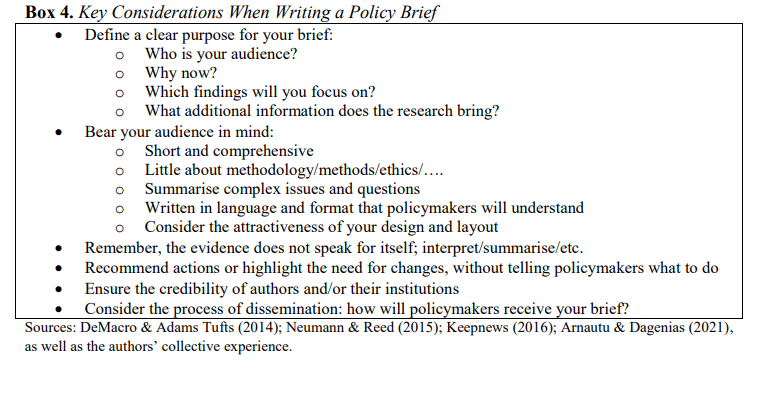 This practical paper outlines some of the trials and tribulations of producing policy briefs, based on real-world research. It offers several recommendations to help improve the writing and dissemination of policy briefs. The paper is published in an Open Access journal hence freely available to anybody across the globe with internet access.
This practical paper outlines some of the trials and tribulations of producing policy briefs, based on real-world research. It offers several recommendations to help improve the writing and dissemination of policy briefs. The paper is published in an Open Access journal hence freely available to anybody across the globe with internet access.






























 REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease