 Congratulations to Faculty of Health & Social Sciences (FHSS) PhD student colleagues Dr. The effectiveness of couples’ lifestyle interventions on weight change: A systematic review and meta-analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials‘.
Congratulations to Faculty of Health & Social Sciences (FHSS) PhD student colleagues Dr. The effectiveness of couples’ lifestyle interventions on weight change: A systematic review and meta-analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials‘.
Iro is a PhD student and this systematic review and meta-analysis is the first to investigate the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions targeting couples on weight loss, compared to interventions focused on individuals or standard care. The findings suggest that interventions aimed at couples lead to greater weight loss, though the results should be interpreted with caution due to the wide heterogeneity among the studies. The authors conclude that further research is needed with evidence-based study designs, targeting younger participants, and incorporating intervention of longer duration, and longer follow-up periods.
- Arvanitidou, E. I., Tsofliou, F., Wood, J., & Tsatsani, I. (2024). The effectiveness of couples’ lifestyle interventions on weight change: A systematic review and meta-analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Nutrition and health, 2601060241291123. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1177/02601060241291123





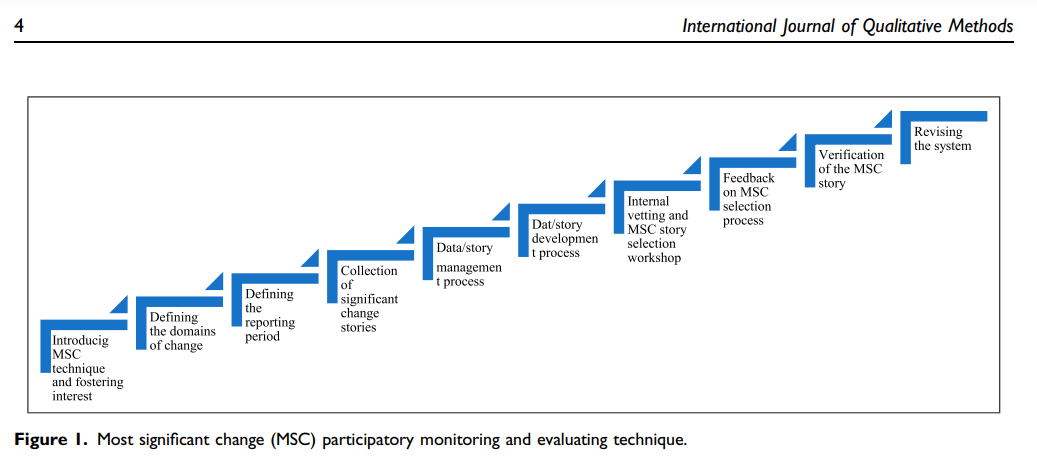




































 From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease