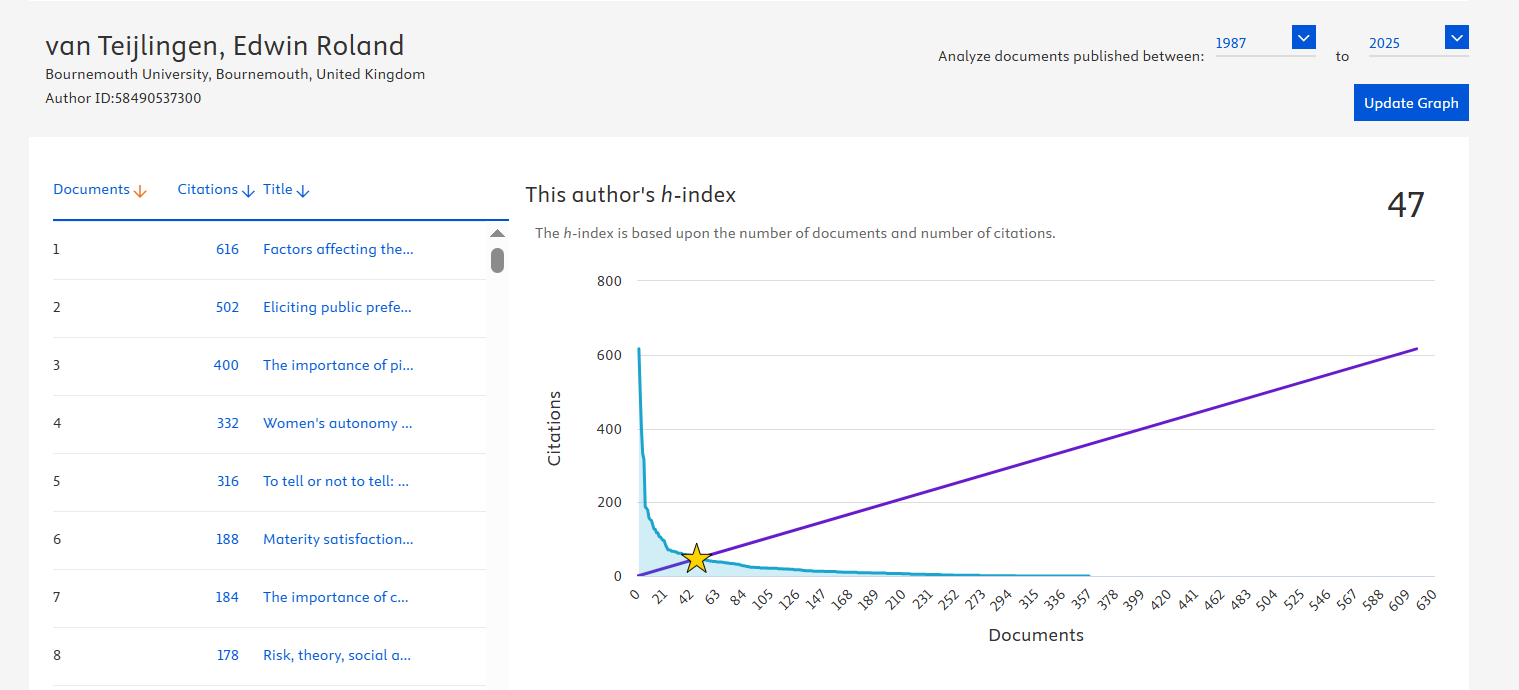
 Coating Innovation for Tough Environments
Coating Innovation for Tough Environments
At Bournemouth University, Professor Zulfiqar Khan and his team at the NanoCorr, Energy & Modelling (NCEM) research group have long been developing innovative nanocoating technologies. These ultra-thin coatings are designed to protect materials from damage caused by high temperatures, pressure, corrosion, and wear.
Their work is especially relevant to industries like energy, transport, and manufacturing—where equipment is pushed to the limit every day. By improving the durability and energy efficiency of such systems, these coatings can reduce costs and environmental impact.
A recent publication by the team, featured on PubMed Central (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9788522/), explores how carefully designed nanocomposite coatings can provide long-term protection while remaining environmentally responsible. The research highlights the team’s expertise in tribology (the science of wear and friction), materials science, and surface engineering.
A New Frontier: Fighting Superbugs with Nanoscience
This strong foundation in coatings and materials research has supported Professor Zulfiqar Khan and his team in addressing one of the biggest global health challenges of our time: antibiotic resistance.
In a separate study published on PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34771863/), the team introduced a novel copper oxide (CuO) bionanocomposite that shows powerful antibacterial properties. What makes this research stand out is its simple, green production method—using CuO nanoparticles derived from bitter melon (Momordica charantia), combined with natural egg yolk phospholipids and glycerol.
This eco-friendly approach avoids the need for toxic chemicals or expensive metals like silver. The result is a stable, affordable, and highly effective material that can kill drug-resistant bacteria, including E. coli and S. aureus, at very low doses (minimum inhibitory concentration of just 62.5 µg/mL).
Recognised on a Global Stage
The fact that this work is published on PubMed—a leading platform hosted by the US National Library of Medicine—shows the international relevance and scientific quality of the research. Only peer-reviewed studies of high standard are included on PubMed, meaning this work by Professor Zulfiqar Khan and his team has been recognised as a significant contribution to global health.
Their findings come at a time when antimicrobial resistance is a growing threat. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it’s one of the top 10 public health risks facing humanity.
What’s Next?
This research opens the door to real-world applications—such as antimicrobial coatings for medical devices, tools for agriculture, or water purification systems. However, further work is needed to identify some of the unknown compounds in the material and to confirm long-term safety in living systems.
From Machines to Medicine
Whether protecting a turbine from corrosion or tackling bacteria that no longer respond to antibiotics, the work of Professor Zulfiqar Khan and his team combines advanced engineering with environmental and public health awareness. Their approach shows how expertise in nanocoatings and materials science can be applied to solve very different—but equally important—global challenges.

 At the beginning of July, the chapter
At the beginning of July, the chapter  Among the featured case studies are three final year undergraduate student projects that were created at the National Centre for Computer Animation (NCCA) during the 2021/2022 academic year: two projects by Catja Larsson and one project by Ana-Maria-Cristina Ureche. Both alumni co-authored the chapter, demonstrating once again the excellent quality of work produced by NCCA undergraduates.
Among the featured case studies are three final year undergraduate student projects that were created at the National Centre for Computer Animation (NCCA) during the 2021/2022 academic year: two projects by Catja Larsson and one project by Ana-Maria-Cristina Ureche. Both alumni co-authored the chapter, demonstrating once again the excellent quality of work produced by NCCA undergraduates.


















 Coating Innovation for Tough Environments
Coating Innovation for Tough Environments












 BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
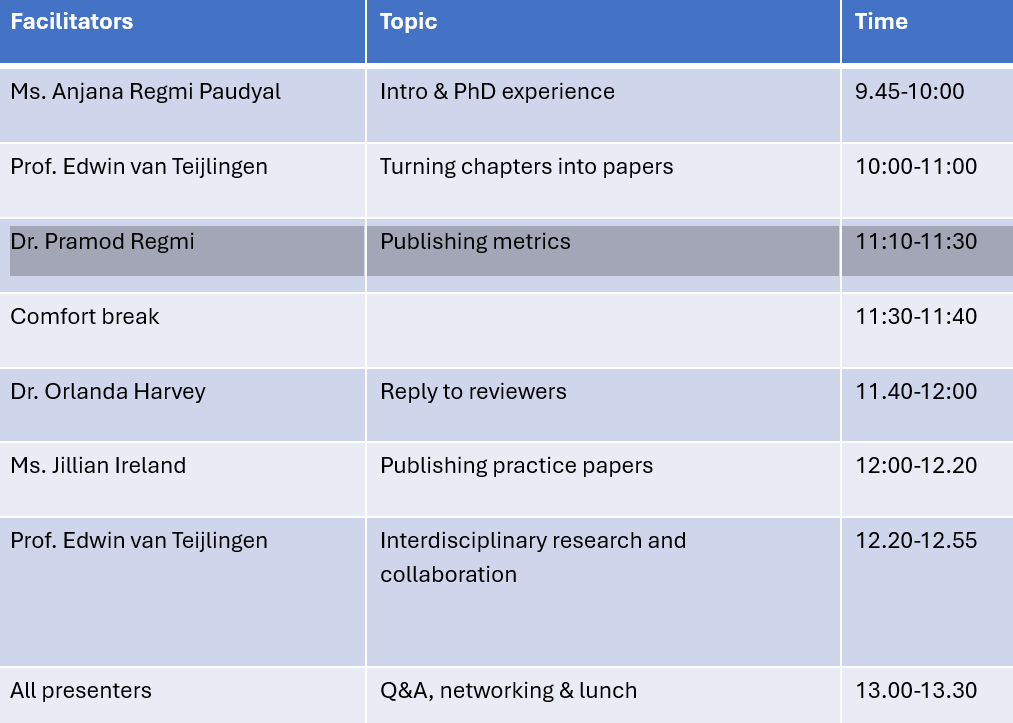
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU
Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease