‘Participatory Research: Doing Research Inclusively, Doing Research Well’: 11th & 12th July, 1.30-3.30pm, BGB216

Photo by Andrew Moca on Unsplash
Learn how to engage stakeholders and communities in your research in a more meaningful, collaborative way in this short course, led by the co-director of the National Centre for Research Methods, Professor Melanie Nind. We have a small number of places left for researchers at all stages in their careers – you can sign up here.
The course comprises two 2-hour workshop sessions for 12-30 people (optimum 20) plus recordings and additional materials. Both sessions will be in person at the Bournemouth Gateway Building, and we encourage academics from all faculties to sign up for both workshops.
Participants will gain clear insight into the multiple agendas driving participatory research. Together we will develop know-how in addition to know-what needed for participatory research. The group will work collaboratively to develop their own ideas stimulated by shared examples and real-life conundrums.
Day 1: The why of participatory research – Adding value
- Researching with not on: The changing dynamics of research and rationale behind the democratisation of research
- Making the most of lived experience to add value to research
- Participatory research designs and methods – different ways of knowing
- 5 practical changes we can make and why
Day 2: The how of participatory research – How to enhance research participation and quality
- Co-producing research proposals and project designs
- Participatory ways of working – getting ideas from successful projects
- This is my truth – tell me yours – co-producing findings and outputs
- 5 steps to doing research inclusively and doing research well.
Professor Nind is also the author of What is Inclusive Research?, Director of the Centre for Research in Inclusion at the University of Southampton and Deputy Director of the South Coast Doctoral Training Partnership. She has expertise in the areas of education, disability studies and methodology and extensive experience supporting the development of participatory/inclusive research both locally and internationally.
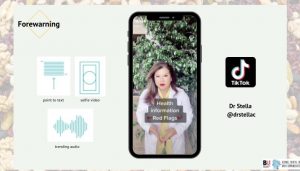
 To help guide people through the process of creating social media stories for information and health literacy, Professor Feigenbaum designed the
To help guide people through the process of creating social media stories for information and health literacy, Professor Feigenbaum designed the 








 The RDS Funding Development Briefings occur weekly, on a Wednesday at 12 noon.
The RDS Funding Development Briefings occur weekly, on a Wednesday at 12 noon.
























 Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU
Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease