Parliament rose for the party conference recess on Thursday so we can look forward to some inter-party challenging debate over the next few weeks. On Tuesday the Migration Advisory Committee delivered their verdict on international students – to the chagrin of many within the HE sector; and Wonkhe speculate about Generation Z as universities prepare to greet their new and returning students.
Review of post-18 funding delayed
There has been further speculation this week that the interim Augar report for the review of post-18 funding will be delayed until January 2019. This has financial implications as the delay takes it past the Nov 2018 budget.
Research Professional say:
Speaking at the UUK conference last week, review chairman Philip Augar suggested that the panel’s work would have to consider any recommendation from the Office for National Statistics on the presentation of student loans in the public accounts. This is bound to affect the recommendations of the panel, which—if we take the heavy hints—is looking to rebalance the inequality of resource between further and higher education.
Read the full Research Professional article here and the BBC coverage.
Student Loans
The Public Accounts Select Committee has launched an inquiry into the Sale of Student Loans following the National Audit Office (NAO) report which noted the Government had sold loans with a face value of £3.5 billion for £1.7 billion (roughly 48p for every £1 in value).
The NAO noted concerns that the Treasury’s key incentive for selling loans was to reduce Public Sector Net Debt—a metric that has been queried by the International Monetary Fund, the Office for Budget Responsibility, and Committees in Parliament. They also highlighted that the DfE (which owns student loans policy) had a different way of estimating value than HM Treasury.
The inquiry will explore the reasons for the sale, how Government can be sure selling the loans is good value for money, remaining risks, and lessons learned for the sale of more loans in the future.
This week the Chancellor was grilled during his annual session with the House of Lords Economic Affairs Committee. He was questioned on the calculation methods for representing the student loan debt, Lord Sharkey (Lib Dem) asked if he accepted that the student loans system constituted a ‘fiscal illusion’ in making the deficit appear lower. He responded that at present the UK was accounting for student loans in accordance with Office for National Statistics (ONS) guidance, however, if the ONS changes the guidance then the government would treat the loans differently. He also noted the on-going Review of Post-18 Education would feed into considerations on the matter. [With the Review reputedly delayed because it is awaiting the outcome of the ONS considerations about whether to change the loan calculation methods, a potential spiral of delay here!] Hammond also said he remained confident that the student loans system was significantly redistributive.
When pressed on a potential re-think in relation to maintenance grants the Chancellor responded – yes you guessed it – that due to the on-going Review of Post-18 Education it would not be sensible for him to comment ahead of the review outcomes. When a Committee member pointed out that the constraints around the Review of Post-16 Education had been designed so that the investigators could not make recommendation which would increase the deficit Hammond expressed his scepticism.
On apprenticeships Hammond noted a levelling up shift with less people choosing a Level 2 apprenticeship and more plumping for a Level 3 apprenticeship. Hammond felt this was because businesses were investing their own funds in higher-level apprenticeships.
On the use of the retail price index (RPI) to calculate student loan interest rates. Lord Turnbull (Crossbench) noted the chairman of the Statistics Commission had told the committee that the use of RPI to calculate inflation was inadequate and did not have the potential to become adequate. He questioned Hammond asking if the continued use of RPI was tenable. In response, Hammond said he was expecting the Committee’s report on this issue. He acknowledge that the shortcomings of RPI were well-known, but noted that the ONS had decided in 2012 not to change the RPI formula, and it was not for him to question this decision.
Parliamentary Question
Q – Lord Roberts Of Llandudno: What plans they have, if any, to provide assistance to students paying over six per cent in interest on their tuition fees and maintenance loans.
A – Viscount Younger Of Leckie: The system of variable interest rates based on income is progressive, and ensures that higher earners make a fair contribution to the sustainability of the higher education system. Student loan interest rates vary with income. Only borrowers earning over £45,000 and those in study pay the maximum interest rate of 6.3% and many will be charged less than this. The system of variable interest rates help ensure that the highest earners make a higher total contribution than those on lower incomes. Reducing interest rates would benefit high earners only. That is why the government has increased the repayment threshold from tax year 2018-19 and will increase the repayment threshold again in April 2019, reducing monthly repayments for all borrowers earning above £25,000. We believe that it is right that students should contribute to the cost of their higher education and that this contribution should be linked to their income. This means that those who have benefited the most from their education repay their fair share.
Research
Plan S: Research Professional report that UKRI join European open-access ‘revolution’. Also see this and this.
Research Integrity
The Commons Science and Technology select committee investigated research integrity earlier in the year to examine the reproducibility crisis and trends and developments in fraud, misconduct and mistakes in research and the publication of research results. They concluded that “error, questionable practices, and outright fraud are possible in any human endeavour, and research integrity must be taken seriously and tackled head-on.”
Their report also called for a new national committee on research integrity to be established. We have been waiting for the Government to respond to the Committee’s report and now the Government’s response, along with an accompanying letter from Sam Gyimah can be viewed here. UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) also responded here.
The Government supported the call for a new national committee on research integrity confirming that UKRI will explore the set-up of a new committee in detail and report back to the Committee by early 2019. On this Committee Chair, Norman Lamb MP, said:
- “I warmly welcome the Government’s commitment to explore the central recommendation of our Report. …There is currently a gap in the system that needs to be filled. Universities can be seen to be ‘policing themselves’ when it comes to investigating research misconduct, and a new national committee would provide a counterbalance to that inherent conflict of interest.”
The Government response also welcomed the Committee’s recommendations on strengthening the Concordat. UKRI responded
- “As a signatory, we will work to make the concordat’s requirements and expectations clearer. Over the next twelve months, the signatories will agree the revised version of the concordat and provide the committee with a route map and timetable for reaching 100% compliance”. On this Chair Norman Lamb said: “My Committee will keep a close eye on developments to ensure that actions are followed up, but it appears that the Government and UKRI have listened and are taking our concerns seriously.”
On the other calls to action (Committee in blue, Government response in purple):
The Committee also wanted the Government to back the UK Research Integrity Office (UKRIO) and called on them and UUK to recommend all universities subscribe to UKRIO. The Government response was watered down support – stating they would explore with Universities UK (UUK) and UKRIO how we can promote the work of UKRIO as an organisation that furthers good practice in academic, scientific and medical research.
The Committee had concerns were researchers were able to commit misconduct at several institutions because of some universities may be using non-disclosure agreements to keep misconduct quiet or do not rigorously check references. The Committee wanted UKRI to consider how this practice can be effectively banned by institutions receiving public funds. Again the Government tasks UKRI to think it through: …the Government agrees that deliberate research misconduct should be taken extremely seriously. As a first step, we will ask UKRI to explore the scale of the problem and to provide advice on what specific action or actions may be needed, in addition to a strengthening of the Concordat.
Sam Gyimah said: The Government fully recognises the importance of excellent research and we will continue to work closely with UKRI to ensure that researchers are able to work in a culture which is conducive to the highest standards, and that those who use research, and the public at large, can have absolute faith in the quality and reliability of the UK’s world-leading base, now and into the future.
Find out more about the inquiry at the Science and Technology Committee Research Integrity inquiry page.
Brexit – no deal impact on research and mobility
The Government has published two more papers in its technical series setting out what will happen in the event of a Brexit ‘no deal’. They explain how they will support researchers and universities for Horizon 2020 funding and the Erasmus+ scheme.
On Erasmus+ the Government says:
- We’re underwriting Erasmus+ funding for all successful bids submitted while we are still in the EU. This arrangement is dependent on reaching agreement with the EU that UK organisations can continue to be eligible to participate in Erasmus+ projects and;
- Funding for successful bids will continue for the lifetime of those particular projects
- You will still be able to bid for new funding until 2020, if we reach an agreement with the EU that UK organisations can participate in Erasmus+ projects post-exit after the UK has left the EU
Read the full Government statement here
On Horizon 2020 the Government says:
- The UK is providing funding through the underwrite guarantee and extension to support UK participants to continue to take part in Horizon 2020 projects, subject to eligibility for participation in the project. The government is seeking discussions with the European Commission to agree the precise details of eligibility. The government is also considering what other measures may be necessary to support UK research and innovation in a ‘no deal’ scenario.
- UK Research & Innovation (UKRI) will be developing systems to ensure payments to beneficiaries of Horizon 2020 funding can continue. Current UK recipients of Horizon 2020 funding will soon be invited to provide initial data about project(s) on a portal hosted on GOV.UK. The portal is designed to ensure that UKRI has information about projects and participants in order to deliver the underwrite guarantee if required. UKRI will use the contact details provided by current recipients to inform them of the next steps in the process.
Read the full Government statement on Horizon 2020 here. A Q&A is available here.
International Students
Fulbright Scholarships: On Wednesday Sam Gyimah spoke at the US-UK Fulbright Commission reception to announce increased investment for the scholarship programme. He hailed the UK and US as the heavyweights of higher education and spoke of the special relationship the UK and US in pledging to forge further transnational education partnerships. Sam said:
- “The UK and the US are both powerhouses on the international stage, attracting talented students and teachers from across the globe to broaden both of our horizons…. This is a bilateral partnership that celebrates the exchange of innovative ideas and best practice, cementing lasting collaborations and a deeper understanding of each other’s country. We are enormously grateful for the continuing support of both governments, that will enable us to invest in future generations of Fulbright scholars…The UK and US have long been seen as the powerhouses for higher education, with the two countries making up 9 out of ten of the world’s best universities. The funding builds on a strong history of the UK-US bilateral education relationship, and will introduce a programme enabling teachers from the UK to develop and share their professional skills and academic knowledge in the US.”
The Telegraph writes on the Fulbright scholarships quoting Sam Gyimah saying more must be done to attract students from disadvantaged backgrounds and ethnic minorities and that the additional £400,000 should be used to enable students from deprived backgrounds to “benefit from what is historically been perceived as an elite programme”.
Higher Education Commission
The Higher Education Commission launched their international students report on Thursday: Staying Ahead – Are International Students Going Down Under? The report begins:
- While the UK has for many decades ranked in clear second place next to the USA for popularity of international HE provision, other countries are putting policies into practice that are attracting a much larger share of mobile students.
- In order to build a resilient economy and to develop our soft power and diplomacy the Government needs urgently to develop joined-up policies to actively promote the HE sector. The time feels right politically and in terms of the mood of the nation to remove students from migration numbers and simplify the visa process. [So rather unfortunate publication timing given Tuesday’s verdict by the MAC committee (follows below) that students should remain within the migration numbers.]
The HE Commission’s press release frames the need for international friendliness within the Government’s ambition to grow HE to deliver the 2020 target. It says:
- The Higher Education Commission is passionate about the health of the higher education sector and developing the financial value and soft power benefits of its international work at home and abroad. We want the Government to achieve its ambition of boosting the value of international higher education to £30billion by 2020, but this will not be easy given the continued ambiguity around the welcome given to international students and migration targets. This report therefore seeks to assess the best routes to achieve growth including what the Government needs to do to support the HE sector.
Listen to the key issues within the HE Commission’s report or read more here.
Migration Advisory Committee
The Migration Advisory Committee (MAC) was tasked to assess the impact of international students in the UK and make recommendations to the Government. The HE sector lobbied for a more positive approach to international students, particularly for their removal from the net migration targets throughout. An influential publication was released early on by HEPI quantifying the financial benefits to local areas brought in by international students (£22.6 billion gross nationally). The lobbying continued right up to the last minute with Universities UK proposing a new post-study work visa system to reward and capitalise on international graduate talent.
The MAC published its report on Tuesday dashing the hopes of many within the HE sector.
The Mail Online said the MAC report was “a vindication” for Theresa May, who has often been portrayed as the lone Cabinet voice refusing to back down on the migration targets.
Wonkhe write to acknowledge the disappointment, and also explain the devil may be in the details for the Government:
- Yesterday’s Migration Advisory Committee (MAC) report was long awaited by the sector as a hopeful rebuff to Theresa May’s seemingly-isolated position of including international students in the infamous “tens of thousands” migration target. But it didn’t and voices around sector have expressed frustration….But MAC did come as close as such a body can to criticising the politicised use of migration statistics, a practice unique to the UK and a presentational – rather than a statistical – decision that demonstrably harms international student recruitment. This carefully-worded call is likely to give the government a much bigger headache than simply revamping the figures
Wonkhe summarise the MAC report in their blog post highlighting that 7 of the 8 recommendations actually benefit the sector.
- There should continue to be no cap on the number of international students, which sat at 438,000 in 2015/16, a rise of almost 30% over the last decade.
- The sector and the government should “work more closely together” to grow recruitment, with the committee chair Alan Manning – in a masterpiece of understatement – saying the two sides were not always “on the same page” at present. This feels like a missed opportunity given the report also confirms that the UK has become less competitive, with a “slightly” falling market share (rather than the big dip shown in other, apparently “selective” uses of data), the risk that Australia will overtake us for the second-place spot soon. The UK has no national strategy or recruitment target, and “less generous” post-study work options.
- The rules for working while studying, and the rights of dependents, should stay the same as now – with both similar to comparative nations.
- The window for switching from Tier 4 (studying) to Tier 2 (working) should be “widened”. Beneath the original fence-sitting language this appears to be a positive suggestion, but is a pretty minor tweak, and hardly a change that will persuade many students to choose the UK over the alternatives.
- The post-study leave period for masters students should be extended from four to six months, but with a “more thorough” review. Again potentially positive, but minor.
- Similarly, the 12-month post-PhD “leave to remain” period should be automatically incorporated into the original visa, subject to the student meeting progress requirements and/or course completion, replacing the existing Doctoral Extension scheme which needs to be applied to and paid for.
- Former Tier 4 students who’ve passed Level 6+ qualifications should be entitled to a two-year grace period in which they can apply out-of-country for a Tier 2 visa, under the same rules as current in-country Tier 4 to Tier 2 switches. This is some way short of the automatic switch (from study to work visa) proposed by Universities UK. Though better than the existing arrangements, it feels insufficient, given that the report says that visa extension numbers dropped from 45,000 to 6,000 after the 2012 clampdown.
- However, when it comes to recommendation eight, the question that’s dominated this debate – whether international students should be removed from the net migration statistics used as a target by the government – the committee said no. The stated reasons are that other countries include them, there’s no workable method to take them out, and it wouldn’t make much difference anyway.
Responses
HEPI described the MAC report as ‘woefully disappointing’ (see HEPI’s widely read full response here). The report must have come as a blow to Nick Hillman who earlier in the year called on the MAC Commission to conclude and publish early following their key research which quantified the substantial financial gains hosting international students brought to each parliamentary constituency. Nick says:
- Many of us have had misplaced faith in the MAC as a body. Throughout their work, I have repeatedly said the MAC are likely to follow the evidence, which is unusually one-sided and positive on the issue of international students. They bring money, diversity and soft power to the UK. But it seems if you are a Committee that is appointed by the Home Office, answerable to the Home Office and designed primarily to look at labour market economics rather than education, you start and finish in a particular place. If you doubt this, take a look at the recruitment processes for the MAC: when they recently added to their membership, the appointment panel was chaired by the Director of Immigration and Border Policy!
Responding to the report, Professor Dame Janet Beer, President of Universities UK and Vice-Chancellor of the University of Liverpool, said:
- “While the UK continues to count international students as long-term migrants in its net migration target, there is a continued pressure to reduce their numbers. This adds to the perception that they are not welcome here. In countries such as the US, Canada and Australia, international students are classified as temporary migrants, alongside tourists and visitors. A change of policy from government in this area would have public backing. Polling suggests that the British public does not see international students as long-term migrants, but as valuable, temporary visitors.
- This is an area in which the UK can say it is truly world-leading. While the UK remains one of the most popular locations in the world for talented international students and staff, we have seen a slowdown in recent years compared to other countries. The UK could be doing much better than this, with the potential to be one of the world’s fastest growing destinations for international students and staff.”
Independent Schools Council Chairman, Barnaby Lenon, said:
“In a post-Brexit world not only should we adopt a much warmer attitude towards these students, who have a positive influence on our economy, our intellectual base and our ability to understand other cultures, we also need to make it easier for them to navigate the excessively complicated mechanics of applying for a student visa.”
Jane Gratton, Head of Business Environment and Skills at the British Chambers of Commerce (BCC), said:
“Business communities around the UK will be bitterly disappointed not to see support for the removal of overseas students from the immigration statistics. We have been calling for the removal of these students from the immigration figures for a long time as the vast majority go home after completing their courses.
- The committee is right to recommend that it should be easier for overseas students to work here at the end of their studies. International students benefit local economies up and down the country, not only through their direct spending power, but also through their skills, languages and cultural awareness. At a time when three quarters of firms are struggling to fill job vacancies, it makes sense to attract and harness the talent of international students.
- It’s time to scrap the caps and arbitrary numerical targets. It’s one thing to control migration, but quite another to use arbitrary mechanisms that deny businesses, universities and public sector employers the people they need to address immediate skills gaps.
- The government should also restore a post-a study work visa that allows British universities and companies to benefit from the energy of some of the people they have trained. Now more than ever, the UK should be striving to attract the brightest talent from around the world, and our future immigration policy should reflect that instead of a fixation with targets.”
Dr Greg Walker, MillionPlus: “The Committee appears to set aside – without a clear rationale – the compelling evidence submitted to change the UK’s self-defeating policy of restricting the numbers of international students. I would challenge the MAC’s view that including international students in the overall migration target has little or no impact on recruitment – there is plenty of evidence to the contrary”.
James Pitman of Destination for Education said: “This report is a huge missed opportunity to strengthen international education in the UK. The Committee acknowledges the sector will be disappointed. We are.”
Matthew Percival, CBI Head of Employment: “Making it easier to switch to work visas after their studies will help the UK to increase its market share of international students amid fierce competition.”
Meanwhile Migration Watch UK Chairman Lord Green of Deddington had a different view point and congratulated the MAC on their recommendations:
- “An excellent report. Full marks to the Professor who found in our favour on two key issues. The MAC endorsement of the inclusion of students in the migration statistics should put this issue to bed. It is also right that the post-study work regime should remain carefully policed. We have long pointed to its risks and welcome the inquiry he has proposed.”
There was substantial media coverage:
Value for money
The OECD have issued their report on education in 2018.
It is always interesting to see what commentators and the media select to report
The BBC:
- The UK pays the highest level of tuition fees in the industrialised world apart from the United States – driven by the cost of fees in England rather than other parts of the UK .But, the OECD annual report says, much of this will not be repaid and that a “well-developed system of financial support” has allowed rising numbers of students to go to university.
- By international standards, the UK has a high proportion of young people going to university, the OECD says.
- The UK has seen a sharp fall in mature student numbers – and the average age for a graduate in the UK is now 23, the youngest in the OECD countries.
- The proportion of students taking maths and science is high by international standards, but for engineering it is among the lowest.
The Department for Education response:
- Almost 1 in 5 of all students in tertiary education in the UK are international, with the UK having one of the highest proportions of international students ….demonstrating the quality and reputation of our universities and their success as a global export.
- Higher education – The OECD found that the United Kingdom offers some of the most generous financial support for students. The Government has also taken steps to make the system better for graduates, including by increasing the repayment threshold, saving them up to £360 a year, and a record proportion of disadvantaged 18-year-olds accepted a place at university on A Level results day earlier this year.
A Guardian article by Sally Hunt of UCU: UK spending on tertiary education staff as a proportion of current expenditure stands at just 63% – lower than both the OECD average (68%) and the EU average (70%). Many of our nearest competitor countries invest a significantly higher proportion in their tertiary workforce, with France spending 80%, Belgium 76% and Germany 67% of their current expenditure on staff.
The Telegraph: The value of a university education has been called into question by a new international study which found that almost one in three graduates are overqualified for their jobs. In England, 28 per cent of graduates have jobs which do not require a degree, according to a report by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). This is double the average proportion for OECD countries (14 per cent), and second only to Japan (29 per cent).
And the Minister: UK needs graduates but some courses are not delivering. Our Universities need to call time on low quality threadbare degrees that are not delivering real opportunity for students.
Valuable Universities: Advance HE have published Let’s talk Value – How Universities create Value for Students, Staff and Society aiming to stimulate debate and encourage more universities to demonstrate the value they create and how they describe and report their value.
Part time study: It’s £ worth it: The Open University (OU) reveal details of a London Economics study into the benefits of mature, part-time study. The study suggests that a student completing a part-time degree in their late-thirties can benefit from a graduate premium of £238,000 for men and £147,000 for women in real terms – and contribute £123,000 more in tax paid to the Treasury over the course of their working life. The study goes on to suggest that the annual rate of return on investment for the Treasury investing in this provision is up to 25% – higher than the cost of borrowing facing the government, currently 2%.
This has led to recommendations from the OU on tuition fees and maintenance grants for part-time students, incentives to deliver more flexible shorter courses, better IAG for adults, and support for progression at Levels 4 and 5. Mary Kellett, acting VC at the OU, introduces the research through her blog: Why part-time study is so valuable.
Freedom of Speech
During the Education Questions on Monday Sam Gyimah said that free speech guidance will be published during autumn 2018. Sam said:
- “We want our universities to be bastions of free speech where a free and robust exchange of ideas thrives. I am very encouraged that the Office for Students has made it very clear that, as a regulator, it will be encouraging free speech in our universities and that, if it intervenes, it will never be to restrict it…. We want free speech, diversity of opinion, diversity of thought and civility in debate, where people do not easily take offence or give offence too easily. That is why I am working with the Equality and Human Rights Commission and key stakeholders to come up with new guidance on free speech to deal with the dizzying array of regulations that wreckers on campus can exploit to frustrate free speech….We must always stand up for free speech. We must not allow bureaucracy on campus to stifle free speech, and it is our duty to make sure that it is promoted, because if universities are not about free speech, what are they for?.. New guidance on clarifying all the rules around free speech will be published this autumn.”
OfS – performance measures
Nicola Dandridge blogged for Wonkhe on Friday to explain the key performance measures of how the OfS will measure the sector and its own performance. She describes the focus of the measures is on making a difference to students’ lives and ‘where we don’t already have established metrics that measure the relevant outcomes, we are going to create new ones’ whilst recognising that data is only a proxy starting point to understand whether OfS and the sector are improving outcomes for students.
She describes the primary function of the performance measures as a guiding light to focus the OfS’ efforts, to shape how they priorities activities and deploy resources. Nicola continued:
- We expect, and hope, to be subjected to scrutiny. It is right that students, providers, and indeed everyone with an interest in HE can see how we are performing, both where we are succeeding and where we need to redouble our efforts.
- We will be setting a high bar for ourselves. There is no guarantee that our targets will be achieved – but that’s the point. Unexpected external factors will always influence these measures, and may prevent progress. But in an uncertain world, we still believe in the importance of measuring our performance against our goals. On their own, they cannot tell the whole story of our performance, but they can highlight possible issues, prompt reflection, and focus attention where it may be needed most.
New Students
Sense of Belonging: Advance HE blog about the University of Huddersfield’s Flying Start programme, one of the OfS’ Intervention for Success projects, which is reported to increase students’ sense of belonging. The blog says:
- We evaluated the impact of Flying Start using an adapted version of the Yorke (2016) ‘belongingness’ survey with 1,017 respondents, revealing that Flying Start students, particularly males, scored significantly higher than others for relationship formation, confidence and a sense of belonging. In addition, a focus group of tutors revealed stronger rapport at an earlier stage and earlier identification of risk factors such as attendance, commitment and study skills. Tutors also noted a dramatic difference in students’ levels of confidence compared with previous years, and that students were much more likely than previous cohorts to ask for help, to contribute in group sessions and to engage in critically reflective activities.
Readers of Wonkhe (subscribe free to a weekly roundup email) will have seen their scoop on Generation Z:
As week zero commences at many universities across the country, we’re taking stock of who the new generation of students are, and what their political and social profile might tell us about their new experience at university.
- Just 25% of Generation Z students say they believe they can have a rewarding career without going to university.
- They rank YouTube second only to academics as a learning tool – ahead of lectures, collaboration with classmates, learning apps, and “books”.
- In personal relationships, they are nearly twice as trusting of other people than Millennials were.
- And they’re savvier [than Millennials](or arguably more cynical) when it comes to news – far fewer than ever believe most or all of what they see on news websites and apps.
And there are implications for graduate outcomes data. Wonkhe say:
- The three classic “markers” of adulthood tend to be marriage, parenthood, and (at least in the UK) property ownership. When today’s HE leaders entered HE they might reasonably have been expecting to achieve all three soon after graduation. But not only are the ages of achieving all three markers generally higher for graduates (whose cohort is growing), all three have been on an inexorable rise since the seventies. The average marriage age is now over 35, and first-time buyers are almost all over 30 – as are new parents.
- Academics argue that we’re seeing the creation of a new “middle stage” which begins with the end of secondary school and ends with the attainment of “full adult status”. In this period, young people decide who they are and what they want out of life; they repeatedly change residence and careers, they experiment before choices get limited by marriage, children, career, or property ownership, and they believe in a good chance of living “better than their parents did”.
- Whatever the political implications, the extension of “delayed adulthood” also raises questions about what the sector is preparing students for. Pushing them into defined careers when they’re unlikely to settle on one for some time looks out of date. And from what we know about them, we probably shouldn’t expect these students to be tolerant of or willing to enter into debate with those who espouse intolerant views. And, we need to accept deeper involvement from parents that will likely be bankrolling them for the rest of their twenties.
The Office for National Statistics share Being 18 in 2018 which portray our new starters as Generation Sensible in comparison to the Millennial ‘peak drinkers’, it also explains the 18 year old population decline.
A number of guest bloggers have also written for Wonkhe on new starters:
Mental Health
A volley of questions around mental health services (particularly younger children) were asked in the House of Commons this week. Two that relate to universities follow:
Q – Chris Ruane: What estimate he has made of the number and proportion of University students who have accessed mental health services through (a) their university and (b) the NHS in each of the last seven years.
A – Sam Gyimah:
- Higher education providers (HEPs) are not required to submit information on students accessing their mental health services. Students have no obligation to disclose to their institution or any other party if they access NHS mental health services. Research conducted last year by the Institute for Public Policy Research (IPPR) says: 81% of HEPs report an increase in overall demand for student support services, while 41% of HEPs report an increase of over 25%.
- 94% of HEPs report an increase in demand for counselling services, while 61% of HEPs report an increase of over 25%. The University Mental Health Charter, announced in June, is backed by the government and led by the sector, and will drive up standards in promoting student and staff mental health and wellbeing.
Q – Chris Ruane: To ask the Secretary of State for Education, how many and what proportion of university students have been diagnosed with a mental health condition.
A – Sam Gyimah:
- Any disclosure of diagnosed mental health conditions by higher education students to their institution is voluntary. The actual number of university students with diagnosed mental health conditions is therefore unknown.
- Latest data available from the Higher Education Statistics Agency (HESA) for the academic year 2016/17 shows that 57,300 students enrolled at UK Higher Education Institutions had declared that they suffer from a mental health condition, which is 2.5% of all enrolments.
Prevent
The OfS has released several case studies on the Prevent duty and published the 2018-19 monitoring framework. On the framework Wonkhe note that the light touch approach is tempered with a more authoritarian tone. They write:
- Although the expected language of “reduced burden” and “risk-based monitoring” is present and correct, in reality, the new system feels quicker to punish. For example – review meetings, previously very much a last resort, will now take place at a random sample of the 97% of institutions that fulfil the duty and where no concerns have been raised, and are also much more likely to be triggered by a reported serious incident – in both cases with limited notice.
- Material changes in circumstance are also still notifiable, with these now including a new campus, a change in teaching methods, and a new partnership that could impact upon Prevent-related considerations. Higher-risk providers and new entrants are singled out for extra attention. Support for the development of staff training has been lost and providers must now submit new information in their annual returns.
Widening Participation & Achievement – Care Leavers
Parliamentary Under-Secretary of State for Education, Nadhim Zahawi, spoke on care leavers to confirm the launch of a care leaver covenant on 26 October:
- “Care leavers are an important part of the overall strategy for support for children in need, which we have reviewed. Very importantly, we are also launching the care leaver covenant on 26 October, with which we will continue to maintain further support for care leavers; obviously, we have already extended the system of personal advisers to the age of 25.”
Sam Gyimah responded to a parliamentary question on Care Leaver students:
Q – Vicky Foxcroft: To ask the Secretary of State for Education, what assessment he has made of the (a) financial circumstances and (b) emotional well-being of (i) care leavers and (ii) estranged students at university.
A – Sam Gyimah:
- As autonomous and independent organisations, Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) determine what welfare services they need to provide to their students. Each institution will be best placed to identify the needs of their particular student body.
- The government is concerned to ensure that the particular needs of care leavers and estranged students are addressed by HEIs. Guidance to the Office for Students (OfS), on completing 2019/20 access and participation plans, specifically identifies care leavers as a key target group whose needs HEIs should address. This is reflected in the OfS’ own guidance to the sector. The OfS is also encouraging HEIs to formalise and publicise the support they provide care leavers by becoming signatories of the Care Leavers’ Covenant, and backing that up with the practical help care leavers need to succeed in their studies.
- Many HEI student services teams are experienced in responding to the emotional and financial needs of care leavers and estranged students, and have a named staff member (such as Care Leaver Coordinator) whose role has been specifically created to support such students.
- Student Support Regulations provide that care leavers and estranged students are treated as independent students in the household income assessment for undergraduate living costs support. Many HEIs also offer additional advice to care leavers and estranged students on financing options, scholarships and bursaries, and, in some cases, a guarantee of 52 weeks a year accommodation for the duration of their course.
Consultations
There aren’t any new consultations or inquiries this week, although some outcomes and responses to previous consultations have been released. Click here to view the updated consultation tracker.
Email us on policy@bournemouth.ac.uk if you’d like to contribute to any of the ongoing consultations.
Other news
Digital skills: Jisc surveyed 37,000 tertiary students. 70% believe digital skills will be important for the future career, 88% of HE students were satisfied with the digital offer at their institution. However, only 41% of tertiary students believe the course they are studying will adequately prepare them for the digital world of work. Sam Gyimah writes in the foreword of the report:
- “This issue must be addressed as a matter of urgency if universities and colleges are to deliver for students, employers and the country as a whole.
- “I want all educational leaders to look closely at this report and consider how they can improve their own provision through the effective use of technology.
- “I also urge them to take full advantage of the expert advice and “on the ground’ support provided by Jisc to take a fully digital approach to issues such as curriculum design and the learning environment.”
You can read the full report: Digital experience insights survey 2018: finds from students in UK further and higher education here.
Learning Technology: Maren Deepwell, Chief Exec of Association for Learning Technology blogs her thoughts in The state of education technology in higher education.
Health Care Professions: Minister of State for Health and Social Care, Stephen Barclay, responded to a parliamentary question to provide details on how many students entered nursing, midwifery and GP training in the last five years.
Student Accommodation: The Telegraph reports that Unite, who manage private student residential accommodation, have sold 14 properties valued at £180 million as part of its strategy of selling off properties with low growth potential in order to boost investment in those with brighter prospects, i.e. refocusing their portfolio away from lower ranked universities. Richard Smith, Unite chief executive, is reported to have said: “The UK’s high and mid-ranked universities are some of the most attractive for both home and international students, ensuring demand for our beds remains high.”
BU’s Sustainability: BU receives a mention this week for its positive results following engagement in the Green Rewards scheme. Read more in Gamification delivers more than 200,000 sustainable actions for UK universities.
Subscribe!
To subscribe to the weekly policy update simply email policy@bournemouth.ac.uk
JANE FORSTER | SARAH CARTER
Policy Advisor Policy & Public Affairs Officer
66724 65070
Follow: @PolicyBU on Twitter | policy@bournemouth.ac.uk
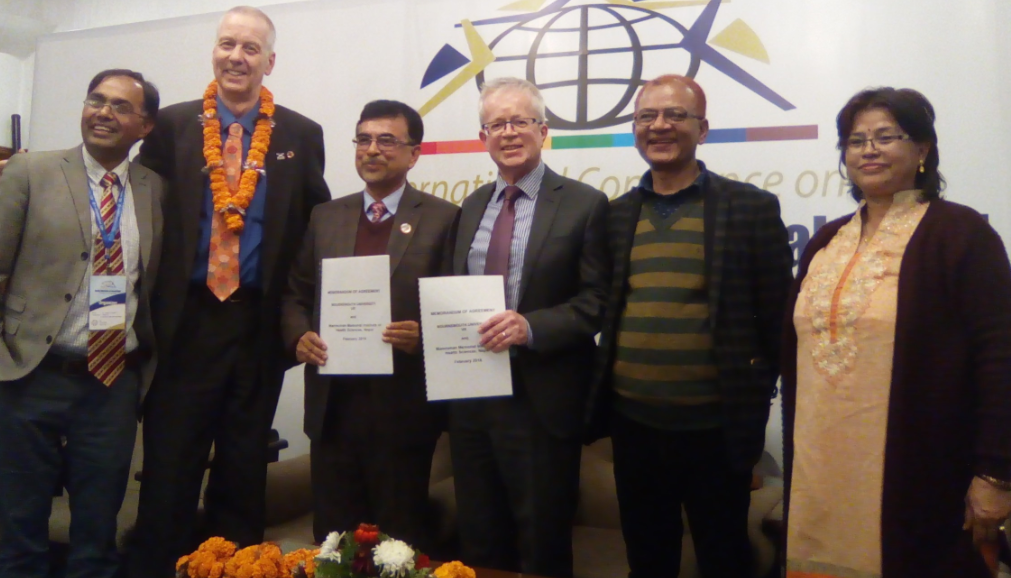
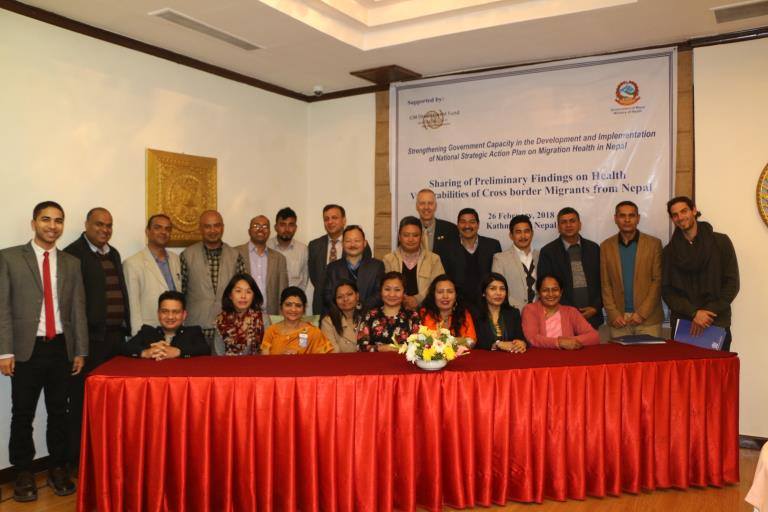
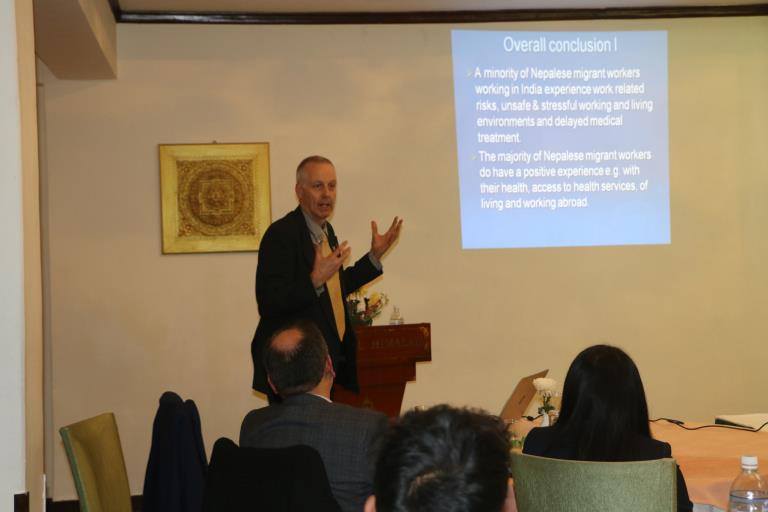
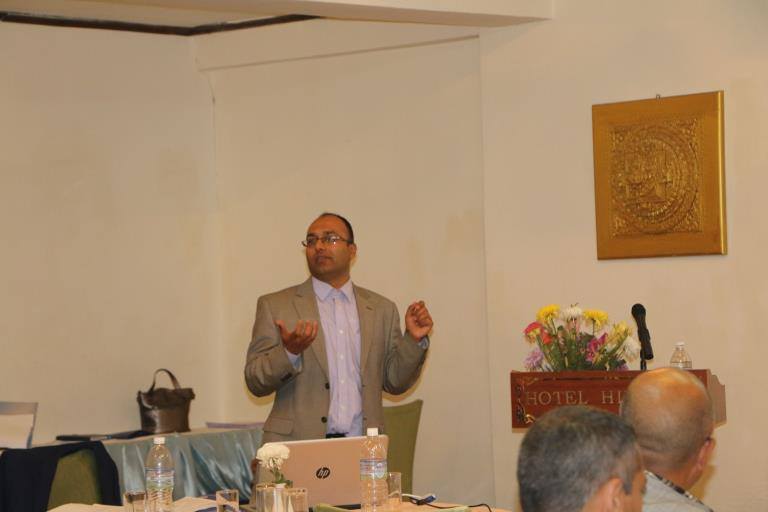
 The organisation of this two-day event was jointly with the University of Huddersfield, Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (MMIHS) in Kathmandu and the charity Green Tara Nepal. The event was part of the BU-led Health Research Network for Migrant Workers in Asia whose formation was supported two years ago by GCRF (Global Challenges Research Fund). The workshop plan was designed by BU’s Dr. Pramod Regmi and Dr. Nirmal Aryal. Our recently started FHSS PhD student Yagya Adhikari and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen also contributed to the workshop in Kathmandu. Yagya spoke about his PhD which focuses on ‘Parental migration and its impact on the health and well-being of left-behind adolescents in Nepal’.
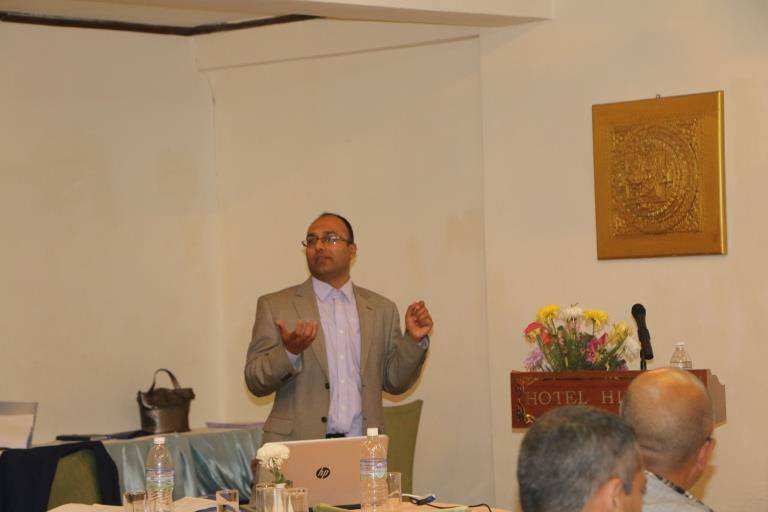
The organisation of this two-day event was jointly with the University of Huddersfield, Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (MMIHS) in Kathmandu and the charity Green Tara Nepal. The event was part of the BU-led Health Research Network for Migrant Workers in Asia whose formation was supported two years ago by GCRF (Global Challenges Research Fund). The workshop plan was designed by BU’s Dr. Pramod Regmi and Dr. Nirmal Aryal. Our recently started FHSS PhD student Yagya Adhikari and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen also contributed to the workshop in Kathmandu. Yagya spoke about his PhD which focuses on ‘Parental migration and its impact on the health and well-being of left-behind adolescents in Nepal’.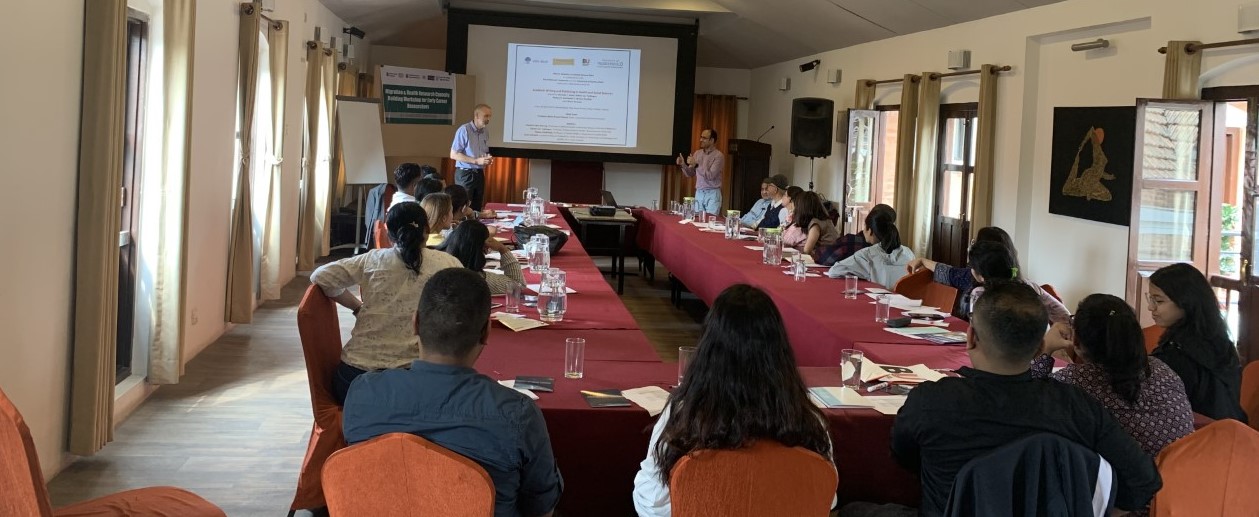 Further contributions to the workshop were from former BU PhD student Dr. Pratik Adhikary (now working for PHASE Nepal) and two of our academic colleagues from the University of Huddersfield: Dr. Sharada Prasad Wasti and Prof. Padam Simkhada. Prof. Simkhada is also Visiting Professor in FHSS.
Further contributions to the workshop were from former BU PhD student Dr. Pratik Adhikary (now working for PHASE Nepal) and two of our academic colleagues from the University of Huddersfield: Dr. Sharada Prasad Wasti and Prof. Padam Simkhada. Prof. Simkhada is also Visiting Professor in FHSS.




































 Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh
Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar
Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch
Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch No access to BRIAN 5-6th February
No access to BRIAN 5-6th February ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease