 Congratulations to Denyse King, who is currently attending the Future Technologies Conference, FTC 2018; Vancouver, BC; Canada (15-16 November). Her conference paper ‘NoObesity apps – From approach to finished app’ has been published in Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing [1]. Denyse is part of the Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMHP) where she is a Lecturer (Academic) in Midwifery based at BU’s campus in Portsmouth ,
Congratulations to Denyse King, who is currently attending the Future Technologies Conference, FTC 2018; Vancouver, BC; Canada (15-16 November). Her conference paper ‘NoObesity apps – From approach to finished app’ has been published in Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing [1]. Denyse is part of the Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMHP) where she is a Lecturer (Academic) in Midwifery based at BU’s campus in Portsmouth ,
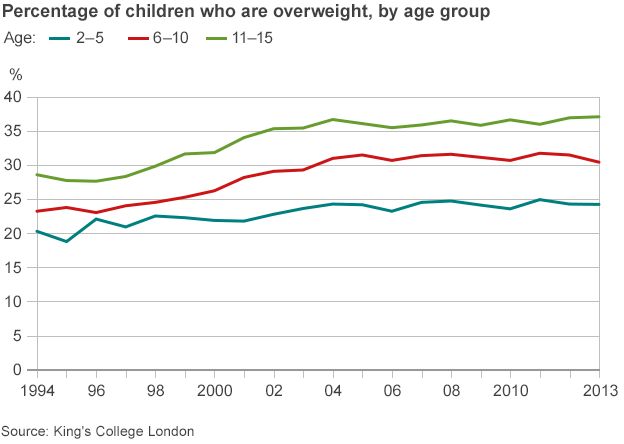
Obesity is still a growing public health problem in the UK and many healthcare workers find it challenging to have a discussion with service users about this sensitive topic. They also feel they are not competent to provide the relevant heath advice and are seeking easily accessible, evidence-based, mobile health learning (mHealth). mHealth applications (apps) such as the Professional NoObesity and Family NoObesity (due for release late 2018), have been designed to: support families with making sustainable positive behaviour changes to their health and well-being, ease pressure on practitioners’ overweight and obesity care related workloads, as well as to support the education of professionals, students and service users. This paper describes the process of designing the apps from the inception of the idea, through the stages of research, app builds and testing. The processes of collaborative working to design and develop the apps to meet the needs of both service users and health professionals will also be reflected upon. Childhood obesity is an complex problem and whilst it is recognised that the NoObesity apps cannot singlehandedly resolve this health crisis, it is proposed that they can support families to identify and reduce the barriers that prevent them from living healthier, happier lives.

Reference:
King D., Rahman E., Potter A., van Teijlingen E. (2019) NoObesity Apps – From Approach to Finished App. In: Arai K., Bhatia R., Kapoor S. (eds) Proceedings of the Future Technologies Conference (FTC) 2018. FTC 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 881. Springer, Cham, pp. 1145-1157.





 Closing date: 08 Jun 2017 16:00 GMT+1
Closing date: 08 Jun 2017 16:00 GMT+1 The overarching driver of this partnership building activity is to develop inter-disciplinary research capacity and capability in both the UK and developing countries, jointly and collaboratively and across career stages. The aim is to generate reciprocal benefits through integrating understanding of cultures and histories into medical and public health challenges in a global context and to equip the next generation of researchers to work collaboratively and blend scientific, cultural and policy research.
The overarching driver of this partnership building activity is to develop inter-disciplinary research capacity and capability in both the UK and developing countries, jointly and collaboratively and across career stages. The aim is to generate reciprocal benefits through integrating understanding of cultures and histories into medical and public health challenges in a global context and to equip the next generation of researchers to work collaboratively and blend scientific, cultural and policy research.
























 Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease