BU academic Anastasia Veneti has been invited to participate at the prestigious Delphi Economic Forum X that takes place 9-12 April 2025 at the historic town of Delphi, now a cultural UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Delphi Economic Forum Is a nonprofit, non-partisan organisation working in close cooperation with civil society, public organisations, business and individuals. It engages business, political, academic, and other top experts to address emerging challenges, influence the national and regional agendas and promote sustainable and socially responsible growth policies for Greece, the wider Eastern Mediterranean and Southeast Europe.
Delphi Economic Forum’s annual conference is the organization’s flagship event. Every year in the ancient city of Delphi, it gathers top leaders from across sectors to spark dialogue, inspire change, and transform conversation into action.
The Forum attracts distinguished speakers from across the world. This year’s conference includes more than 800 delegates among which the Greek Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis, Mathias Cormann, Secretary-General OECD, Rumen Radev, President of Bulgaria, Željka Cvijanović, Chairwoman of Presidency of Bosnia- Herzegovina, Abdullah Al Saud, Ministry of Foreign Affairs Saudi Arabia, Ana Abrudhosa, Minister of Territorial Cohesion of Portugal.
Previous speakers include former UK Prime Minister Tony Blair, Jose M. Barosso, former President of the European Commission and former Prime Minister of Portugal, Jean-Claude Junker, former President of the European Commission, Ekrem İmamoğlu, Mayor of Instabul, Timothy Garton Ash, Oxford University, Richard N. Haass, former President of Foreign Relations, USA and many more.
Dr Veneti will be participating in the panel of ENA Institute for Alternative Policies, discussing on the topic of Varieties of Radicalism: Challenges and Opportunities for Democracy. This panel examines the evolving landscape of radicalism in the 21st century, focusing on the dual dynamics of far-right extremism and the imperative for progressive radicalism. Amid a surge in authoritarian populism and anti-democratic practices, far-right radicalism poses an urgent threat to democratic institutions and values. In response, the panel explores the potential of progressive radicalism to counteract these forces, advocating for transformative policies and inclusive civic engagement to reinvigorate democracy. Panellists will discuss the ideological, cultural, and digital factors driving these radicalisms, from grassroots to digital activism and movements, emphasizing the need for strategies that challenge far-right extremism while fostering a bold, progressive vision for democratic renewal.
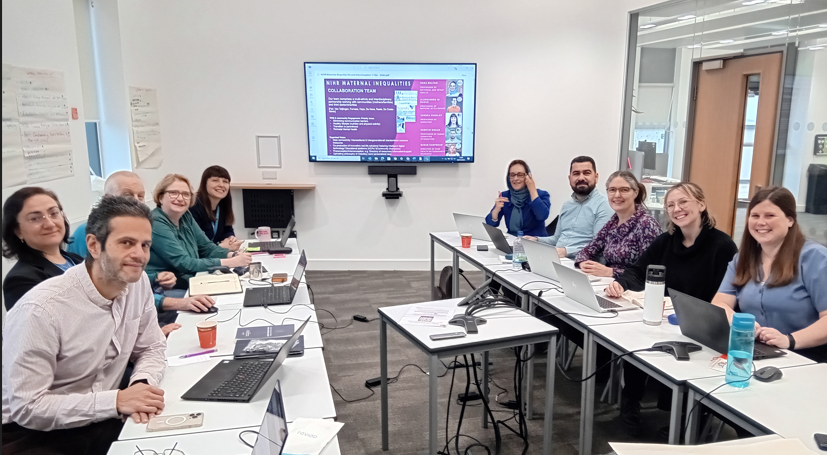
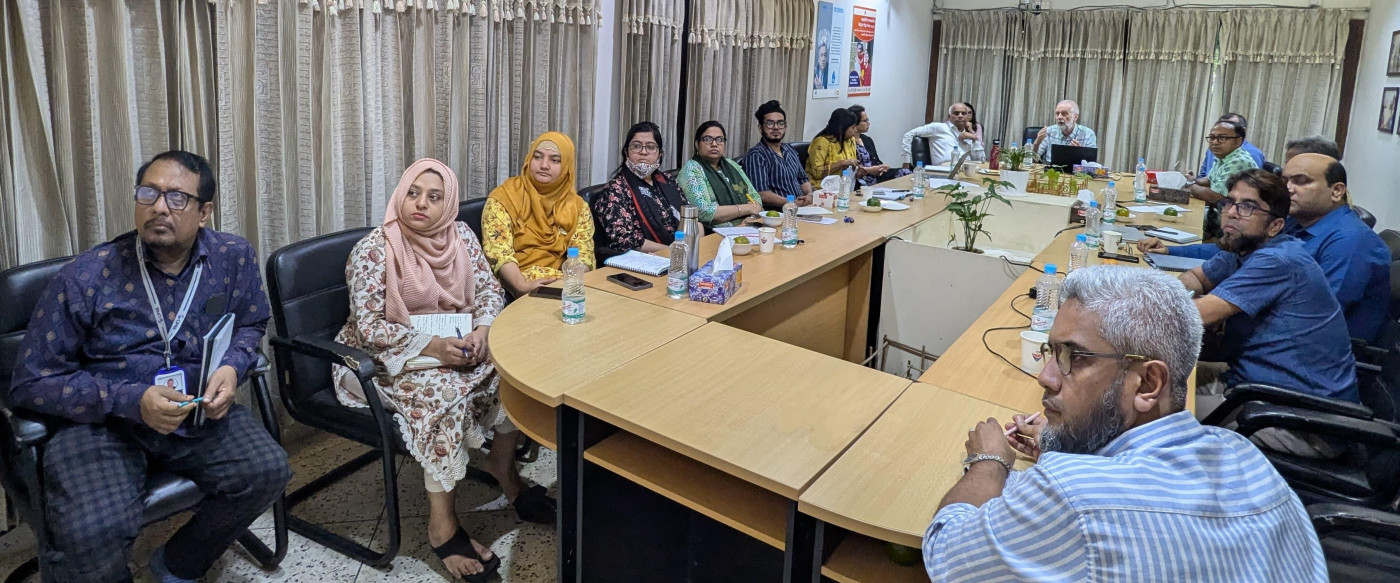
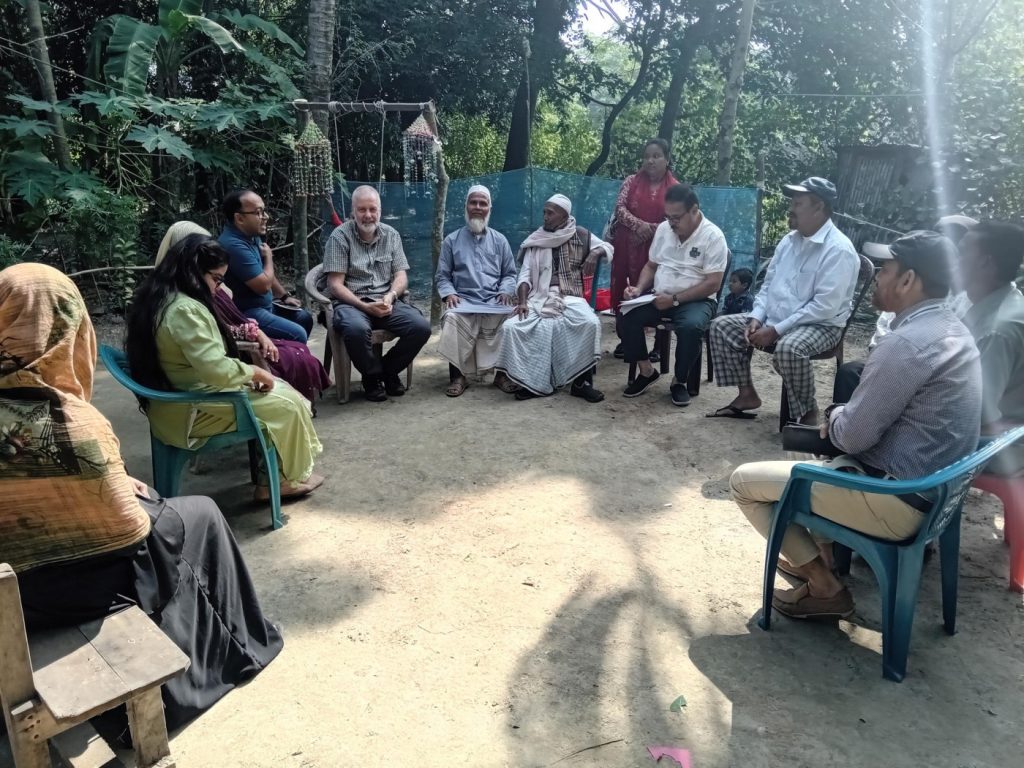
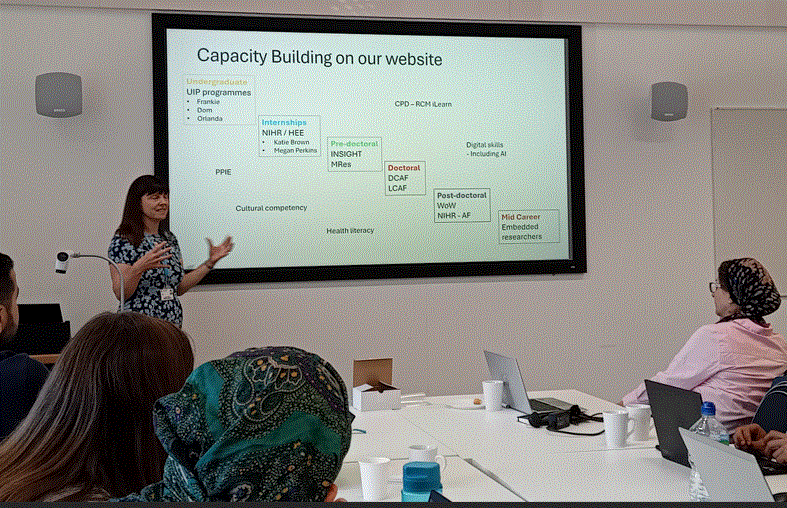 Today was the first day of strategic planning for the MIHERC project. Our collaborators from Sheffield and Doncaster came down to Bournemouth University to discuss progress, meet with midwifery practitioners from University Hospital Dorset NHS Foundation Trust,
Today was the first day of strategic planning for the MIHERC project. Our collaborators from Sheffield and Doncaster came down to Bournemouth University to discuss progress, meet with midwifery practitioners from University Hospital Dorset NHS Foundation Trust, and plan action for the coming year.
and plan action for the coming year.  MIHERC comprises an interdisciplinary team, led by Prof. Hora Soltani at Sheffield Hallam University, which has members from ethnically and professionally diverse colleagues from Sheffield Hallam University, Bournemouth University and Doncaster City Council.
MIHERC comprises an interdisciplinary team, led by Prof. Hora Soltani at Sheffield Hallam University, which has members from ethnically and professionally diverse colleagues from Sheffield Hallam University, Bournemouth University and Doncaster City Council.







































 UK Turing Scheme: My student mobility programme in Nepal
UK Turing Scheme: My student mobility programme in Nepal Bournemouth University psychologists publish new book
Bournemouth University psychologists publish new book Connecting Research with Practice: FoodMAPP Secondment in Austria and France
Connecting Research with Practice: FoodMAPP Secondment in Austria and France Health promotion paper read 8,000 times
Health promotion paper read 8,000 times The Beautiful Work Challenge: On Birth
The Beautiful Work Challenge: On Birth MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease