The NanoCorr, Energy & Modelling (NCEM) Research Group, led by Professor Zulfiqar Khan at Bournemouth University, has made pioneering developments in the field of thermal energy storage, an area critical to the future of renewable energy. Their groundbreaking work in enhancing the performance of latent heat storage systems using phase change materials (PCMs) has been featured on the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) website—marking a prestigious global endorsement of their innovations in clean energy technologies.

A Leap Toward Sustainable Energy
As the world shifts from fossil fuels to renewable sources, the ability to capture and store energy efficiently is a central challenge. PCMs—materials that absorb and release heat during phase transitions (like melting and solidifying)—offer an ingenious solution. NCEM’s research focuses on improving these materials’ thermal conductivity, stability, and compatibility with various containers, making energy storage more efficient, stable, and commercially viable.
Their study reviews and categorises organic paraffins and inorganic salt hydrates, the most promising groups of PCMs, highlighting enhancements like encapsulation, multi-PCM integration, and advanced container geometries. These techniques significantly boost energy capture rates and storage capacity, making clean energy more practical for widespread use.
Real-World Impact and Innovation
Backed by five industry-funded and match-funded projects, NCEM’s efforts have not only led to commercial patents in the UK and USA, but have also influenced engineering solutions for solar heating, industrial heat recovery, and smart building technologies. These contributions align strongly with several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs):
Goal 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
Goal 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
Goal 17: Partnerships for the Goals
Global Recognition: Why the IAEA Feature Matters
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), an influential global body under the United Nations, works to promote the peaceful use of nuclear and clean energy technologies. Being featured on their platform is a significant milestone—it underscores the global relevance, technical merit, and strategic value of Professor Khan’s research. It also places Bournemouth University and NCEM at the heart of international discussions on sustainable energy systems.
This acknowledgment by the IAEA is a testament to the NCEM team’s commitment to tackling real-world problems with innovative science. It further demonstrates the potential of UK-led clean energy solutions to contribute to a low-carbon, energy-secure future for all.
A Bright Future for Clean Energy
The research led by Professor Zulfiqar Khan exemplifies how innovative materials science and engineering can drive change on a global scale. With continued support and collaboration between academia and industry, NCEM is set to play a pivotal role in accelerating the transition to clean, resilient energy systems worldwide.
Acknowledgements: Dr Zakir Khan (NCEM ex PGR/ Post Doc) and Professor A Ghafoor.













 Coating Innovation for Tough Environments
Coating Innovation for Tough Environments

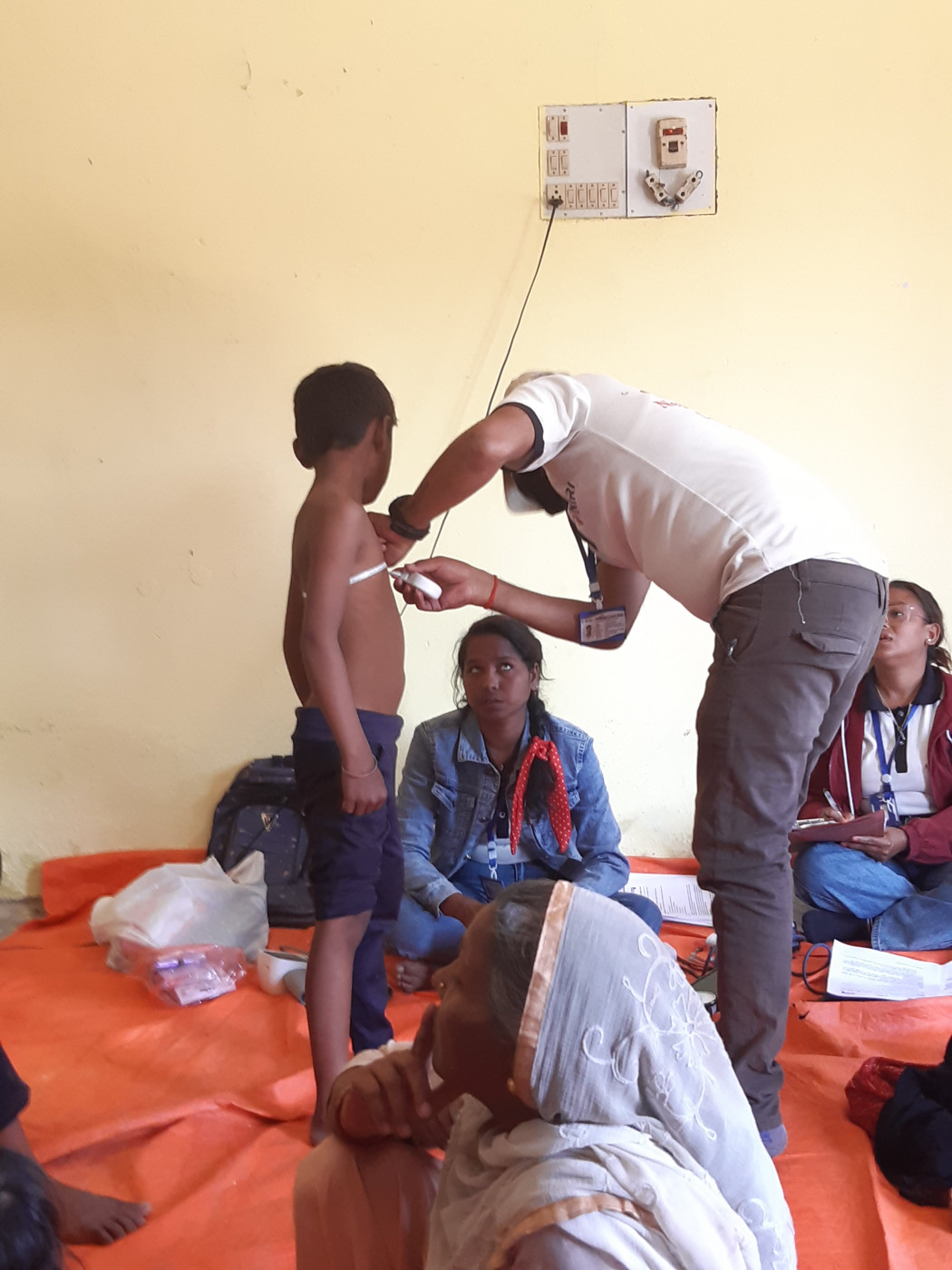








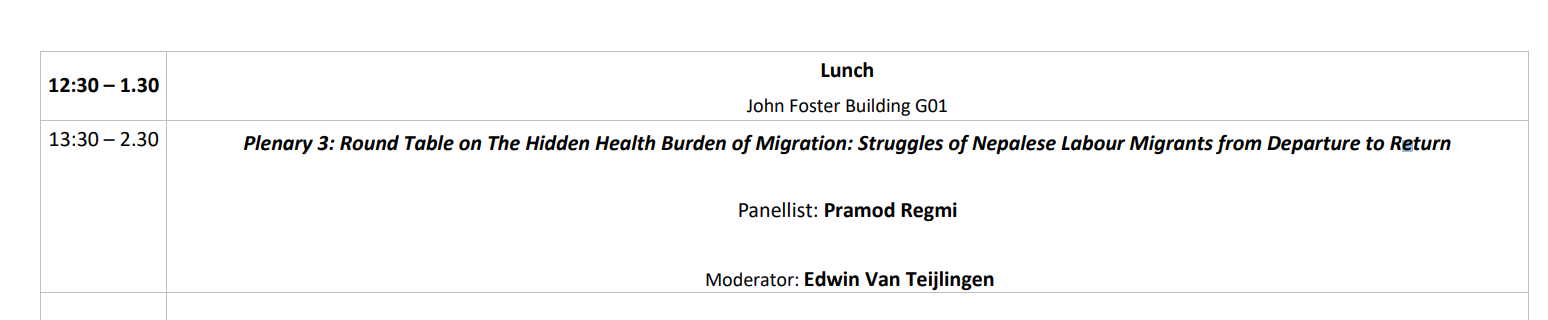



















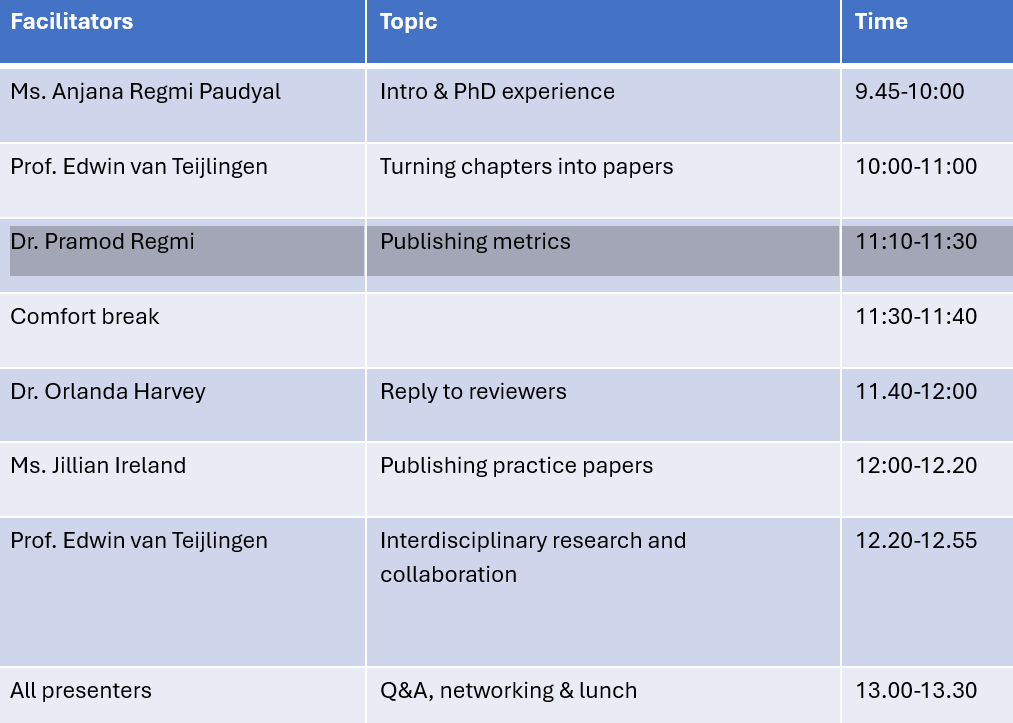
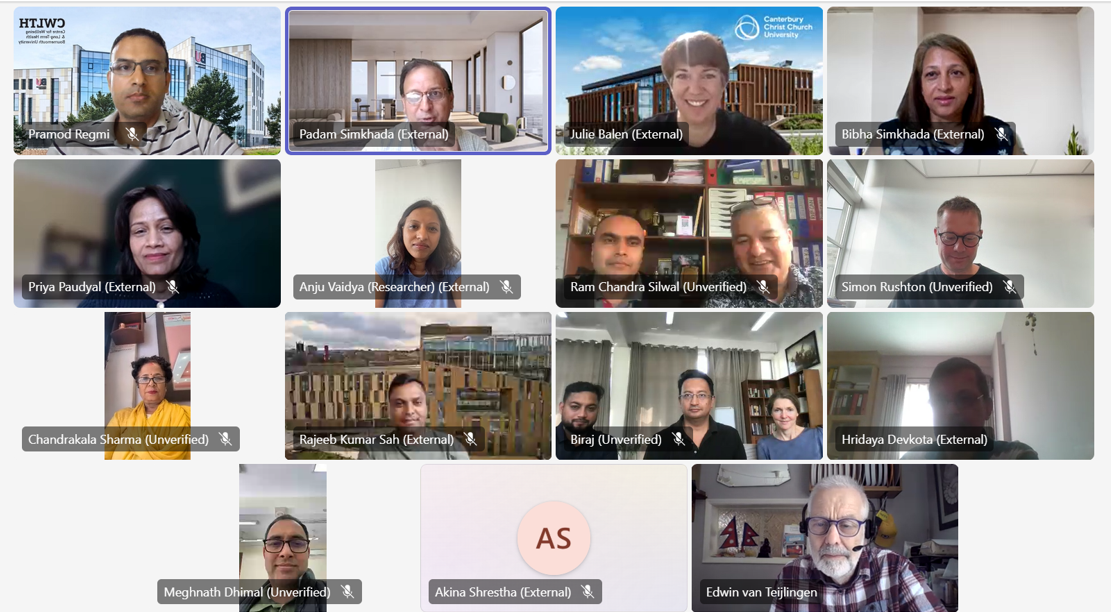
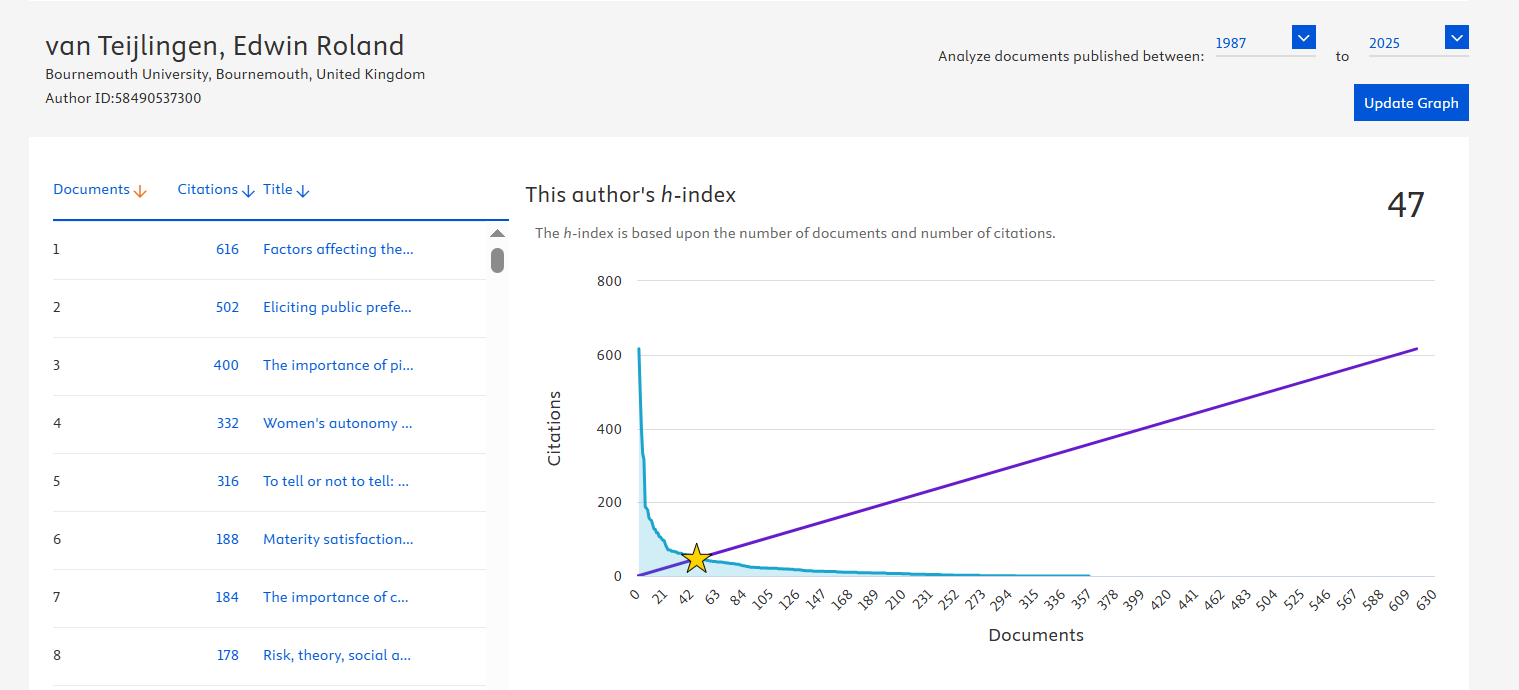
 Nursing Research REF Impact in Nepal
Nursing Research REF Impact in Nepal Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation
Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation ESRC Festival of Social Science 2025 – Reflecting back and looking ahead to 2026
ESRC Festival of Social Science 2025 – Reflecting back and looking ahead to 2026 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Cookies – Tuesday 13 January 10-11am
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Cookies – Tuesday 13 January 10-11am Dr. Chloe Casey on Sky News
Dr. Chloe Casey on Sky News ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease