On 25-26 Apr 2017, BU will be hosting the highly valued and increasingly popular BCUR (http://www.bcur.org/). Almost 400 UG students from across the country attended BCUR 2016 at Manchester Metropolitan University. Hosting BCUR will be hard work, but also a great opportunity to promote BU’s excellent facilities and postgraduate opportunities. Undergraduates of all levels are invited to submit an abstract to BCUR, abstracts are peer-reviewed and works accepted can be presented in a variety of formats (oral presentations, posters, art displays, workshops and performances).
Prof Gail Thomas (Head of CEL), Dr Luciana Esteves (SciTech) and Dr Mary Beth Gouthro (Faculty of Management) are co-chairing BCUR 2017 and are currently setting up the organising committee. If you are interested in helping organising the event, please contact one of the chairs. Representatives from all Faculties, SUBU and central services are welcome.
You can also help by stimulating your students to submit their abstracts to BCUR – your incentive is the most important factor influencing students’ decisions in taking part of extra-curricular activities. Submissions are likely to be open between Oct-Dec – so watch this space!
BU’s application to host BCUR was one of the successful outcomes of the Fusion-funded SURE project (Showcasing Undergraduate Research Excellence). The project has delivered two SURE conferences (March 2015 and 2016), an extra-curricular opportunity open to all BU UG students (across all levels and programmes). You can find a brief summary of the two conferences in this CEL blog.
BU students taking part in the SURE conferences not only gain valuable transferable skills and experience, they can win fantastic awards and prizes (see below) and be selected to present their work in the Posters in Parliament event. You can read about this year’s BU research showcased in Parliament here.
SURE Conference award winners:
Research Excellence (MSc or MRes fee waiver): Jozef Kulik, Psychology (2015); Rosie Lumley, Nutrition (2016)
Best oral presentation (funds to present at an external conference): Ben Hayes, Physiotherapy (2015); Charlotte Fodor, English (2016)
Best poster (iPad): Emma Packer, Biological Sciences (2015); Christopher Dwen, Forensic Science (2016)

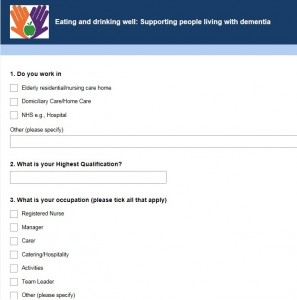
 When applying to become a Research Assistant for this project I expected mostly data collection and being involved in the recruitment of participants. With a background in psychology, and having worked as a voluntary Research Assistant before, I found the aim of my work slightly different. When joining the research team and the Nutrition and Dementia project in January, I got happily surprised of my part in the project. I was greatly welcomed by Dr Jane Murphy RD RNutr, Joanne Holmes RNutr and Cindy Brooks, Research Assistant.
When applying to become a Research Assistant for this project I expected mostly data collection and being involved in the recruitment of participants. With a background in psychology, and having worked as a voluntary Research Assistant before, I found the aim of my work slightly different. When joining the research team and the Nutrition and Dementia project in January, I got happily surprised of my part in the project. I was greatly welcomed by Dr Jane Murphy RD RNutr, Joanne Holmes RNutr and Cindy Brooks, Research Assistant.






 Doing a PhD may appeal to midwives and other NHS health professionals, but it often involves having to make difficult choices. Undertaking a part-time PhD means studying on top of a busy clinical position, but starting full-time study involves stepping away from practice, which may lead to a loss of clinical skills and confidence. The Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH) at Bournemouth University has come up with a novel solution making it easier for midwives to undertake a doctorate while still maintaining their clinical skills. This approach is highlighted in the latest publication by Dr. Susan Way and colleagues, describing a process where CMMPH collaborate with NHS partners to apply for a match-funded PhD. [1] The first partnership was with Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (PHT), with later partners expanded to cover the Isle of Wight and Southampton. Currently there are negotiations with Dorset Country Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and Poole Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Non NHS organisations have also showed an interest with the Anglo European Chiropractic College (AECC) our likely next collaborator.
Doing a PhD may appeal to midwives and other NHS health professionals, but it often involves having to make difficult choices. Undertaking a part-time PhD means studying on top of a busy clinical position, but starting full-time study involves stepping away from practice, which may lead to a loss of clinical skills and confidence. The Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH) at Bournemouth University has come up with a novel solution making it easier for midwives to undertake a doctorate while still maintaining their clinical skills. This approach is highlighted in the latest publication by Dr. Susan Way and colleagues, describing a process where CMMPH collaborate with NHS partners to apply for a match-funded PhD. [1] The first partnership was with Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (PHT), with later partners expanded to cover the Isle of Wight and Southampton. Currently there are negotiations with Dorset Country Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and Poole Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Non NHS organisations have also showed an interest with the Anglo European Chiropractic College (AECC) our likely next collaborator.


 of the programme. Applications recently closed and the events management course in the Faculty of Management has some hopeful applications in the mix. The Fastforward15 graduation and instalment of new mentees takes place at the Langham Hotel in London at the end of April.
of the programme. Applications recently closed and the events management course in the Faculty of Management has some hopeful applications in the mix. The Fastforward15 graduation and instalment of new mentees takes place at the Langham Hotel in London at the end of April.






















 Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar
Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch
Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch No access to BRIAN 5-6th February
No access to BRIAN 5-6th February ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease