By Dr Maxine Gee and Dr Rachel Moseley
Back on a rainy November day in 2022, Drs Maxine Gee and Rachel Moseley transported members of the public into a future where robots and humans live and work together. The public met our future confederates and were posed the task of identifying which of the two was human and which was a robot. Our mission: to increase understanding and empathy for autistic people.
You might ask: What on earth do robots and the future have to do with autism? How can science-fiction have anything to say on this topic?
This event was held as part of the ESRC Festival of Social Science, an annual, UK-wide, free celebration of the social sciences to which BU has contributed for over ten years.
Our underlying research

Wall-E (Photo by Michael Marais on Unsplash)
The idea for the activity was based on shrewd observations by Dr Maxine Gee, Principal Academic in Screenwriting (Faculty of Media and Communications). Dr Gee studies how post-human characters (e.g. robots and other forms of artificial intelligence) are portrayed in media. What kind of qualities are written into these characters to signal to the audience that they’re not human? What qualities do screenwriters use to communicate that they’re not to be trusted, and what qualities make us root for them? You might think about Wall-E, whose expressive features and gestures make him highly lovable, or Data from Star Trek, whose attempts to understand and mimic the people around him endear him to the audience. Compare them with the Terminator or HAL, whose logic and unemotionality in pursuing their objectives inspire fear or distrust.
Dr Gee found that in science fiction screenwriters often distinguish human characters by expressions of emotion, and by the ability to tell stories so these characters can connect with others, express themselves and their identity, and also sometimes to lie or con their way out of situations. Moreover, characters in these films and television shows are perceived more positively when they express these characteristics.
These assumptions are based on a fundamental error: the idea that there is just one, ‘right’ way that humans express emotions and communicate. While each one of us is unique, most ‘neurotypical’ people have brains that work more similarly than dissimilarly to one another. People who are ‘neurodivergent’, though, have brains which function in more markedly different ways. This colours everything about the way they move through and experience the world, and gives rise to different ways of expressing emotions and communicating.
Autistic people are one such group, and this makes life very difficult for them. Being autistic is like having a mind which works on a different operating system, an apple mac in a world of Microsoft PCs. Because non-autistic people speak a slightly different social and emotional language, they can sometimes overlook or misunderstand autistic expressions of emotion, leading to stereotypes of autistic people as ‘wooden’ or, indeed, ‘robotic’.

Humanoid robot (Photo by Maximalfocus on Unsplash)
You might have heard of the Uncanny Valley effect in robotics – the more human-like a robot appears, the more unnerved people are by the slight deviations that shockingly reveal their artificiality. Research suggests that a similar process might be at work when autistic and non-autistic people interact, where differences in emotion and social behaviour can be unnerving for non-autistic people. From a very early age, non-autistic children distance themselves from autistic peers, while not necessarily being able or willing to consciously explain why. Autistic people are often socially excluded or bullied for their differences.
Dr Gee chatted to Dr Rachel Moseley, principal academic in Psychology, whose research focuses on mental health in autistic people. They noticed a parallel where many media portrayals of autistic people display traits which tend to mark out non-human characters in science-fiction – unemotionality, “cold” logic, rigidity in manner and movement. Since these features are often written to portray non-human characters less than sympathetically, we wondered whether there might be a link between these “less than human” portrayals of autistic people and the stigma they face.
Our public engagement activity
With the help of Bournemouth’s general public, we performed a field experiment. The public were told that one of our two colleagues from the future was a robot, and asked them a series of questions to try identify who was human. While we did have one robot and one human character, both were in fact carefully written to reflect different portrayals of autistic people. In the portrayal where autism stereotypes dovetail with robot characters, “Chris” (our robot) was logical and unemotional, without a lot of humour. In contrast, “Alex” was playful but diffident, constantly eager to please.
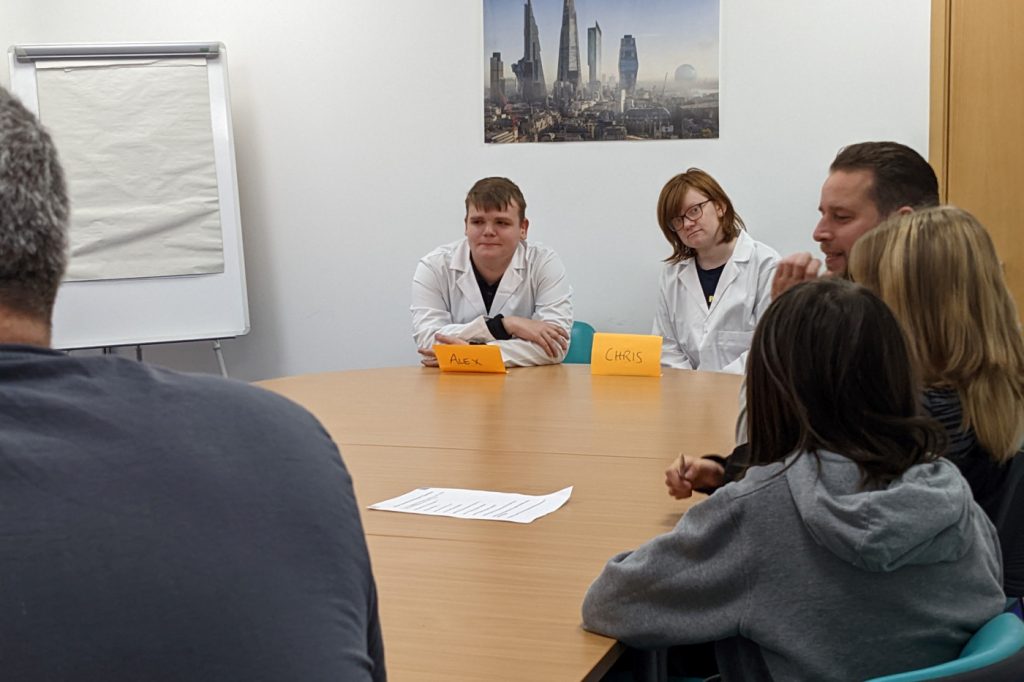

“Chris” and “Alex”, two of our actors.
They were based on autistic descriptions of camouflaging, which is when neurodivergent people consciously try to hide their differences and ‘act neurotypical’, from the way they make eye-contact, to copying their body language and speech mannerisms. Just like non-human characters are perceived more positively when they express emotions and social behaviours, autistic people are perceived more positively when they perform camouflaging behaviours, and it helps them avoid bullying or social exclusion. The problem is that camouflaging is exhausting, and it reinforces a sense of low self-worth. Autistic people who spend a lot of time camouflaging tend to have poorer mental health and also be more vulnerable to suicide.
We wondered whether the general public, who might be used to depictions of non-human characters, would be led to identify Chris (our stereotypical autistic portrayal) as the robot. Actually, we found that people were conflicted, with guesses balanced between the two characters. People noticed the Uncanny Valley aspect of Alex’s mannerisms, and knew there was something different about this character.
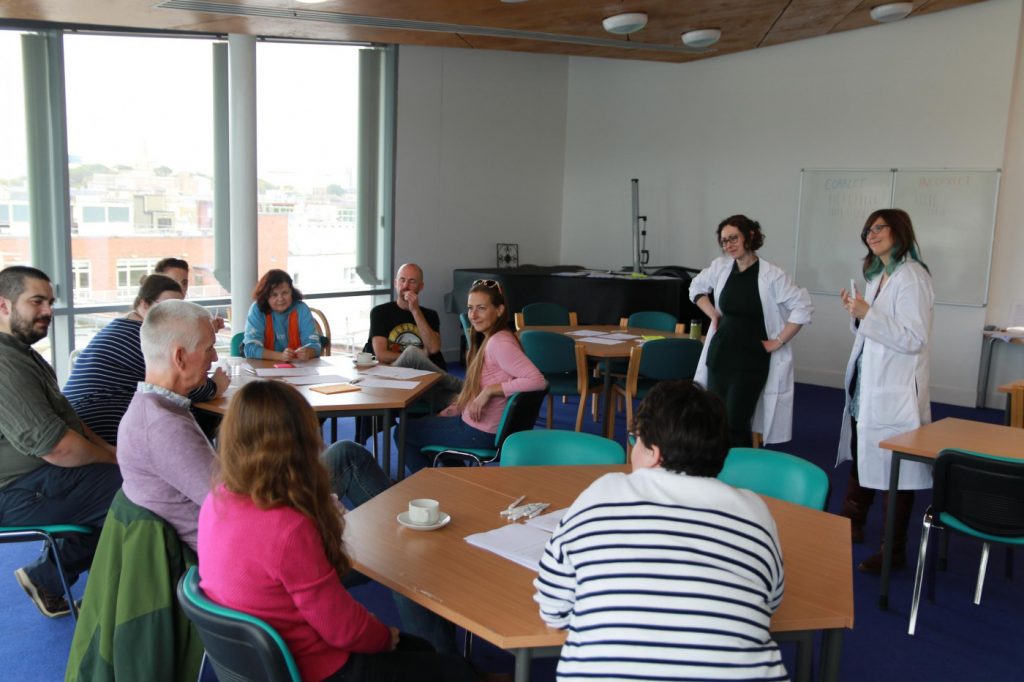

Max and Rachel in a discussion session with a group.
We explored their ideas about the traits they tended to associate with robot characters, and pointed out how these overlapped with representations of autism. In explaining how different types of brain give rise to different ways of socialising and communicating, we spoke about the painful efforts that autistic people go to hide their differences in order to be accepted. Concluding, we invited people to think about their assumptions of what it means to be human (and the inherent flip side of ‘not-human’), and the harm these assumptions could cause for people who don’t display those most common ways of behaving.
We measured the impact of this activity on attendees using surveys, the results of which might also feed into future research. Asked if the event increased their understanding of autism and empathy for autistic people, most of our respondents gave positive responses on the day. Those who responded two weeks later likewise gave mainly favourable responses, with one commenting “It was a very clever and accessible way to teach people about autism”, and others suggesting we should take the performance to schools. We especially valued one response by an autistic person in our audience: “I thought while watching that both could very easily be autistic and was scared that they might just say that being autistic was just like being a robot and that we had no feelings. Very happily surprised”
We ran the activity in thirty-minute slots throughout the day, welcoming over fifty attendees in total. Our immense gratitude goes to the Public Engagement team, our fantastic student actors, and our many colleagues who helped us during this event. We feel that the event was especially special in that it was co-produced, written and acted by an evenly split team of autistic and non-autistic people. One of our autistic actors had a fascinating and poignant insight into the double-bluff of playing a character who was camouflaging their autism just obviously enough for the audience to notice:
“Because I was so used to hiding it all … It was hard to not automatically revert back to covering it all up. Because the aim of being just an autistic person in real life is to try and not show your autism… So, it’s interesting to have to do that, force myself into that kind of corner in a way. … really seeing it and going, “Ah, but this isn’t what I usually do,” or “This is what I usually do,” or “Maybe I can do this in the future,” sort of thing. It almost made me feel slightly more comfortable taking in, kind of, showing a little bit more of me”
As we’re passionate about working towards a world where different ways of existing as a human are valued equally, we’re delighted with this feedback and look forward to taking our work further.
If you’re interested in engaging the public with your research, start by exploring what support is on offer at BU for research communications, impact and engagement. If you’d like to take part in this year’s ESRC Festival of Social Science, explore the other events that took place last year and look out for the call for proposals in March 2023.


































 From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease