There is a renewed focus on funding for the sector amidst talk about elections. Student visas are back on the agenda and UKRI have been reviewing arrangements to support knowledge exchange.
Elections
Local elections were held in England on 4 May. Dorset Council did not have an election. Locally, BCP issued an update:
“The Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole Council local elections have resulted in no overall control, with the largest number of seats held by the Liberal Democrat party. Liberal Democrats won 28 seats, the next largest party was Conservatives with 12 [down from 34], followed by Labour, Christchurch Independents, the Green Party, Poole People, Poole Engage and five Independent candidates….The new leader of BCP Council will be elected at a meeting on the 23 May, and a new Cabinet formed.”
With the general election looming before January 2025 the local results were being watched very closely to predict outcomes, but of course as always it is very hard to tell and there is time for lots to change before then.
Impact of requiring voter ID
This was also the first election where photo ID was required and pre-election concerns centred on voters being turned away at the polls, particularly the young, old and marginalised groups. There will likely be discussion of the impact of voter ID (and its potential to bias the election outcome through the groups that will find providing ID easier) over the next week. The impact of the photo ID requirement is being formally reviewed, initial findings are due in June and the report is scheduled for September.
However, early indications come from the Guardian who say: Anecdotal evidence of issues, but no clear picture of impact yet…Peter Stanyon, the chief executive of the Association of Electoral Administrators, said there had been “no reported incidents of any major concern” as the UK rolled out new voter ID requirements for the first time. And Peter Walker and Jessica Murray report that fears of widespread chaos did not materialise. But by the end of the day, there were anecdotal reports of a number of people, many from marginalised groups, being unable to cast their ballots. The Electoral Reform Society said there were “countless examples”. ITV News reported that polling station tellers in Oxfordshire estimated that 10-25% of would-be voters had been turned away. The Electoral Commission said that the election was “well run” overall but “some people were regrettably unable to vote”.
The Financial Times reported last night (£) that ministers plan to widen the forms of photo identification that will be valid in future if turnout is shown to have fallen – a U-turn in government policy.
The Telegraph has a more positive spin on the success of the photo ID requirement.
Student Voting
Earlier this week HEPI published political polling of current full time UK undergraduates on voting intention.
- 85% expect to vote at the next general election
- 89% are registered to vote, and 64% who are registered to vote say they are registered only at their home address (so less influence of the young vote in election towns than has previously been claimed).
- 78% understood they will needed photo ID to vote (and 61% think this is a good idea)
- 46% of students would vote Labour if there were a general election ‘soon’, 11% would vote Green and 7% would vote Conservative
On student fees and funding (see also below), the polling shows student opinion:
- Tuition fees:
- 28% of students domiciled in England want Labour to commit to abolishing tuition fees in England,
- 23% want Labour to reduce fees to £6,000,
- 20% want Labour to back the current system of fees capped at £9,250,
- 15% want Labour to cut fees to £3,000,
- 4% want Labour to introduce a graduate tax, and
- 3% want Labour to let the current fees rise with inflation
- Living costs:
- 52% of students think living costs should be covered by targeted grants and top-up loans, while
- 25% want a mix of grants, loans and parental contributions
- Maintenance support:
- 46% of students think maintenance support should be between £10,000 and £12,500 each year
- 19% think it should amount to under £10,000 and
- 18% think it should be between £12,501 and £15,000
- Student opinion priorities: 77% of students say the NHS is a high priority for them, 58% rate education as high priority, 46% reducing poverty, but few students give priority to defence (6%), migration (5%) or international development (2%)
Nick Hillman, Director of HEPI, said:
- Our poll suggests it is wrong to think of students as apathetic or disengaged from party politics. Most students plan to vote and they care about the same issues as other voters, most notably the NHS.
- The results won’t make happy reading for the Conservative Party, who now have minimal support among undergraduates. While they will make happier reading for Labour, it is clear there is no single student funding model that would be overwhelmingly popular with students. This will make the Opposition’s job harder as they firm up their policies in the run up to the next election.
International Student visa restrictions
The press report the Government are considering visa restrictions to prevent postgraduate students’ dependants from accompanying them. Financial Times:
- The surge in legal net migration is boosting the size of Britain’s workforce but the issue is politically problematic for the prime minister….
- Students have been one of the main drivers of the the…surge in migration…with 135,788 visas granted to dependants in 2022, up from 16,047 in 2019.
- The Department for Education, the Home Office, and the Treasure are finalising a plan that would stop dependents from travelling with master’s students on one-year courses…
- The Treasury, which normally favours higher migration, has accepted the political need to restrict the number of dependants of overseas students, while Gillian Keegan, education secretary, has also agreed to the plan.
- But government insiders said Keegan was insisting that master’s students should be able to bring family members to the UK if they stay to work in the country after completing their studies.
UUKi’s response: we recognise that the growth in the number of dependents may have exceeded planning assumptions and that this has created some concerns for government, and indeed challenges in some areas of the UK – for example, around access to suitable family accommodation. We are committed to working with Government to understand these issues and to find solutions that ensure the UK continues to welcome international students and that we are able to grow numbers in a sustainable way that protects both the quality of the student experience and the UK’s global competitiveness.
Wonkhe coverage: Dependants of international PGTs won’t be able to get a visa
Fees & Funding
Closely tied to electoral outcome is the wicked problem of HE fees and funding. Here’s a round up of the latest news on the different elements surrounding fees and funding.
We start with a couple of interesting Wonkhe blogs:
Labour’s HE Fee Policy
In last week’s policy update we reported that Labour were reviewing their policy for HE tuition fees giving a clear indication in an interview on BBC Radio 4 that the previous policy of abolishing fees will not survive because of costs concern. This week the media is widely reporting on Labour’s ‘U turn’ on tuition fees i.e. that fees will not be abolished and paid for by the public purse. From the coverage we’ve seen this hasn’t been formally announced but Keir Starmer continues to caveat his interview responses to nudge in this direction, perhaps a soft announcement then. Here is the latest coverage:
- Research Professional: Channel 4 News looks at what Labour leader Keir Starmer has said about the party’s tuition fees plan.
- Wonkhe – The Independent, theBBC, Channel 4, the Mirror, ITV, and the Sun all have pieces examining the Labour Party’s – and others parties’ – stance on tuition fees.
- Research Professional: In The Guardian, Labour is to begin consulting on new ways to fund university education,
- Wonkhe – Labour leader Keir Starmer yesterday told the BBC’s Today programme that Labour is “likely to move on” from its commitment to free university tuition. The Times had earlier reportedcomments from a senior party source that Starmer will later this month deliver a speech on the party’s move away from its 2019 manifesto commitment. The BBC, the Independent, the Telegraph, the Guardian, the Mirror and the National all cover the remarks. There’s also a sketch in the Guardian.
- NEON – Labour leader Keir Starmer announced yesterday that the party is abandoning its commitment to abolish university tuition fees in England. Speaking on Radio 4’s Today programme he said “We are likely to move on from that commitment because we do find ourselves in a different financial situation”. He was critical of the current system describing it as “unfair” and arguing that it doesn’t work for either students or universities. He promised that Labour would set out a “fairer solution” in the coming weeks. The move has drawn criticism from both Labour Students and Momentum.
- Wonkhe blog on the topic: Jim Dickinson runs the numbers.
Wonkhe also reported this morning that Polling company Public First and think tank Progressive Britain have…announced a major national poll and extensive focus group work to test public attitudes to university funding reform. The research will be published prior to party conference season in October, and Public First expects its findings “to play a significant role in the ongoing debate about the future of tuition fees, university funding, and student finance.”
Also from Wonkhe, earlier this week: London Economics has published further modelling on options for the English fees and funding system, building on work conducted in December for the University of the Arts London. The models include an estimate of the impact of Plan 5 reforms – updated due to forthcoming ONS changes in inflation measurements, which significantly reduce the cost to the Exchequer – and two alternative “stepped repayment” models, with repayment rates varying depending on income level.
Landmark divergence in Welsh HE policy
Wales has announced they will retain their current student finance repayment system (despite changes to the English system). This is a break in tradition as historically the Welsh repayment system mirrors England. However, Jeremy Miles, Welsh Minister for Education, is concerned that the new English system would mean Welsh students would repay loans over a longer period of time (England 40 year repayment; Wales 30 years) with higher earners paying less and middle- and lower-income earners paying back more than at present. The Welsh system is more progressive than the English system -Welsh undergraduate students generally repay less as Wales has some non-repayable grants and there is a guaranteed level of maintenance support irrespective of a student’s household income.
The Welsh system will be reviewed annually to ensure sustainability.
Jeremy Miles said: “…the new system in England is not a good deal. The reforms benefit the highest earners and worsen the position for middle and lower earning graduates. Women are also disproportionately affected. We certainly shouldn’t be asking teachers, nurses and social workers to pay more, while the highest earners pay less. I can therefore announce today that we will not move to the system adopted in England but will retain the current system.”
The BBC cover the announcement.
How should universities be funded?
YouGov polling reveals the public do not have a clear consensus on how universities should be funded.
It’s worth looking at the interactive chart on the YouGov site to drill down into the results by different groups (e.g. political affiliation, age, social grade, region, gender).
Parliamentary News
HE (Freedom of Speech) Act
It’s been nearly two years since its first reading and now – three Prime Ministers and six education secretaries later the Government have finally got the legislation over the line and in the form they wanted. The Government played hard ball during the final stage parliamentary ping pong over the contentious tort in the HE (Freedom of Speech) legislation. The Lords weren’t happy, however, their hands were tied by the parliamentary convention that they do not block legislation that the elected Government included within their manifesto.
Wonkhe report on the disgruntlement: Peers agreed to the government’s latest version of the statutory tort, which included language clarifying the availability of redress for pecuniary and non-pecuniary damages, and the possibility of seeking an injunction, without a vote. However, the changes were not universally popular – in particular, Lord Grabiner described the government plans as “blowing away” the previous compromise that saw the tort reserved only for when other avenues had been exhausted, and Lord Willetts raised the spectre of interventions such as this bringing higher education into the public sector.
Cambridge’s Professor Arif Ahmed has been appointed as the OfS Director of Freedom of Speech and Academic Freedom. The role will have the power to investigate universities and student unions in England and Wales that ‘wrongly’ restrict debate. The director will also advise the sector regulator on imposing fines for free speech breaches.
Lifelong Learning
The Lifelong Learning (HE Fee Limits) Bill has completed its initial journey through the House of Commons and is awaiting a date for the second reading of the Bill in the House of Lords. The Second Reading stage is the first opportunity for members of the Lords to debate the key principles and main purpose of the Bill and they will flag up concerns or highlight areas where they believe amendments need to be made. After the Second Reading the Bill will progress to Committee Stage. This is when it is examined in detail, line by line, with discussion and close scrutiny. MPs did not make any amendments to the Bill and it proceeds to the Lords in its original form.
HEPI published Does the Lifelong Loan Entitlement Meet its own Objectives? Spoiler alert: not for part time and distance students – inhibiting it’s transformative effect. Questions still to be answered include:
- How will the credit-transfer mechanism work?
- What will be the rules for students building their own degree?
- How will a wide range of providers be incentivised to provide flexible learning?
- How will the needs of employers be met?
Regulatory – OfS
The Lords Industry and Regulators inquiry into the work of the Office for Students heated up this week when Susan Lapworth (Chief Executive) and Lord Wharton of Yarm (Chair) were called to give evidence. You can read a summary of the session here.
Wonkhe report: In a revealing hearing, we learned that the student panel is being reformed, that quarterly online meetings for vice chancellors are one part of the regulator’s strategy to improve communications, that 30 providers are currently subject to enhanced financial monitoring, and that two thirds of the quality assurance reports submitted by the QAA were not deemed usable for regulation when first submitted.
Wonkhe also have a short blog: Lapworth and Wharton face the committee – But don’t expect answers to everything that previous witnesses have brought up
Concerns over Wharton’s impartiality as a member of the Conservative party were raised. When suggested that senior figures often resign their political affiliations when they take up office Wharton replied Some do…I chose not to. It’s not a requirement.
HE Minister, Robert Halfon, is expected to be questioned next in this high profile inquiry before the proceedings wrap up and the Committee publishes its report.
Research
Research England (RE) published their Review of knowledge exchange funding.
The main themes within the review are data and metrics:
- a key issue to unlock the potential for long-term and more fundamental changes to our methods, including the use of KEF as a basis for allocating HEIF, is the availability of better data, metrics and evidence.
- our current metrics set does not capture the full achievements, nor help describe the ambitions, of HE KE. Better evidence is also a theme in DSIT’s priorities, particularly related to better evidence on HE performance in commercialisation and business collaboration.
- Better metrics are then critical to make more significant changes to our methods in the long run. The issue of better metrics is a theme running through the feedback received and also a central issue in our decisions.
- A major decision of the review then relates to our commitment to a significant work programme to improve metrics and evidence…This is with the intention to have the tools available to make more fundamental changes to our approaches in the longer run.
The bulk of knowledge exchange (KE) related funded (KEF and HEIF) is based on the Higher Education: Business and Community Interactions (HE-BCI) survey. HESA are reviewing the HE-BCI and this report informs that UKRI will piggy back to build upon and widen the review for KE purposes.
…it is essential to add new classes of data, beyond improving the quality of guidance and definitions of existing data fields as is currently being done through the review …we and HESA are agreed that more effort is needed, particularly in the longer-term design of new data collection.
UKRI intend to develop a national capability to be a centre for knowledge exchange and impact evidence, metrics and data.
UKRI will:
- Over 2 years develop UKRI as a national capability centre for university knowledge exchange, impact evidence and metrics, partnering with HESA.
- Present a blueprint (for the national capability) in Spring 2023 at a major metrics conference and establish the blueprint by Spring 2025.
- Our long-term aim following successful culmination of our work on the national capability and centre is to have available the appropriate data to make more fundamental changes to our approaches. Specifically, we aim to bring forward proposals for consultation on the development of KEF for use in funding. As this is necessarily a long-term endeavour, we would not expect to bring forward such proposals before 2025/26 at the very earliest. We note that any subsequent implementation and a phased roll out of an evolved funding method may take several further years.
KEF: Review feedback sees the KEF as having a positive impact on raising the profile of knowledge exchange (KE) and incentivising strategic approaches within HEIs and across the sector, with overall beneficial effects of improving HE KE performance. RE state there is broad agreement that the KEF has been useful within HEPs as a novel tool for benchmarking performance, making useful comparisons, giving greater accountability, and as a prompt to starting discussions on future areas of strategic focus.
However, KEF is not well understood beyond the KE sector and particularly by external users.
KEF will continue in a consistent and stable form in the short term because UKRI see worth in how the KEF provides HEIs with data to understand, benchmark and improve their own performance until at least KEF5 in 2025. RE will drop the KEF aim/purpose to meet the information needs of external (non-HE) partners but will continue to use it for public information purposes. In the long-term RE will bring forward proposals for consultation on development of KEF for use in funding.
HEIF: The review suggested that there is a good degree of confidence in [the] current HEIF approach, including balancing government priorities with HEI funding flexibility (getting the best out of the sector to meet the priorities).
Research England (RE) note points raised:
- Our definitions and scope of HEIF were generally regarded as appropriate. There were a range of views on whether additional activities should be included, but generally it was felt that RE was not getting it wrong. The drivers from research and teaching were flagged and there were discussions as to whether our approaches fully address both.
- There were a range of views put forward on how to measure success, including qualitative approaches. Our substantial work programme on metrics and evidence addresses the need to provide the more sophisticated tools needed to achieve all our objectives.
There are no major changes planned (now) – formula funding and accountability will remain.
However, RE will consider how to manage:
- Problems for HEIs caused by year-on-year fluctuations in HEIF allocations – limiting long-term strategic decisions.
- RE note they cannot commit funding past a government spending review period but could fix allocations for the full spending review period rather than recalculate each year.
- There would be winners and losers to this approach and they note reverting to a less dynamic approach could also depress prompt rewards for improvement (including HEPs below the allocation threshold for the entire SR period).
- The impending general election also pushes any change to the allocation methodology into the medium/long term. However, RE state they will look into this for the future.
- Within the work on improving metrics Research England will look into activities that still generate impact but are not qualifying income-generating.
- We recognise a potential opportunity to be more ambitious to identify and reward all forms of KE achievements in the longer run.
- They will also look at the £250k allocation threshold (tricky as the threshold is a government policy priority handed down to RE), implementation from 2024-25 at earliest.
KE Concordat: The approach to the Concordat is to remain relatively stable.
Feedback showed strong agreement that the KE Concordat processes of self-evaluation and consideration of principles had been a useful exercise for HEPs, raising the profile of KE within their institution and encouraging engagement from across the institution
RE will look into suggestions for process improvement (more on page 11)
Forthcoming actions
- Summer 2023 – publish KEF3, allocate 2023-24 formula funding, consult on eligibility
- Later 2023 – publish HEIF threshold work
- Spring 2024 – Host major metrics conference and launch national capability blueprint
- Summer 2024 – publish KEF 4, allocate 2024-25 formula funding, publish work on dynamism/predictability of HEIF allocations with implementation in 2025/26 if spending review allows. (Note – potential disruption due to general election.)
- Spring 2025 – the national capability and centre for university KE and impact evidence and metrics will be operational
- Summer 2025 – allocate 2025-26 HEIF funding (in whatever form it takes), publish KEF 5.
Useful links:
Research integrity
The Science, Innovation and Tech Committee published a report on Reproducibility and Research Integrity. The background to this report are the increasing concerns that the integrity of some scientific research is questionable because of failures to be able to reproduce the claimed findings of some experiments or analyses of data and therefore confirm that the original researcher’s conclusions were justified.
This report finds and recommends:
- while there are many reports of problems of non-reproducibility, there has been no comprehensive and rigorous assessment of the scale of the problem in the UK, nor which disciplines are most affected and therefore the extent to which this is indeed a ‘crisis’.
- While we welcome the establishment of the new Committee on Research Integrity and note that one of its so-called strategic pillars is to “define the evidence base”, we are concerned about the absence of reproducibility as a priority in the new organisation’s strategy. We recommend that a sub-committee focussed solely on questions of reproducibility in research should be established.
- Evidence to our inquiry raised important concerns about the academic publishing industry in—however unintentionally—giving rise to pressures that can undermine research integrity. To be successful, academics need to establish a strong list of publications in highly-rated learned journals. We heard a widespread view that journals favoured for publication original—rather than repeated—research and work which had striking or new outcomes. This meant that the value of conducting repeated or confirmatory studies was much reduced, and that there were strong incentives to obtain striking research findings. We call upon publishers to commit to publishing without prejudice confirmatory studies and those whose findings turn out not to be novel or striking.
- the short-term tenure of early career academic contracts and research grants provide insufficient time for researchers to ensure that their work is reproducible by others. We call upon funders, including UK Research and Innovation, to consider whether its grants provide the resources necessary to ensure that work that it funds is reproducible, and we recommend that it requires reproducibility as a condition of grants awarded.
- Training researchers in research integrity and the need to ensure reproducibility is inconsistent and often absent. We recommend mandating the provision of such training at undergraduate, postgraduate and early career researcher stages.
- We welcome UKRI’s policy of requiring open access to research that it funds, but we recommend that this should go further in requiring the recipients of research grants to share data and code alongside the publications arising from the funded research.
- We believe that a wider set of measures of academic success than lists of publications should be encouraged. The Future Research Assessment Programme, being carried out by UKRI, should address this and funders should also consider wider use of the ‘resume for researchers’ format in funding calls.
Further information links:
Research – quick news
- AI: MPs Warn Against “Sleepwalking” Into AI Danger Without Rapid Regulation– PoliticsHome
- Business collaboration: The National Centre for Universities and Business published Artificial Intelligence: the present and future of technology to showcase 8 university-business collaborations to address human challenges through AI partnerships
- Parliamentary Question: Whether the Government is taking steps to help ensure that cities and towns which do not have a research-intensive university (a) benefit economically from innovation and (b) create innovation-driven jobs. Answer: to support places across the UK to fulfil their potential for innovation, the Government has pledged to increase domestic public investment in R&D outside the Greater South East by at least 40% by 2030, and by at least a third over the spending review period. UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) invests across the UK with £25.1 billion allocated for 2022-2025. Innovate UK’s Launchpad programme is an innovation cluster development programme with up to £7.5 million funding available for each Launchpad for business-led innovation projects, such as the pilot in Tees Valley. Additionally, UKRI’s Strength in Places Fund provides opportunities for innovation across the UK.
- Doctoral stipend: UKRI announced the minimum doctoral stipend for UKRI funded students will rise to £18,622 for 2023/24. The minimum fee that universities can draw from UKRI training grants will also increase, to £4,712. Research Professional coverage: Sophie Inge reports that campaigners have welcomed plans to increase the minimum stipend for doctoral studentsfunded by UK Research and Innovation to £18,622. And Wonkhe has a blog: UKRI’s work on the PGR new deal.
- Postgraduate childcare: Wonkhe report – The N8 Research Partnership of eight universities in the north of England has writtento the government raising concerns over the ineligibility of postgraduate researchers for government-backed childcare subsidies. This follows a similar call from GW4 Alliance at the beginning of April.
- Health & Wellbeing: Wonkhe report that Wellcome has announced£73m in funding for eight “discovery research platforms” aimed at addressing barriers holding up progress in areas related to health and wellbeing – seven of the platforms will be at universities in England and one at the University of Cape Town.
Students: Parliamentary Questions
- Timely assessment referral and diagnosis of ADHD
- Q: Whether the Government will implement the recommendations made in the APPG for Students report on the impact of the cost of living crisis on students. Answer (excerpt): Together with the HE sector, the department is doing all that it can to support students facing hardship. However, decisions on student finance have to be taken alongside other spending priorities to ensure the system remains financially sustainable and the costs of HE are shared fairly between students and taxpayers, not all of whom have benefited from going to university.
Other news
The University of Exeter and UPP Foundation have published a new guide on university-led tutoring, encouraging other universities to take up the practice, including practical lessons around quality and scale.
The petition for HEIs to hold a statutory duty of care for students will be heard in an evidence session (held by the Petitions Committee) on 16 May. There will also be a debate in the House on 5 June.
Parliamentary Question – the cost of training doctors and nurses.
QAA published advice for providers on how to manage the rapidly increasing use of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) in HE settings. HEPI also have a new blog on the topic: How are HE leaders responding to generative AI?
Publishing: Wonkhe blog – As a new sector agreement with Springer Nature is reached, Libby Homer reminds us that we all have a duty to seek value for money in research publishing.
EO: Wonkhe – The Office for Students has published an independent analysis of the responses received to its consultation on regulating equality of opportunity. The analysis, conducted by Pye Tait Consulting, saw respondents generally welcome the Equality of Opportunity Risk Register (EORR) but seek more clarity on how it would work. Small and specialist providers also stressed data limitations and the need to avoid resource burden.
Turing: Wonkhe – The House of Lords European Affairs Committee has called for an increase in engagement between the UK and EU. In a wide-ranging report, it recommends that the government consider adding a reciprocal student exchange programme to the Turing scheme, pointing at Wales’ Taith programme as a good model – the committee does, however, praise the Turing scheme’s flexibility and emphasis on widening participation. The report also highlights the administrative barriers faced by EU students wishing to study in UK universities.
Subscribe!
To subscribe to the weekly policy update simply email policy@bournemouth.ac.uk. A BU email address is required to subscribe.
External readers: Thank you to our external readers who enjoy our policy updates. Not all our content is accessible to external readers, but you can continue to read our updates which omit the restricted content on the policy pages of the BU Research Blog – here’s the link.
Did you know? You can catch up on previous versions of the policy update on BU’s intranet pages here. Some links require access to a BU account- BU staff not able to click through to an external link should contact eresourceshelp@bournemouth.ac.uk for further assistance.
JANE FORSTER | SARAH CARTER
VC’s Policy Advisor Policy & Public Affairs Officer
Follow: @PolicyBU on Twitter | policy@bournemouth.ac.uk
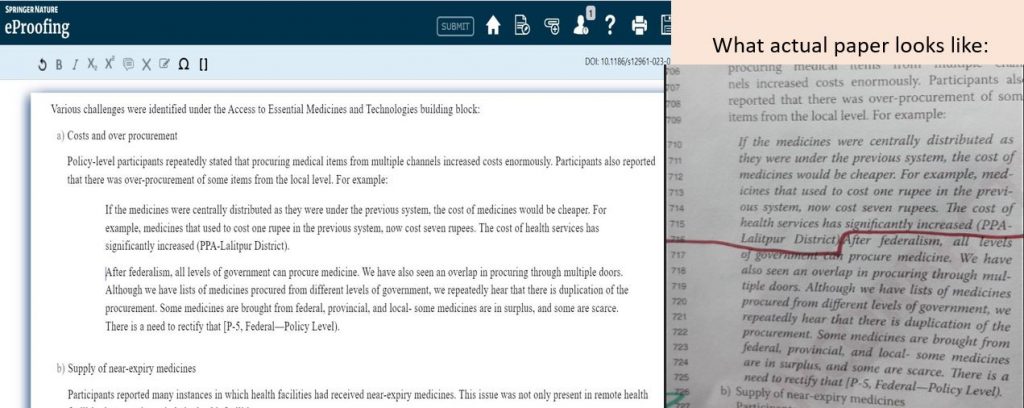

 I dutifully read and edited the proof of the actual text, but I never check the short introduction with the authors’ names which an editor had added to the final proofs. When the paper came out in print to transpired that this editor has changed the author order, i.e. my name was first, probably because I had submitted the paper on behalf of my co-author. This cause some problems with my co-author, made all the worse since I am married to her.
I dutifully read and edited the proof of the actual text, but I never check the short introduction with the authors’ names which an editor had added to the final proofs. When the paper came out in print to transpired that this editor has changed the author order, i.e. my name was first, probably because I had submitted the paper on behalf of my co-author. This cause some problems with my co-author, made all the worse since I am married to her.












 Last we took a new step into the academic publishing by submitting a paper to Qeios. This Open Access journal publishes papers for free, more or less immediately and after the paper has appeared online peer-reviewers are being invited. The paper ‘
Last we took a new step into the academic publishing by submitting a paper to Qeios. This Open Access journal publishes papers for free, more or less immediately and after the paper has appeared online peer-reviewers are being invited. The paper ‘

















 BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease