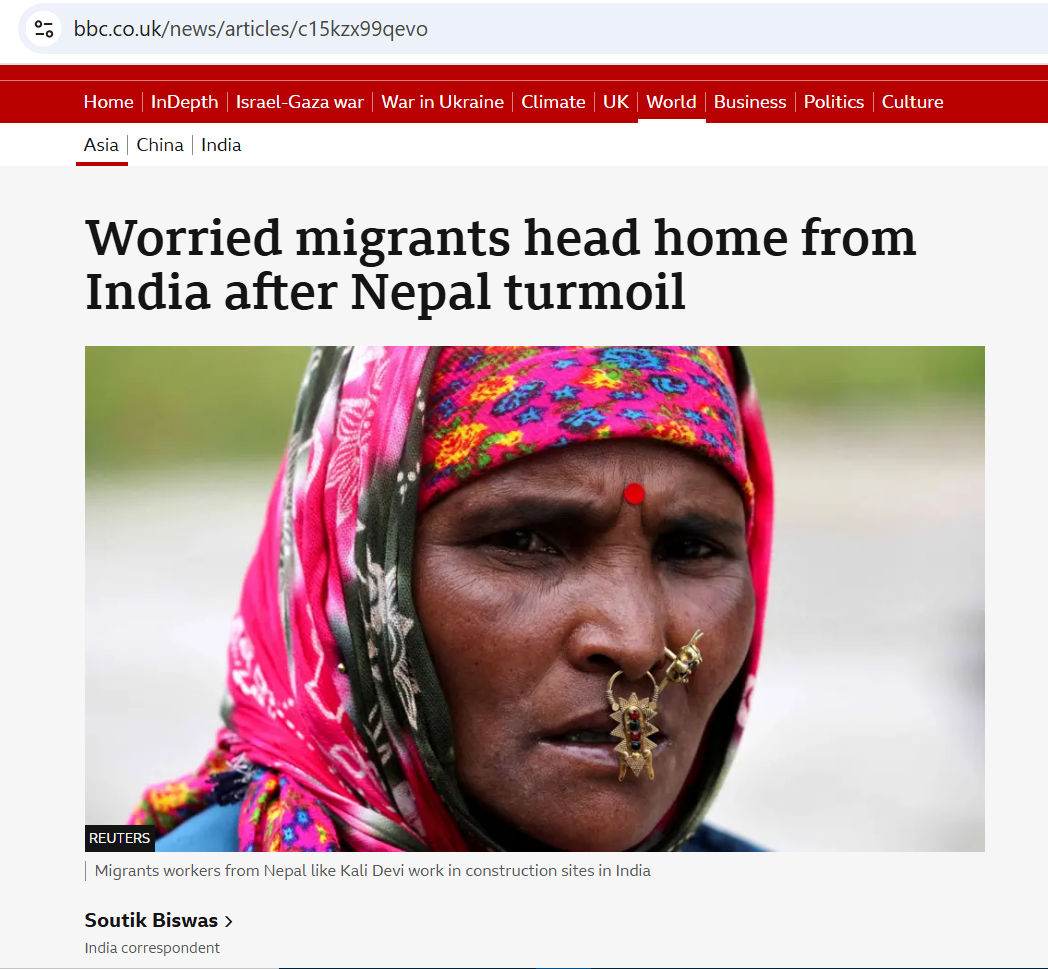
 Prof. Sujan Marahatta from Nepal will be presenting at Bournemouth University about Competency-based education of health professionals in Nepal. He will be speaking on Monday March 9th in a session jointly organised by the Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) and the Centre for Wellbeing and Long-Term Health (CWLTH). The session will be in the Bournemouth Gateway Building (BGB) room 407 from 10.00 till 12.00. Prof. Marahatta is currently the Director of the Medical Education Commission in Nepal overseeing the education on the country of a wide range of health professionals including nurses and midwives. Prof. Marahatta is Visiting Professor in the Faculty of Health, Environment & Medical Sciences (FHEMS)and has been so for nearly a decade. He is also a co-author on many publications with several past and present academics in the Faculty of Health, Environment and Medical Sciences [1-20]. Former BU academics with whom Prof. Marahatta is a co-author include: Bibha Simkhada, Nirmal Aryal, Malcolm McIver, Preeti Mahato, Elaine Asbridge, Jana Kuncova, and Anneyce Knight, whilst co-authors currently based at BU include: Dr. Catherine Angell, Prof. Carol Clark, Dr. Pramod Regmi, Prof. Vanora Hundley, and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen.
Prof. Sujan Marahatta from Nepal will be presenting at Bournemouth University about Competency-based education of health professionals in Nepal. He will be speaking on Monday March 9th in a session jointly organised by the Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) and the Centre for Wellbeing and Long-Term Health (CWLTH). The session will be in the Bournemouth Gateway Building (BGB) room 407 from 10.00 till 12.00. Prof. Marahatta is currently the Director of the Medical Education Commission in Nepal overseeing the education on the country of a wide range of health professionals including nurses and midwives. Prof. Marahatta is Visiting Professor in the Faculty of Health, Environment & Medical Sciences (FHEMS)and has been so for nearly a decade. He is also a co-author on many publications with several past and present academics in the Faculty of Health, Environment and Medical Sciences [1-20]. Former BU academics with whom Prof. Marahatta is a co-author include: Bibha Simkhada, Nirmal Aryal, Malcolm McIver, Preeti Mahato, Elaine Asbridge, Jana Kuncova, and Anneyce Knight, whilst co-authors currently based at BU include: Dr. Catherine Angell, Prof. Carol Clark, Dr. Pramod Regmi, Prof. Vanora Hundley, and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen.

References:
- Simkhada P, van Teijlingen E, Marahatta SB. Mental health services in Nepal: Is it too late? Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences 2015:1(4):1-2.
- Simkhada P, van Teijlingen E, Winter RC, Fanning C, Dhungel A, Marahatta SB. Why are so many Nepali women killing themselves? A review of Key issues. Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences 2015:1(4):43-49.
- Simkhada B, Mackay S, Khatri R, Sharma CK., Pokhrel T, Marahatta SB., Angell C, van Teijlingen E, Simkhada P. (2016) Continual Professional Development (CPD): Improving Health Prospect15 (3):1-3.
- Regmi PR, Simkhada P, van Teijlingen E, Pant PR, Kurmi O, Marahatta SB. What can we learn from the Nepal Health Facility Survey 2015? JMMIHS 2017;3 (1):1-5.
- van Teijlingen E, Marahatta SB, Simkhada P, McIver M, Sharma JS. Developing an international higher education partnership between high and low-income countries: two case studies.
- Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences 2017;3 (1):94-100.
- Simkhada P, van Teijlingen E, Simkhada, B, Regmi P, Aryal N, Marahatta SB. Experts warn Nepal government not to reduce local public health spending. Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences. 2018;4(1):1-3.
- Regmi PR, van Teijlingen E, Neupane SR, Marahatta SB. Hormone use among Nepali transgender women: a qualitative study. BMJ Open 2019;9:e030464. doi:10.1136/ bmjopen-2019-030464
- Adhikarya, P., Balen, J., Gautam, S., Ghimire, S., Karki, J., Lee, A., Marahatta, SB., Panday, S., Pohl, G., Rushton, S., Sapkota, S., Simkhada, P.P., Subedi, M., van Teijlingen, E., & the Nepal Federal Health System team (2020) The COVID-19 pandemic in Nepal: Emerging evidence on the effectiveness of action by, and cooperation between, different levels of government in a federal system, Journal of Karnali Academy of Health Sciences 2020;3;3-9.
- Sathian, B., Asim, M., Mekkodathil, A., van Teijlingen, E., Subramanya, S.H., Simkhada, P., Marahatta, S.B., Shrestha, U.M. (2020) Impact of COVID-19 on community health: A systematic review of a population of 82 million, Journal of Advanced Internal Medicine 2020; 9(1): 4-11. https://www.nepjol.info/index.php/JAIM/article/view/29159
- Khatri, RJ, van Teijlingen, E, Marahatta, SB, Simkhada, P, Mackay, S and Simkhada, B. Exploring the Challenges and Opportunities for Continuing Professional Development for Nurses: A Qualitative Study with Senior Nurse Leaders in Nepal. Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences. 2021 7(1):15-29.
- Sapkota S, Panday S, Wasti, S.P., Lee, A., Balen, J., van Teijlingen, E., Rushton, S., Subedi, M., Gautam, S., Karki., J., Adhikary, P., Marahatta SB et al.,Health System Strengthening: The Role of Public Health in Federal Nepal JNEPHA. 2022;7(1):36-42.
- van Teijlingen, E., Thapa, D., Marahatta, S.B., Sapkota, J.L., Regmi, P. Sathian, B. (2022) Editors and Reviewers: Roles and Responsibilities, In: Wasti, S.P., et al. (Eds.) Academic Writing and Publishing in Health & Social Sciences, Kathmandu, Nepal: Himal Books: 32-37.
- Mahato P, Adhikari B, Marahatta SB, et al. (2023) Perceptions around COVID-19 and vaccine hesitancy: A qualitative study in Kaski district, Western Nepal. PLOS Glob Public Health 3(2): e0000564. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0000564
- Marahatta SB, Regmi P, Knight A, Kuncova J, Asbridge E, Khanal DP, van Teijlingen E. Staff-student exchange between MMIHS and Bournemouth University. Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences. 2023;8(1)1-5
- Sapkota S, Dhakal A, Rushton S, van Teijlingen E, Marahatta SB, Lee ACK, Balen J. The impact of decentralisation on health systems: a systematic review of reviews. BMJ Global Health 2023;8:e013317. doi:10.1136/ bmjgh-2023-013317
- Sapkota, S, Rushton S, van Teijlingen E. Marahatta SB et al. Participatory policy analysis in health policy and systems research: reflections from a study in Nepal. Health Research Policy & Systems 22, 7 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-023-01092-5
- Wasti SP, van Teijlingen E, Simkhada P, Rushton S, Balen J, Subedi M, Marahatta SB et al. Selection of study sites and participants for research into Nepal’s federal health system. WHO South-East Asia J Public Health 2023;12:116-9.
- Clark CJ, Marahatta SB, Hundley VA. The prevalence of pain catastrophising in nulliparous women in Nepal; the importance for childbirth. PLoS ONE 2024;19(8): e0308129. https://doi. org/10.1371/journal.pone.0308129.
- Sapkota, S., Rushton, S., van Teijlingen, E., Subedi, M., Balen, J., Gautam, S., Adhikary, P., Simkhada, P., Wasti, SP., Karki, JK., Panday, S., Karki, A., Rijal, B., Joshi, S., Basnet, S., Marahatta, SB. (2024) Participatory policy analysis in health policy and systems research: reflections from a study in Nepal. Health Research & Policy Systems, 22(7) https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-023-01092-5 .


































 Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU
Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease