The general effects of lockdown on healthy individuals range from a general annoyance to a major limiting factor in life, especially in lockdown affects someone livelihood and/or mental health. These effects have been well documented in the media. At a societal level these effects are more mixed, first and foremost, there is positive outcome in terms of a reduced spread of the infectious disease COVID-19. Further positive effects include a reduction in air pollution, water pollution levels (in Venice), traffic jams, but also fewer break-ins (as more people are at home for more of the time). Whilst negative effects include not only economic decline, but also a lack of opportunity to travel for work or leisure, children missing education and people avoiding health care professionals for screening and treatment of diseases other then COVID-19. We have also learnt that lockdown affects different groups in society differently, some quite unexpectedly. For example, AbilityNet highlighted that “For students living with physical impairments and long-term health conditions, the benefits of studying from home and avoiding the exhausting experience of accessing face-to-face learning has left them with more energy to apply to their studies” [1]. Even before the first lockdown universities in the UK had been pro-active in their response to the pandemic [2]. One of the practical responses was to move to webinars, online teaching, marking and meetings. Before March most university academics don’t much about Zoom, Teams, Jitsi Meet or Google Meet, and today most academics will have used most of these platforms (and several others) for research meetings, webinars and conferences.
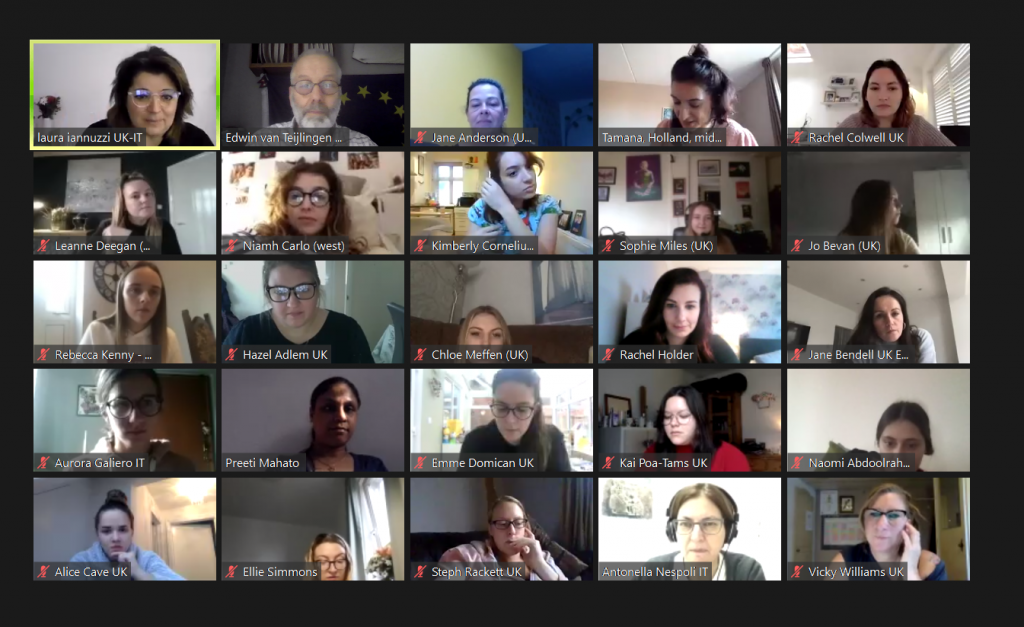 With lockdown this all has changed, like my BU colleagues I teach every week using Zoom, meet colleagues online through a range of platforms, meet students for individual tutorials through Skype or Teams. Although having the occasional limitation, there is a great opportunity as it removed the need for staff and students to be in the same room. One example of a BU education innovation was last week’s International Student Midwives’ Networking Day held on November 18th. With the restrictions of lockdown on midwifery students the BU Midwifery Team led by Dr. Laura Iannuzzi and Dr. Juliet Wood used the opportunities provided by Zoom to bring together midwifery students from across the globe. Using their long-established research links [3-16], BU academics manage to bring together student midwives from Italy, Nepal and the Netherlands to discuss midwifery and maternity issues with fellow midwifery students at BU. The day was nicely broken into two with a lunchtime event called ‘Zoom the midwife’, which as the third of its kind. In this ‘Zoom the midwife’ webinar BU’s Dr Rachel Arnold and BU Visiting Faculty Margaret Walsh shared their experience of working in different cultures for projects in Afghanistan and Nepal respectively.
With lockdown this all has changed, like my BU colleagues I teach every week using Zoom, meet colleagues online through a range of platforms, meet students for individual tutorials through Skype or Teams. Although having the occasional limitation, there is a great opportunity as it removed the need for staff and students to be in the same room. One example of a BU education innovation was last week’s International Student Midwives’ Networking Day held on November 18th. With the restrictions of lockdown on midwifery students the BU Midwifery Team led by Dr. Laura Iannuzzi and Dr. Juliet Wood used the opportunities provided by Zoom to bring together midwifery students from across the globe. Using their long-established research links [3-16], BU academics manage to bring together student midwives from Italy, Nepal and the Netherlands to discuss midwifery and maternity issues with fellow midwifery students at BU. The day was nicely broken into two with a lunchtime event called ‘Zoom the midwife’, which as the third of its kind. In this ‘Zoom the midwife’ webinar BU’s Dr Rachel Arnold and BU Visiting Faculty Margaret Walsh shared their experience of working in different cultures for projects in Afghanistan and Nepal respectively.
Our second example is a project to support midwifery education in Nepal. The Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH) in collaboration with Dalarna University in Sweden and University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust produced a draft Bridging Course for nursing lecturers in Nepal who are currently teaching midwifery and maternity care. This project is funded by GIZ (Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit). As part of this project BU offers academics at NAMS (National Academy of Medical Sciences) in Kathmandu support in their professional and pedagogic development.
Following the lockdown and seeing the success of online teaching of BU’s students earlier in 2020 we decided to try out online teaching with midwifery lecturers at NAMS. Since many people in Nepal only have a one-day weekend (Saturday) Sunday is usually a working day and due to time difference early Sunday morning are ideal times for webinars. To date online sessions in Kathmandu have been delivered by Juliet Wood, Michelle Irving, Edwin van Teijlingen and CMMPH Visiting Faculty Jillian Ireland (Professional Midwifery Advocate in Poole). The sessions proved very popular with 30 to 40 people regularly attending online from Nepal.
With challenges to delivering face-to-face lectures and tutorials at universities, online teaching and webinars have opened a whole set of new opportunities to internationalise our education.
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMMPH
References
- Universities UK (2020) Universities rise to Covid-19 challenges, online news item 7 April https://www.universitiesuk.ac.uk/news/Pages/Universities-rise-to-Covid-19-challenges-.aspx
- Low, A. (2020) Covid-19 silver linings: how the pandemic has increased opportunities for disabled university students. https://www.universitiesuk.ac.uk/blog/Pages/covid-19-disabled-students-increased-opportunities.aspx
- Dani, C., Papini, S., Iannuzzi, L. and Pratesi, S., 2020. Midwife-to-newborn ratio and neonatal outcome in healthy term infants. Acta Paediatrica, International Journal of Paediatrics, 109 (9), 1787-1790.
- Daly, D., Iannuzzi, L. et al., 2020. How much synthetic oxytocin is infused during labour? A review and analysis of regimens used in 12 countries. PLoS ONE, 15 (7 July).
- Setola, N., Naldi, E., Cocina, G.G., Eide, L.B., Iannuzzi, L. and Daly, D., 2019. The Impact of the Physical Environment on Intrapartum Maternity Care: Identification of Eight Crucial Building Spaces. Health Environments Research and Design Journal, 12 (4), 67-98.
- Skoko, E., Iannuzzi, L. et al., 2018. Findings from the Italian babies born better survey. Minerva Ginecologica, 70 (6), 663-675.
- Nieuwenhuijze, M., van Teijlingen, E., Mackenzie-Bryers, H. (2019) In risiko’s denken is niet zonder risiko (In Dutch: Thinking in terms of risk, it not with its risk). Tijdschrift voor Verloskundigen (in Dutch: Journal for Midwives), 43 (4): 6-9.
- Bogren M, van Teijlingen E., Berg M. (2013) Where midwives are not yet recognized: A feasibility study of professional midwives in Nepal, Midwifery 29(10): 1103-09.
- Bogren, M.U., Berg, M., Edgren, L., van Teijlingen, E., Wigert, H. (2016) Shaping the midwifery profession in Nepal – Uncovering actors’ connections using a Complex Adaptive Systems framework, Sexual & Reproductive Healthcare 10: 48-55.
- Dhakal Rai, S., Poobalan, A., Jan, R., Bogren, M., Wood, J., Dangal, G., Regmi, P., van Teijlingen, E., Dhakal, K.B., Badar, S.J., Shahid, F. (2019) Caesarean Section rates in South Asian cities: Can midwifery help stem the rise? Journal of Asian Midwives, 6(2):4–22.
- Bogren, M.U., Bajracharya, K., Berg, M., Erlandsson, K., Ireland, J., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2013) Nepal needs midwifery, Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (JMMIHS) 1(2): 41-44. www.nepjol.info/index.php/JMMIHS/article/view/9907/8082.
- Milne, L., Ireland, J., van Teijlingen, E., Hundley, V., Simkhada, P. (2018) Gender inequalities and childbearing: Qualitative study two maternity units in Nepal, Journal of Asian Midwives 5 (1):13-30.
- Ekström, A., Tamang, L., Pedersen, C., Byrskog, U., van Teijlingen, E., Erlandsson, K. (2020) Health care provider’s perspectives on the content and structure of a culturally tailored antenatal care programme to expectant parents and family in Nepal. Journal of Asian Midwives 7(1):23–44.
- Wrede, S., Benoit, C., Bourgeault, I., van Teijlingen E., Sandall, J., De Vries, R. (2006) Decentered Comparative Research: Context Sensitive Analysis of Health Care, Social Science & Medicine, 63: 2986-97.
- De Vries, R., Wiegers, T., Smulders, B, van Teijlingen E (2009) The Dutch Obstetrical System: Vanguard of Future in Maternity Care. In: Davis-Floyd, R., Barclay, L., Tritten, L, Daviss B.-A. (eds.) Birth Models that Work. Berkeley: University of California Press, 31-54.
- van Teijlingen E, Sandall, J., Wrede, S., Benoit, C., DeVries, R., Bourgeault, I. (2003) Comparative studies in maternity care RCM Midwives Journal 6: 338-40.
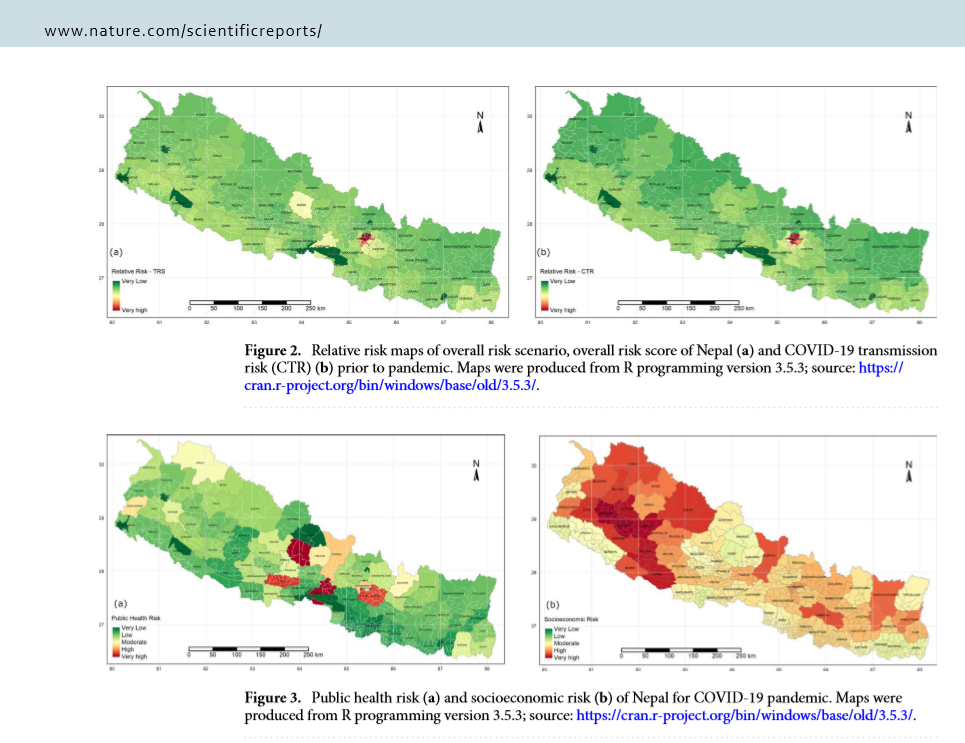
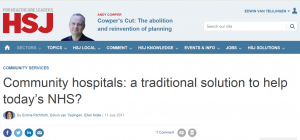
 The year 2021 started in many ways in the same way as it had ended with a country gripped in COVID-19 and a national lock down to limit the spread of the disease. It is appropriate timely that the first publication from our international collaboration, studying the health system in Nepal, focuses on COVID-19 [1]. This academic paper forms part of our on-going study of the decentralisation of the Nepal health system. The study is run by the University of Sheffield, the University of Huddersfield and Bournemouth University in the UK and PHASE Nepal and Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences in Nepal. The study is funded by the UK Health Systems Research Initiative.
The year 2021 started in many ways in the same way as it had ended with a country gripped in COVID-19 and a national lock down to limit the spread of the disease. It is appropriate timely that the first publication from our international collaboration, studying the health system in Nepal, focuses on COVID-19 [1]. This academic paper forms part of our on-going study of the decentralisation of the Nepal health system. The study is run by the University of Sheffield, the University of Huddersfield and Bournemouth University in the UK and PHASE Nepal and Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences in Nepal. The study is funded by the UK Health Systems Research Initiative.



 Staying Active and Independent for Longer (SAIL) is an EU funded project which began in 2017. The project aimed to use the concept of social innovation to develop 10 pilots across 4 countries (France, Belgium, The Netherlands and the UK) that would enable older people to be more active. The members of the research team from Bournemouth University (Prof. Ann Hemingway Prof. Adele ladkin and Dr. Holly Crossen-White) have just published a paper in Quality in Ageing and Older Adults on how social innovation can be applied to develop services that support the needs of older people. The paper entitled, The application of social innovation as it relates to older people and the implications for future policymaking: a scoping review presents research evidence into the use of soical innovation in relation to services for older people and identifies exisitng knowledge gaps. A key point to emerge from the scoping review was that although social innovation has the potential to act as a policy driver, to be effective, it is necessary to devise robust strategies to ensure full user-engagement and active involvement of communities. Furthermore, any future research into social innovation needs to focus upon the process of delivery as this is an aspect of social innovation that has to date received little attention.
Staying Active and Independent for Longer (SAIL) is an EU funded project which began in 2017. The project aimed to use the concept of social innovation to develop 10 pilots across 4 countries (France, Belgium, The Netherlands and the UK) that would enable older people to be more active. The members of the research team from Bournemouth University (Prof. Ann Hemingway Prof. Adele ladkin and Dr. Holly Crossen-White) have just published a paper in Quality in Ageing and Older Adults on how social innovation can be applied to develop services that support the needs of older people. The paper entitled, The application of social innovation as it relates to older people and the implications for future policymaking: a scoping review presents research evidence into the use of soical innovation in relation to services for older people and identifies exisitng knowledge gaps. A key point to emerge from the scoping review was that although social innovation has the potential to act as a policy driver, to be effective, it is necessary to devise robust strategies to ensure full user-engagement and active involvement of communities. Furthermore, any future research into social innovation needs to focus upon the process of delivery as this is an aspect of social innovation that has to date received little attention.





























 BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease