 BU is going through a process of re-commissioning its research centres this month. Existing centres, like ours CMMPH (the Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health) were required to submit evidence of their contribution to BU’s research capacity to deliver our strategic plan BU2025.
BU is going through a process of re-commissioning its research centres this month. Existing centres, like ours CMMPH (the Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health) were required to submit evidence of their contribution to BU’s research capacity to deliver our strategic plan BU2025.
 This process was an interesting stock-take exercise and offered an opportunity to reflect on our successes. Our friends and associates will be aware of some of our work through our collaborations, joint publications, posts on BU’s award-winning Research Blog as well as our newsletter three times a year. The phrase commonly heard on the television programme Love Island, “You’re my type on paper”, reflects the notion here that a description on paper never quite reflects reality. The same goes for the research centre description of CMMPH, on a structured application form some of the subtle success can be overlooked. First of all, being a research centre is the main function of CMMPH, but certainly not the only one.
This process was an interesting stock-take exercise and offered an opportunity to reflect on our successes. Our friends and associates will be aware of some of our work through our collaborations, joint publications, posts on BU’s award-winning Research Blog as well as our newsletter three times a year. The phrase commonly heard on the television programme Love Island, “You’re my type on paper”, reflects the notion here that a description on paper never quite reflects reality. The same goes for the research centre description of CMMPH, on a structured application form some of the subtle success can be overlooked. First of all, being a research centre is the main function of CMMPH, but certainly not the only one.
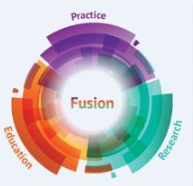 CMMPH is much more a university centre in the sense of FUSION, bringing together and creating a synergetic effect between research, Education and Practice. This FUSION enables research to be meaningful and has the ability to impact on the student experience through education as well as ‘real life’ issues and challenges in midwifery practice. This notion of being more than a research centre is reflected in our newsletters which always have sections on Research, Education and Practice.
CMMPH is much more a university centre in the sense of FUSION, bringing together and creating a synergetic effect between research, Education and Practice. This FUSION enables research to be meaningful and has the ability to impact on the student experience through education as well as ‘real life’ issues and challenges in midwifery practice. This notion of being more than a research centre is reflected in our newsletters which always have sections on Research, Education and Practice.
To highlight this synergetic effect of being a properly fused centre, CMMPH has built a reputation for developing innovative student-led clinics: i) Student Midwife integrated Learning Environment (SMiLE) postnatal clinic in collaboration with Portsmouth NHS Trust; and ii) Newborn infant feeding clinic, in collaboration with the AECC University College. These clinics are underpinned by a growing body of evidence (=Research) from studies undertaken within CMMPH, which identifies their effectiveness in terms of a unique learning environment (=Education) to offer women better maternity care (=Practice). Both student-led clinics are being evaluated by PhD students at BU, one being match-funded with Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust and the other a self-funded chiropractic student.
On a different note, in the past four years our academics have been involved in organising five international conferences. CMMPH held two, high profile, international conferences focusing on research in midwifery education (2015, 2018); it organised the BNAC (British-Nepal Academic Council) conference at Bournemouth University in April 2017 (https://blogs.bournemouth.ac.uk/research/2017/03/24/nepal-conference-at-bu/ and CMMPH staff co-organised a conference in India on Mixed-Methods Research at the Mahatma Gandhi University (2019), and an education conference in Nepal (2018). Prof. Steve Tee, FHSS Executive Dean and National Teaching Fellow, gave a key note speech at the 2018 International Conference on ‘Challenges and Prospects of Quality Education in Nepal in Federalism Era in Nepal’.

Research team includes Ann Luce, Marilyn Cash, Vanora Hundley, Helen Cheyne, Edwin van Teijlingen and Catherine Angell
CMMPH was on the BU Research Blog this week celebrating its latest media and midwifery publication (to see click here!). This paper is paper of a growing body of interdisciplinary research at BU across faculties and across the UK (see photo left). In addition last month Dr. Chris Chapleo from the Faculty of Management submitted a grant application to the ESRC under the title ‘Rebranding childbirth: understanding the role of marketing in influencing uptake of health services’, a joint application with CMMPH staff (Hundley & van Teijlingen) and Dr. Ann Luce in the Faculty of Media & Communication.
CMMPH is internationally recognised for its midwifery and maternity care research, education and publications. It has strong international links which includes active partnership agreements (MoA) with the University of Ljubljana in Slovenia, Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (MMIHS) in Nepal and University of Texas Health Science Centre, School of Nursing in the USA.
Did I mention that CMMPH academics sit on the editorial boards of (or are editors of) all top four world-leading midwifery research journals: Birth, Midwifery, Women and Birth and BMC Pregnancy & Childbirth. Not only is this unique in the UK, as no other midwifery research group can claim this, it is also unique at BU as no other research centre can claim this kind of global coverage! And, last but not least CMMPH staff can claim to have written the eighth most quoted article in the international journal Midwifery (out if 2,626 published papers over the past 35 years).
All in all, on paper, 100% a centre to be proud of.
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMMPH
 Yesterday Dorset Healthcare University NHS Foundation Trust held an away day for its clinical staff to learn more about health research. The event was hosted by the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences on its Lansdowne Campus. The organiser, Dr. Ciarán Newell, a Consultant Nurse Eating Disorders as well as Dorset Healthcare’s Facilitator for Research and Development organised the event to increase research collaborations between Dorset Healthcare and Bournemouth University.
Yesterday Dorset Healthcare University NHS Foundation Trust held an away day for its clinical staff to learn more about health research. The event was hosted by the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences on its Lansdowne Campus. The organiser, Dr. Ciarán Newell, a Consultant Nurse Eating Disorders as well as Dorset Healthcare’s Facilitator for Research and Development organised the event to increase research collaborations between Dorset Healthcare and Bournemouth University. 


















 The article titled “The effects of 8 weeks of inspiratory muscle training on the balance of healthy older adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study” has been published by Physiological Reports.
The article titled “The effects of 8 weeks of inspiratory muscle training on the balance of healthy older adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study” has been published by Physiological Reports.



























 Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop
Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives
SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives BRIAN upgrade and new look
BRIAN upgrade and new look Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh
Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease