The EU-funded Reconciliation Network of civil society organisations of the Western Balkans, known as RECOM, in conjunction with the Belgrade-based Humanitarian Law Centre, on 21st and 22nd of December 2020, organised and ran the 13th Forum for Transitional Justice online. In three panels, the invited academic experts and practitioners discussed the state of the process of dealing with the past in the post-Yugoslav space. They assessed and explored the state of transitional justice, memorialization and missing persons in the wider region.
Giulia Levi is a doctoral candidate at Bournemouth University and member of the Centre for Seldom Heard Voices: Marginalisation and Societal Integration at BU. Based on her practice experience with civil society initiatives working towards peace building in Bosnia and Herzegovina since 2005, she is currently completing a comparative, VC-funded PhD project called ‘Bridging societal divisions in post-Brexit referendum UK, learning from Bosnia’. This article was originally published on the website of the AHRC project Changing the Story that investigates how the arts, heritage and human rights education can support youth-centred approaches to civil society building in post-conflict settings across the world.
What about the survivors? The importance of a victim-centred approach to transitional justice in the Western Balkans – Reflections on a conference
Since the end of the Yugoslav succession wars of the 1990s, people living in the former Yugoslav countries have been dealing with the consequences of wartime violence and the societal divisions this caused. The path of transitional justice has proven difficult and discontinuous, yet it has had a real impact on the lives of ordinary citizens. Survivors’ families and associations, who invested the most emotional labour in the process, however, have often felt left out of the official transitional justice processes and, today, often find themselves disappointed, disillusioned, and exhausted. It is generally held that a lack of sufficiently addressing the needs and grievances of survivors of massive human rights violations inhibits chances for lasting peace and reconciliation between the previously warring parties. Open questions include whether there can be a universal approach to dealing with the past and with survivors’ needs or whether, rather, Transitional Justice can and should be tailored to every individual’s needs. However, would the latter even be realistic, given the challenging complexities at stake? Furthermore, would any kind of justice delivery sufficiently satisfy those who have suffered so much because of the war; or what justice needs, or even other needs, have to be addressed for peace building to have a genuine chance? One commentator at the conference suggested that, in order to build the future of the post-Yugoslav countries, it might be better to focus on the respective societies as a whole rather than on individual grievances. The discussions during the conference revolved around these types of complex questions. Most of the experts and practitioners present highlighted, through insights from their personal research or based on first-hand experience, the importance of taking individual survivors’ needs into account while understanding these as being interconnected with the situation in their wider, respective societies.
Contrary to other countries like South Africa or Rwanda, which established truth commissions to deal with the crimes of the past, the region of former Yugoslavia has relied mainly on retributive justice. This model consists of a top-down approach, punishing perpetrators through trials. Despite the important role played by the International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia in establishing a record of what happened during the war, scholars and practitioners have long pointed to the limitations of formal tribunals as tools of delivering reconciliation. As noted during the conference, retributive justice has often been blamed for “overpromising and underdelivering”, while promoting normative discourses that can contrast with the lived realities of people. High sounding principles of ‘peace’, ‘justice’ and ‘reconciliation’, despite seemingly universal, might carry specific meanings for people on the ground. Policies that promote their implementation have often resulted in unintended consequences such as further dividing ethnic communities and being detrimental to, rather than supportive of, survivors’ causes[1].
The formation of the Regional Commission (RECOM) constituted an attempt to propose an alternative approach to dealing with the past. In 2005, three human rights organizations based in Belgrade, Sarajevo and Zagreb and opposed to the top-down approach of foreign organizations and domestic political institutions, promoted a platform with the aim of involving survivors’ organizations more actively in shaping efforts towards truth finding and dealing with the past. At the same time, due to the regional nature of the Yugoslav wars, the RECOM founders believed that the formal participation of all the national governments in the region was a prerequisite for establishing the facts of the war and for preventing a manipulation of the 1990s conflicts for political gains. Today, RECOM includes over 2,000 organizations and individuals of the wider Western Balkan region, representing an unprecedented effort towards inclusiveness and local ownership. From 2007 to 2011, RECOM carried out 127 consultations throughout the seven former Yugoslav countries, which involved civil society organizations to discuss the establishment of a Regional Commission aimed at ascertaining the facts about the war crimes committed on the territory of the former Yugoslavia between 1991 and 2001. Despite this, the reluctance of almost all involved national governments to participate, formally and continuously, in this initiative, and the unwillingness of EU member states to play a stronger role in the process, have proven obstacles that prevented RECOM to fully achieving its aims.
All national governments in the wider region still display a lack of political will to engage in collaborative efforts of building a shared vision of the past. Instead, the narratives of the past, as these are constructed, expressed and performed across the region, especially during public commemorative events, continue to be of an exclusionary, ethno-nationalist character. The conference speakers reflected on the contemporary ‘memory industry’ in Bosnia, Croatia, Serbia and Kosovo. They found that political leaders still politicise survivors’ experiences, often attributing value to them only if they can support the respective political rhetoric. For example, Lejla Gačanica addressed the case of the town of Srebrenica, where the Bosnian Serb political leaders still refuse to acknowledge the extent of the crime committed in July 1995 against the Bosnian Muslim population. This case exemplified the ways in which manipulation and outright denial of established facts of war still heavily impact on the everyday life of ordinary citizens who suffered from these. Vjollca Krasniqi for Kosovo and Sabina Čehajić-Clancy for Bosnia emphasised the role of civil society organizations in fighting denial and breaking homogeneous narratives of the past by nurturing the public space for diverse experiences and storytelling. The collection and presentation of personal stories, with their uniqueness, for example through arts or media events, can help to change the ways in which the ‘Other’ is imagined.

Srebrenica. Credit: Giulia Levi, 2018.
If finding space for individual narratives to emerge can help defy solidified versions of the past, the search for missing persons is a fundamental step in giving dignity to individual survivors rather than treating them just as numbers in political struggles. Manfred Nowak, Expert Member of the UN Working Group on Involuntary or Enforced Disappearances during the war, reminded the audience that, still today, “the persistence of missing persons represents one of the main obstacles for people to come together and trust each other”. The uncertainty about somebody’s loved ones’ whereabouts and the circumstances of the death of each individual effectively undermines relations between communities and makes sustainable peace most difficult to achieve. Nataša Kandić, director of the Humanitarian Law Centre, advocated for the issue of missing persons to be treated not just as a humanitarian, but a political issue. This is because any progress in this work strongly depends on the political will of the involved nation-states to lead by example and share information on the location of mass graves and individual gravesites. At the same time, she insisted that “it is extremely important to look at each individual victim and find all the names, not numbers, but names. We have to publish the data on the disappearances and just by doing that we can cast light on what happened, and we can hope that citizens who have information will feel confident to come forward”. Listening to individual stories, whether of former victims, perpetrators or witnesses of war crimes is thus paramount to establishing the truth.
If compared with other contexts where mass disappearances took place like Iraq, Argentina or Sri Lanka, the massive work done in former Yugoslavia by the International Commission of Missing Persons (ICMP) in locating mass graves and identifying remains, represents a success story. Nevertheless, 10,170 persons are still missing across the region. The speakers underlined how state authorities have done too little in the last years to move the work required forward. With time passing and the soil gradually mutating, it is increasingly difficult to locate the remaining burial sites, leaving surviving families’ questions about the circumstances in which their loved ones died forever unanswered.

Lake Perucac, border between Bosnia and Serbia and site of exhumation of victims’ remains from the Bosnian and the Kosovo wars. Credit: Giulia Levi.
The issue of missing persons, in particular, shows how the fate of every single individual burdens not only the survivors’ families, but entire societies. Focusing attention on the nexus between survivors’ needs and societal problems could help counterbalance the appeal that nationalism exerts on people, who feel disappointed and abandoned, as Stephanie Schwandner-Sievers demonstrated for her ethnographic Kosovar case studies. She argued that disenfranchised people might look for a sense of security in solidified narratives, which can result in further ethnic segregation and, where discontent persists, be passed on across the generations. Far from being just a concern of the post-Yugoslav area, nationalist ideologies work as messianistic narratives for those who are on the losing end, a ‘shield’ that is thought to protect against perceived external threats. Therefore, as Slađana Lazić elaborated, transitional justice should take a more ‘transformative’ turn, widening its scope, beyond criminal justice, to socio-economic injustices. Such focus would allow “find[ing] a different policy entry point to link, [for example,] wartime rape and children born out of rape and the present-day problem of femicide and gender-based violence”. Empirical research insights such as these supported the conference’s main finding that sustainable change can only arise from taking the needs of individual survivors into account while, at the same time, addressing structural inequalities that are important for the whole society.
The panelists and moderators of the discussions at the Forum were UN experts Manfred Nowak, Thomas Osorio and Ivan Jovanović; EC expert David Hudson; academics Sabina Čehajić, Vjollca Krasniqi, Slađana Lazić, Lejla Gačanica, Sven Milekić, Jelena Đureinović, Stephanie Schwandner-Sievers and Lea David; as well as former Head of the Commission on Detainees and Missing Persons of the Republic of Croatia, Ivan Grujić; and RECOM Reconciliation Network members Žarko Puhovski, Tea Gorjanc Prelević and Nataša Kandić. The conference over two days was divided into three panel discussions: 1) Review of Transitional Justice – Opportunities; 2) Remembrance Policies and Victim Commemoration; and 3) The Issue of Missing Persons – The Priority of Regional Cooperation.
[1] Dragović-Soso, Gordy, 2010; Subotić, 2015; Baker, Obradović-Wochnik, 2016; Hughes, Kostovicova 2019.
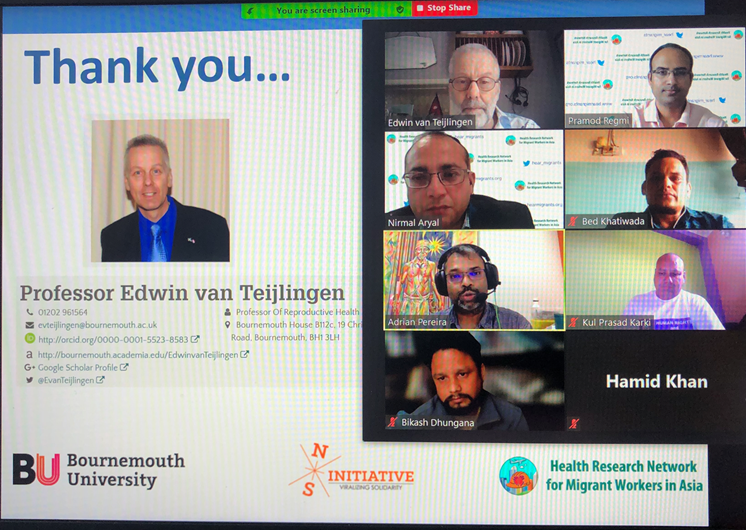 Perhaps there is an element of online-working fatigue, but I am beginning to see more and more disadvantages of online conferences. First, the contact with fellow presenters, chairs and the audience is more superficial than at a physical conference. At a conference held in person you meet people over lunch or coffee or people simply stop you in the corridors of the conference centre to discuss or challenge your paper or express their ideas for future studies.
Perhaps there is an element of online-working fatigue, but I am beginning to see more and more disadvantages of online conferences. First, the contact with fellow presenters, chairs and the audience is more superficial than at a physical conference. At a conference held in person you meet people over lunch or coffee or people simply stop you in the corridors of the conference centre to discuss or challenge your paper or express their ideas for future studies.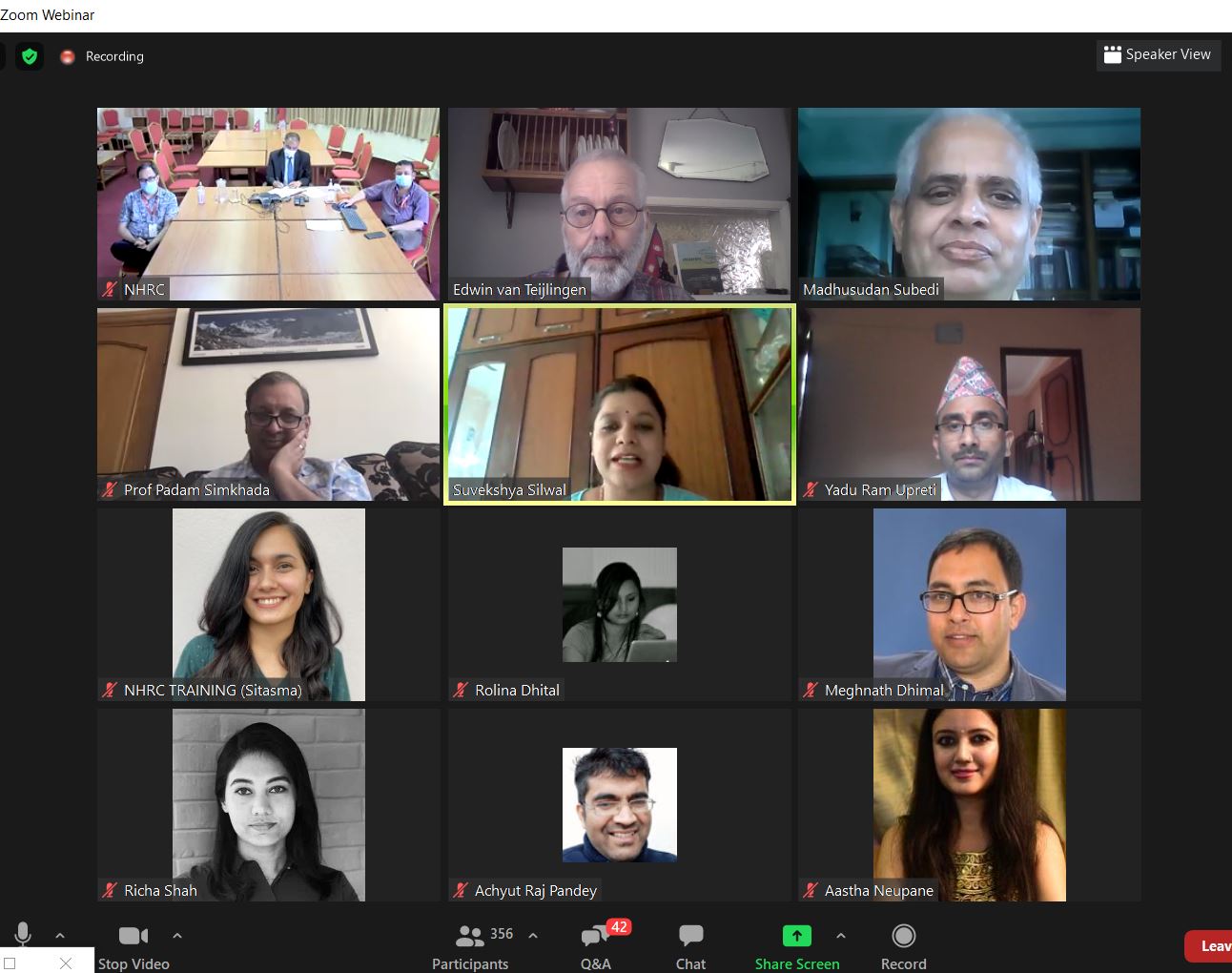 Thirdly, because I was not physically away I didn’t attend as many of the sessions at any of the three recent conferences as I would have liked to. This issue is similar in nature as the ‘old’ problem of attending a face-to-face conference at your own institution. Since you are not away your students, colleagues, etc. manage to find you and expect you to do something else instead of attending the conference. Fourthly, you don’t meet up in person with international colleagues, therefore, you don’t get a chance to discuss long-term ideas, plans, problems over a meal and a beer.
Thirdly, because I was not physically away I didn’t attend as many of the sessions at any of the three recent conferences as I would have liked to. This issue is similar in nature as the ‘old’ problem of attending a face-to-face conference at your own institution. Since you are not away your students, colleagues, etc. manage to find you and expect you to do something else instead of attending the conference. Fourthly, you don’t meet up in person with international colleagues, therefore, you don’t get a chance to discuss long-term ideas, plans, problems over a meal and a beer.












 I invite you to join us in developing our proposal for Sustainable Storytelling for Science & Health as a
I invite you to join us in developing our proposal for Sustainable Storytelling for Science & Health as a 




























 Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration
Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration 3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease