OfS Regulation – Free Speech, Compulsory TEF, Student empowerment
The long awaited (and very long) consultation on the role and functions of the Office for Students was published this week. In fact there are several separate consultations (Wonkhe have helpfully grouped them all on one web page):
- the regulatory framework
- registration fees
- Degree awarding powers and university title
- One about selection of designated quality assessment body for the OfS– QAA is the only candidate
- One about selection of a designated data body for the OfS – HESA is the only candidate
The consultations are open until 22nd December and BU will be reviewing them and preparing responses – please let policy@bournemouth.ac.uk know if you would like to be involved.
There is a huge amount of detail and a lot of areas for discussion here, but interestingly the Minister and the press chose to focus on freedom of speech yesterday. The Times published an interview with Jo Johnson discussing the proposal that measures to protect freedom of speech should be a condition of OfS registration. The Guardian notes proposed powers for the OfS to fine or suspend the registration of universities that fail to protect the freedom of speech on campus, including student unions that ‘no platform’ controversial speakers. There has been a lot of commentary on this – not least that students’ unions are independent organisations. It is really interesting to note that in the summary of the consultation prepared for students by the Department for Education, freedom of speech is not mentioned.
- Johnson: “Our young people and students need to accept the legitimacy of healthy, vigorous debate in which people can disagree with one another. That’s how ideas get tested, prejudices exposed and society advances. Universities mustn’t be places in which free speech is stifled.”
- Sir Michael Barber OfS Chair: “Ensuring freedom of speech and learning how to disagree with diverse opinions and differing views of the world is a fundamental aspect of learning at university. The OfS will promote it vigorously.”
The relevant bit of the consultation starts on page 32 –
- “This consultation includes such a public interest principle, which states that the governing body of an institution must take such steps as are reasonably practicable to ensure that freedom of speech within the law is secured within its institution. This public interest principle will form part of the public interest governance condition…”
- “The OfS will use ‘indicative behaviours’ to assess compliance with the principles; these are set out in the Guidance on registration conditions. With regard to free speech, for example, one behaviour that would indicate compliance would be to have a freedom of speech code of practice. This should set out the procedures which members, students and employees should follow in relation to meetings or activities, and the conduct which is expected of those individuals. Some of the best examples set out clearly what does and does not constitute reasonable grounds for refusal of a speaker, and the disciplinary actions which would follow a breach of the code of practice. A behaviour that might indicate non-compliance would be where a provider fails to abide by its own freedom of speech procedures”.
There has of course been something of a media/social media storm, with rage from both ends of the political spectrum about those with different views allegedly seeking to stifle or prevent free speech, big disagreements on the role of trigger warnings, safe spaces and “no platforming”, and a number of voices pointing out that universities are already subject to legal obligations on both free speech and the Prevent duty and this is all a bit over-played.
But apart from this issue, the consultation has much broader scope. It sets out the broad objectives for the OfS:
- all students, from all backgrounds, are supported to access, succeed in, and progress from, higher education
- all students, from all backgrounds, receive a high quality academic experience, and their qualifications hold their value over time in line with sector-recognised standards
- that all students, from all backgrounds, have their interests as consumers protected while they study, including in the event of provider, campus, or course closure
- that all students, from all backgrounds, receive value for money
The OfS will seek to mitigate the risk that each of these four objectives is not met and:
- “As it does so, the OfS will also seek to mitigate risk that the sector does not deliver value for money for taxpayers and citizens (who are directly involved through the allocation of public grant funding, research funding by UKRI, and the public subsidy to the student finance system). It will also do so while recognising the needs of students from disadvantaged backgrounds, who are less likely to access, succeed in, and progress successfully from higher education, even once their entrance characteristics are taken into account.
- The OfS will also work with UKRI to ensure that the reciprocal risk around the sustainability of providers which contribute to the vibrancy of the research base is monitored and mitigated appropriately. The flow of information between the two organisations will be crucial to achieving this.”
The many other areas covered in detail include
- Making TEF compulsory for all HEIs with >500 students
- Publishing justification of high senior staff salaries
- Transparency about student transfer (between courses)
- Empowering students through clearer student contracts
We will look at some areas in more detail in the following weeks.
The impact of universities
Meanwhile, Universities UK (UUK) published a report on the Economic Impact of Universities in 2014-15. Some highlights:
- In total, the economic activity of universities, the international students they attract and their visitors, supported more than 940,000 jobs in the UK in 2014-15.
- In 2014-15, universities themselves employed 404,000 people, or 1.3 percent of all UK employment
- UK universities, together with their international students and visitors, generated £95 billion of gross output in the economy in 2014-15.
- The gross value added contribution of universities’ own operations to GDP, at £21.5 billion in 2014-15, is larger than that made by a number of sizable industries.
- UK universities, together with their international students and visitors, supported £14.1 billion in tax receipts for the Exchequer in 2014-15.
- In total, universities in the UK earned £13.1 billion in export receipts in 2014-15.
Student Loans and Value for Money
The Treasury Committee launched an inquiry scrutinising recent changes to the student loan system. This week evidence was received from Dr Helen Carasso (Oxford) and Andrew McGettigan (freelance author and lecturer). Key points:
- Experts disagree exactly how much raising the repayment threshold will cost the taxpayer. The system is complex and not even understandable to highly-qualified experts
- The notion that the written off loans will cost to the taxpayer the same amount with the post-92 as the previous £3,000 fees is publically unpopular
- The post-92 higher fees is believed to have created more teaching resources within the system
- McGettigan claimed that higher interest rates for students still studying were purely designed to deal with the rarer issue of rich students taking out loans and investing them elsewhere
- Varying price for tuition fees by programme is nonsensical – students would be discouraged from choosing courses which were priced lower as it has a status implication (McGettigan).
- The system has created a series of disincentives for universities to charge anything other than the highest fee (Carasso).
- Carasso stated an overt graduate tax would be a better accounting method than student loans although it would feel like a penalty. McGettigan expanded suggesting it may destabilise recruitment and retention and potentially encourage drop out or emigration
- On the sale of the loan book McGettigan stated the old mortgage-style loans had already been sold at a profit, but under the new system the sale of loans would not affect public sector net debt, that any price would be lower than fair value and amount to a loss for the government.
- Re: marketization of HE Carasso stated it was very difficult for an applicant to make a fully-informed decision (in relation to price and net cost).
- How should the repayment system best be reformed:
- McGettigan – the main problem is the large graduate debt. A lower starting debt would mean interest rates would not apply in the same way,
- Carasso – if the system is too complex to understand that’s a problem. Fees are probably too high, and why is there not an employer contribution mechanism?
Meanwhile the Economic Affairs Select Committee is examining if students get value for money (HE, FE and technical education) through oral evidence sessions. Follow it here
Widening Participation
50% of students are First in Family – This week the Telegraph drew on UCAS data to report that half of students who started a degree last year were first in family to attend HE. However, the article is disparaging as many of these students attended ‘low’ or ‘mid-ranking’ universities and few studied the ‘top’ subjects (listed as medicine, maths and science). The article went on to raise the current headline grabbing debate over fees and value for money and stated: “critics said last night that the figures showed that too many students were attending low-performing universities which charge “outrageous” fees but fail to improve social mobility.”
Whole-institution approach to WP – This week OFFA called for universities to create a step change and accelerate social mobility goals by adopting a whole-institution approach to widening participation, embedding fair access at all levels of the organisation, across all areas of work, and senior management. To accompany the call OFFA released the commissioned report: Understanding a whole institution approach to WP
Les Ebdon (Director, OFFA) stated: “Excellent progress has been made in widening access to higher education for the most disadvantaged young people. But for too long, this progress has only been incremental. We now need to see transformational change.
“Adopting a genuine whole institution approach – where access is a key priority at every level – is the biggest thing a university or college could do to make change happen. This research offers a vital opportunity to make the further, faster progress we badly need to see.
International academics
Q – Stephen Gethins (SNP): With reference to the Government’s policy paper, Collaboration on Science and Innovation: A Future Partnership Paper, published on 6 September 2017, whether it is her policy to extend visa entitlement to the spouses and dependents of EU academics who can work in the UK after the UK has left the EU.
And
Q – Stephen Gethins (SNP): With reference to the Government’s policy paper, Collaboration on Science and Innovation: Future Partnership Paper, published on 6 September 2017, what representations she has received from universities and national academies on the potential effect of changes to freedom of movement on the UK’s ability to attract and retain high quality researchers.
A: Brandon Lewis (Con): The Government recognises the valuable contribution migrants make to our society and we welcome those with the skills and expertise to make our country better still. But we must manage the process properly so that our immigration system serves the national interest.
We have been clear that after the UK leaves the EU, free movement will end, but migration between the UK and the EU will continue and we are considering a number of options as to how this might work. We will be setting out initial proposals for our future immigration arrangements later in the year.
The Government recognises that it is important that we understand the impacts on the different sectors of the economy and the labour market and want to ensure that decisions on the long-term system are based on evidence. On July 2017, we commissioned the independent Migration Advisory Committee (MAC) to advise on the economic and social impacts of the UK’s exit from the European Union and also on how the UK’s immigration system should be aligned with a modern industrial strategy… The Government will carefully consider any recommendations made to it by the MAC before finalising the details of the future immigration system for EU nationals.
The Government also regularly engages with sectoral bodies – including those in the scientific and academic sectors ¬- to ensure our immigration routes work effectively to enable businesses to access the talent they need. Their views do, and will continue to, inform our decisions on any changes to the system.
Consultations & Inquiries
The Policy team compiles details of the key HE and niche research consultations and select committee inquiries on the consultation tracker. BU responses to HE consultations are managed by Sarah and Jane.
Let us know you’re interested! We invite colleagues across BU to provide response input, however, if there is a consultation in your area of expertise don’t wait for an invite – contact us on policy@bournemouth.ac.uk – we’d love to hear from you so we can access all the pockets of expertise across BU. Take a look at the consultation tracker to find out if there is a current inquiry related to your role.
New consultations and inquiries:
- 5 Higher Education and Research Act consultations
- International students – social and economic impact (link)
- Science budget and the Industrial Strategy (link)
- Intellectual Property
- Decarbonisation in HE sector
- Enabling Gypsies, Roma and Travellers
- Regulation of Nursing Associates in England
(See the consultation tracker for links to all these new consultations and inquiries.)
To view the responses BU has submitted to recent consultations and inquiries across all topics click here.
Other news
Teaching excellence: The University Alliance has published Technical and professional excellence: Perspective on learning and teaching.
TEF Gold: HEPI have released Going for Gold: Lessons from the TEF provider submissions. The report breaks down the influential aspects of the provider submissions which the author suggests may have swayed the panel’s final award decisions. While the report is based on opinion it offers suggestions to providers and Government on how to improve the qualitative aspect of the TEF submission. Spoiler alert: BU features frequently within the document.
Alternative Providers: The National Audit Office has published their Follow-up on alternative HE providers. The report notes several area of progress:
- Non-continuation rates reduced from 38% to 25% (although still 15% higher than the mainstream HE sector) with DfE action taken against 11 alternative providers where dropout rates are unacceptably high. More regular and reliable monitoring data has been called for.
- Reduction in paying student loans to ineligible students from 4% to 0.5%
- DfE have strengthened their oversight framework and are acting on third party reports of non-compliance or under-performance.
- Positive reports of widening access within disadvantaged or under-represented groups of students
However, early data implies graduates from alternative provider’s progress to further study or employment at a lower rate and lower entry salary than graduates from mainstream HE institutions.
Subscribe!
To subscribe to the weekly policy update simply email policy@bournemouth.ac.uk
JANE FORSTER | SARAH CARTER
Policy Advisor Policy & Public Affairs Officer
65111 65070
Follow: @PolicyBU on Twitter | policy@bournemouth.ac.uk
 Please see the calls currently open, or forthcoming, being offered through the Newton Fund scheme. Some calls are newly opened whilst others have been promoted previously via the BU Research blog. In each case, please refer to the call website for full details including eligibility requirements and thematic priorities:
Please see the calls currently open, or forthcoming, being offered through the Newton Fund scheme. Some calls are newly opened whilst others have been promoted previously via the BU Research blog. In each case, please refer to the call website for full details including eligibility requirements and thematic priorities:
 we were fortunate to be included in the programme for
we were fortunate to be included in the programme for  planned for December 15 in Brighton’s Media Centre. Here we will be featuring the stories we are producing based on photographs and audio recordings captured during the workshops. We will also be hearing from some of the storytellers from all three workshops (Bournemouth, Brighton and Sheffield) about their experiences of the workshops and how this opportunity has opened new doors for them.
planned for December 15 in Brighton’s Media Centre. Here we will be featuring the stories we are producing based on photographs and audio recordings captured during the workshops. We will also be hearing from some of the storytellers from all three workshops (Bournemouth, Brighton and Sheffield) about their experiences of the workshops and how this opportunity has opened new doors for them.
 #TalkBU is a monthly lunchtime seminar on Talbot Campus, open to all students and staff at Bournemouth University and free to attend. Come along to learn, discuss and engage in a 20-30 minute presentation by an academic or guest speaker talking about their research and findings, with a Q&A to finish.
#TalkBU is a monthly lunchtime seminar on Talbot Campus, open to all students and staff at Bournemouth University and free to attend. Come along to learn, discuss and engage in a 20-30 minute presentation by an academic or guest speaker talking about their research and findings, with a Q&A to finish. 


 Dr Caroline Ellis-Hill from the Centre for Qualitative Research
Dr Caroline Ellis-Hill from the Centre for Qualitative Research 
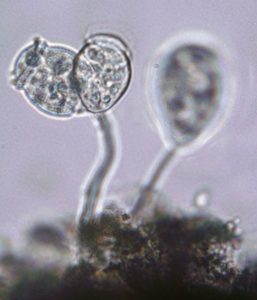 Microscopic investigations of water samples from the half-barrel pond in Christchurch House courtyard have revealed a menagerie of single-celled life. These tiny organisms (smaller than one tenth of a millimetre) are incredibly important as they form the basis of food webs. They also play a major role in maintaining water quality as they feed on bacteria, and stalked species such as Vorticella (image) are responsible for their removal in waste-water treatment plants. The half-barrel “pond” may be almost as small as its inhabitants but it promises to become a treasure of local ‘hidden’ biodiversity!
Microscopic investigations of water samples from the half-barrel pond in Christchurch House courtyard have revealed a menagerie of single-celled life. These tiny organisms (smaller than one tenth of a millimetre) are incredibly important as they form the basis of food webs. They also play a major role in maintaining water quality as they feed on bacteria, and stalked species such as Vorticella (image) are responsible for their removal in waste-water treatment plants. The half-barrel “pond” may be almost as small as its inhabitants but it promises to become a treasure of local ‘hidden’ biodiversity!
 I was given the opportunity to present some preliminary results from an ongoing study I am conducting as part of my PhD, looking into the effects of a multi-nutrient omega-3 fatty acid supplement and exercise on mobility and cognitive function in ladies aged 60+. Analysis of the baseline data revealed relationships between levels of omega-3 fatty acids in the blood with cognitive and gait outcomes, however this effect differed between non-frail and pre-frail participants.
I was given the opportunity to present some preliminary results from an ongoing study I am conducting as part of my PhD, looking into the effects of a multi-nutrient omega-3 fatty acid supplement and exercise on mobility and cognitive function in ladies aged 60+. Analysis of the baseline data revealed relationships between levels of omega-3 fatty acids in the blood with cognitive and gait outcomes, however this effect differed between non-frail and pre-frail participants.

 NERC will commission its second round of Doctoral Training Partnership investment (DTP2) through a fully open competitive call, to be launched in January 2018.
NERC will commission its second round of Doctoral Training Partnership investment (DTP2) through a fully open competitive call, to be launched in January 2018. 










 SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives
SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives BRIAN upgrade and new look
BRIAN upgrade and new look Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh
Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar
Exploring Embodied Research: Body Map Storytelling Workshop & Research Seminar Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch
Marking a Milestone: The Swash Channel Wreck Book Launch ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease