 Yesterday, Sunday 14th January, I was invited by Bournemouth University’s former PhD student Dr. Pratik Adhikary to run a three-hour methods session on semi-structured interviews and focus group discussions at the Nepal Injury Research Centre (NIRC). The workshop was based on work normally presented as part of BU’s Doctoral College Researcher Development Programme.
Yesterday, Sunday 14th January, I was invited by Bournemouth University’s former PhD student Dr. Pratik Adhikary to run a three-hour methods session on semi-structured interviews and focus group discussions at the Nepal Injury Research Centre (NIRC). The workshop was based on work normally presented as part of BU’s Doctoral College Researcher Development Programme.
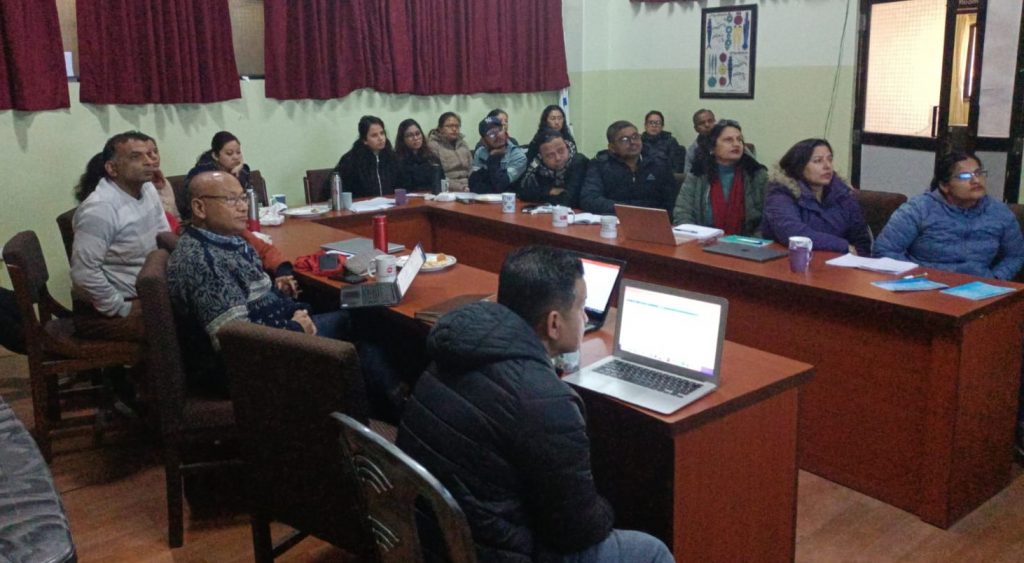 The audience comprised PhD students based at NIRC, as well as at Kathmandu Medical College (KMC), and Nepal’s oldest and largest university, Tribhuvan University. Participants were involved in research into many different research questions, ranging from road traffic accidents to sexual health and the well-being of migrant workers. NIRC was established with funding from the UK National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Global Health Research Programme and it is a partnership between KMC and the University of the West of England, Bristol (UWE).
The audience comprised PhD students based at NIRC, as well as at Kathmandu Medical College (KMC), and Nepal’s oldest and largest university, Tribhuvan University. Participants were involved in research into many different research questions, ranging from road traffic accidents to sexual health and the well-being of migrant workers. NIRC was established with funding from the UK National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Global Health Research Programme and it is a partnership between KMC and the University of the West of England, Bristol (UWE).
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH)
































 Bartholomew V, Hundley V, Clark C, Parris B (2024) The RETHINK Study: Could pain catastrophisation explain why some women are more likely to attend hospital in early labour. Sexual & Reproductive Healthcare
Bartholomew V, Hundley V, Clark C, Parris B (2024) The RETHINK Study: Could pain catastrophisation explain why some women are more likely to attend hospital in early labour. Sexual & Reproductive Healthcare 













 Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week
Second NIHR MIHERC meeting in Bournemouth this week Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian
Dr. Ashraf cited on ‘Modest Fashion’ in The Guardian NIHR-funded research launches website
NIHR-funded research launches website MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease