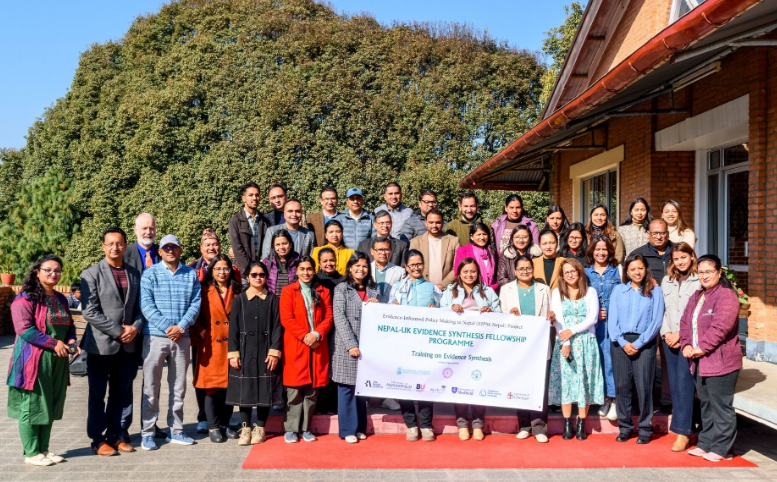
Happy New Year and we hope it will be prosperous and healthy.  On the last day of 2025 the Nepal Journal of Epidemiology published our editorial ‘Progress of the Unique Fellowship in Health Research Evidence Synthesis in Nepal‘ [1]. Co-authors of this editorial include Faculty of Health & Social Sciences Visiting Faculty: Prof. Padam Simkhada and Dr. Bibha Simkhada who are both grant holders on the British Academy grant which also includes BU’s Dr. Pramod Regmi. The journal editor added a photo of our recent three-day event on research capacity building in Dhulikhel (Nepal) to the cover of the December issue.
On the last day of 2025 the Nepal Journal of Epidemiology published our editorial ‘Progress of the Unique Fellowship in Health Research Evidence Synthesis in Nepal‘ [1]. Co-authors of this editorial include Faculty of Health & Social Sciences Visiting Faculty: Prof. Padam Simkhada and Dr. Bibha Simkhada who are both grant holders on the British Academy grant which also includes BU’s Dr. Pramod Regmi. The journal editor added a photo of our recent three-day event on research capacity building in Dhulikhel (Nepal) to the cover of the December issue. Nepalese researchers, academics, policymakers and practitioners are undertaking a unique Fellowship in evidence synthesis and evidence-based policy making. This Fellowship is part of a larger project called ‘Evidence Informed Health Policy Making in Nepal (EHPN)’, funded by the British Academy. After our training event Dr. Regmi had the opportunity to present our (2022) textbook Academic Writing and Publishing in Health and Social Sciences to His Excellency Mr. Madhav Chaulagain, Nepal’s newly appointed Minister of Forest & Environment.
Nepalese researchers, academics, policymakers and practitioners are undertaking a unique Fellowship in evidence synthesis and evidence-based policy making. This Fellowship is part of a larger project called ‘Evidence Informed Health Policy Making in Nepal (EHPN)’, funded by the British Academy. After our training event Dr. Regmi had the opportunity to present our (2022) textbook Academic Writing and Publishing in Health and Social Sciences to His Excellency Mr. Madhav Chaulagain, Nepal’s newly appointed Minister of Forest & Environment.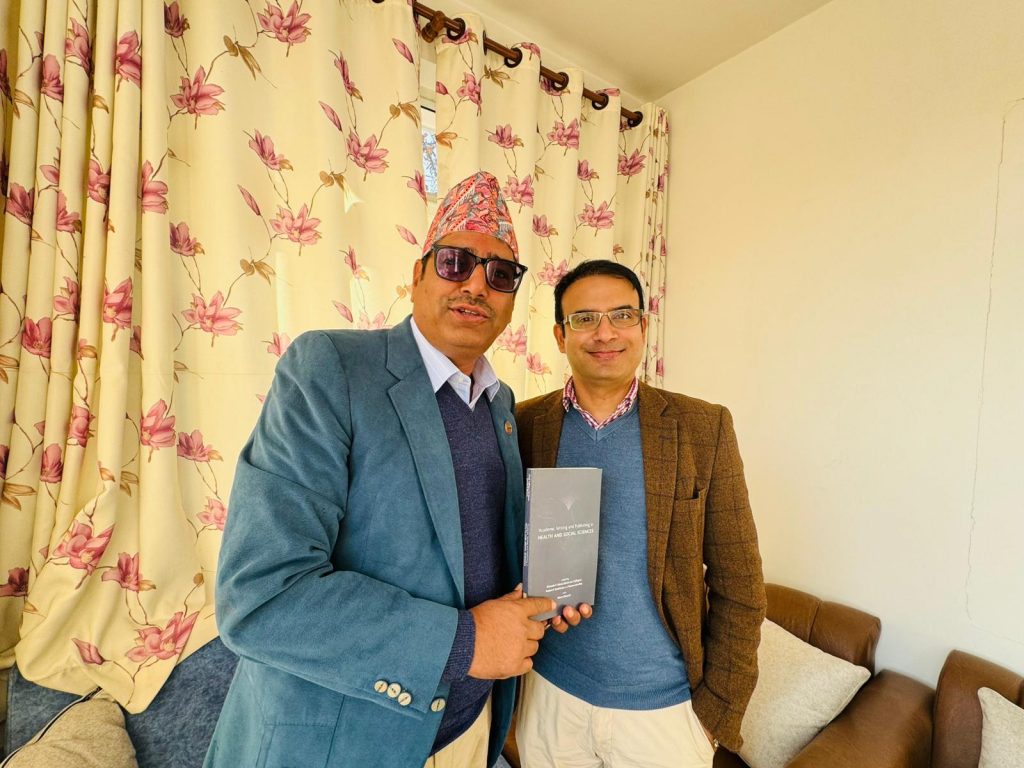
Evidence-informed policy making developed out of the earlier idea of ‘evidence-based policy making’. The central idea behind evidence-based policy making was that it should be largely (or even solely) guided by evidence. Evidence-informed policy making adds that policies should not just be evidence-based they should also be feasible, appropriate for their context and aligned with stakeholders’ values and therefore one would expect meaningful input from these stakeholders. This is the second editorial highlighting our research capacity-building work in Nepal. The first editorial ‘Strengthening Evidence Synthesis for Health Policymaking in Nepal: A New Fellowship Initiative’ appeared in an earlier edition of the Nepal Journal of Epidemiology [2].

Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health

References:
- Vaidya, A., Simkhada, P., Silwal, R. C., Paudyal, P., Dhimal, M., Simkhada, B., van Teijlingen, E. (2025). Progress of the Unique Fellowship in Health Research Evidence Synthesis in Nepal. Nepal Journal of Epidemiology, 15(4), 1397–1398.
- Simkhada, P., Vaidya, A., Regmi, P. P., Paudyal, P., van Teijlingen, E., Dhimal, M., Shrestha, A., Koirala, B., Simkhada, B. (2025). Strengthening Evidence Synthesis for Health Policymaking in Nepal: A New Fellowship Initiative. Nepal Journal of Epidemiology, 15(2), 1379–1380.












































 Dr. Chloe Casey on Sky News
Dr. Chloe Casey on Sky News Final Bournemouth University publication of 2025
Final Bournemouth University publication of 2025 On Christmas Day in the Morning…
On Christmas Day in the Morning… New Nepal scoping review on maternal & neonatal health
New Nepal scoping review on maternal & neonatal health ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published
Horizon Europe 2025 Work Programme pre-Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease