This conference was co-hosted by BU and the National Trust (NT) on the 21st March and attended by over 150 delegates including conservation practitioners, citizen scientist members of the public, researchers and BU students.
Scroll down for pictures from the day
In the morning we heard from 16 speakers from a wide range of wildlife organisations including Natural England, the RSPB, Bioblitz, Field Studies Council and Dorset Wildlife Trust. We also presented our BU-NT collaborative FIF funded Purbeck Heath SERT (Student Environment Research Team) project.
In the afternoon we brain stormed ideas in energetic workshops that explored challenges and solutions to achieving impact of citizen science in wildlife conservation management. The outputs from the workshops will be posted soon after Easter here – Wessex Conservation Forum and video recordings of the morning talks will be available too later.
For more information please email – Anita Diaz adiaz@bournemouth.ac.uk
Thanks very much to inspiring speakers, a wonderfully warm and engaged audience and super support from the National Trust and BU students and staff. We are particularly grateful for the support from the Wessex Conservation Forum and the British Ecological Society and for excellent help from the following BU student volunteers: Adam Pickles, Kimberley Tickner, Melissa Howell and Melissa Stephens.
Conference Scientific Organising Committee – David Brown (National Trust), Michelle Brown (National Trust), Gitte Kragh (BU) & Anita Diaz (BU).
Here are some moments from the day! Also you can take a look here for more #CitSci4Wildlife
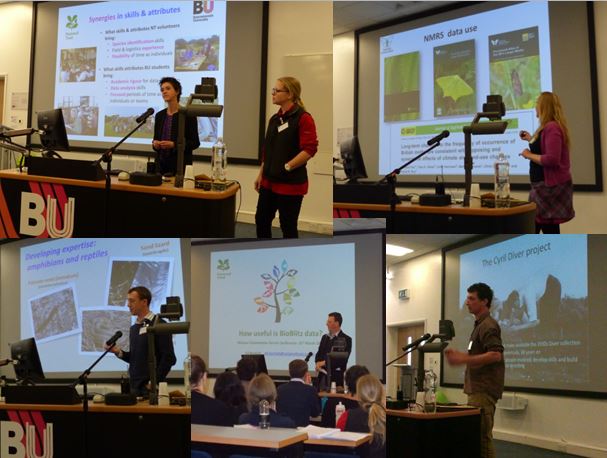

Some of the morning lectures
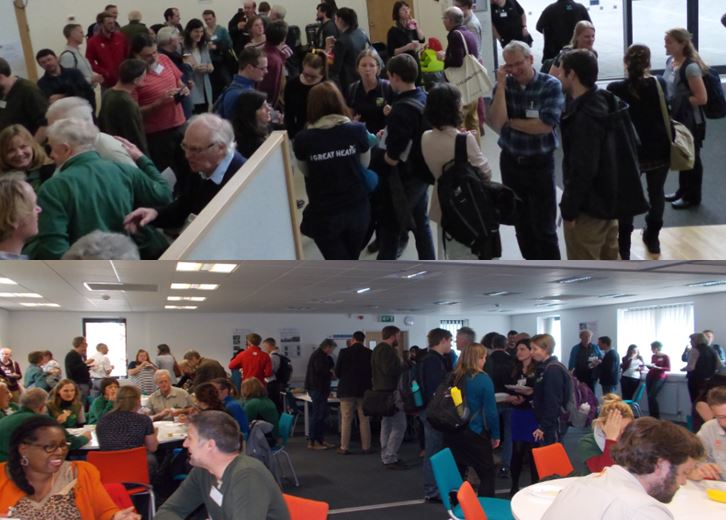

Networking and relaxing over coffee and lunch



Making it happen – some of the staff and student organisers
Some Tweets on tweets on #citsci4wildlife
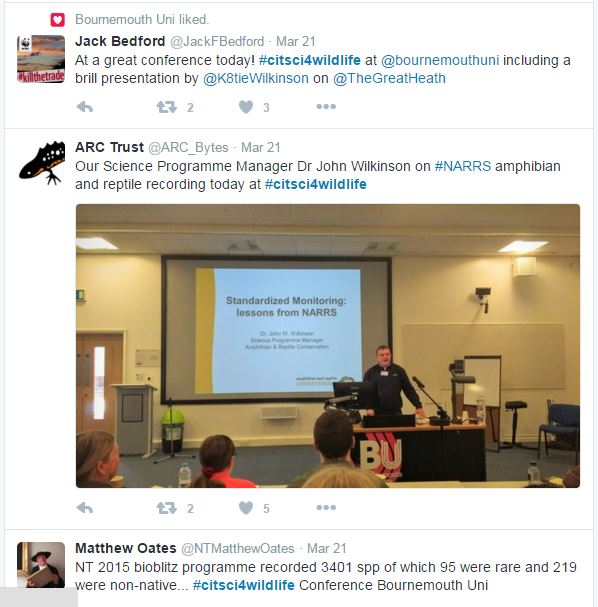
tweets on #citsci4wildlife
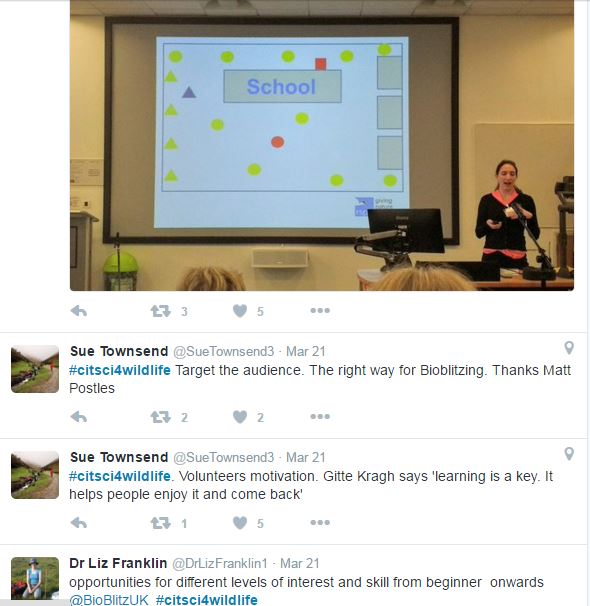
tweets on #citsci4wildlife
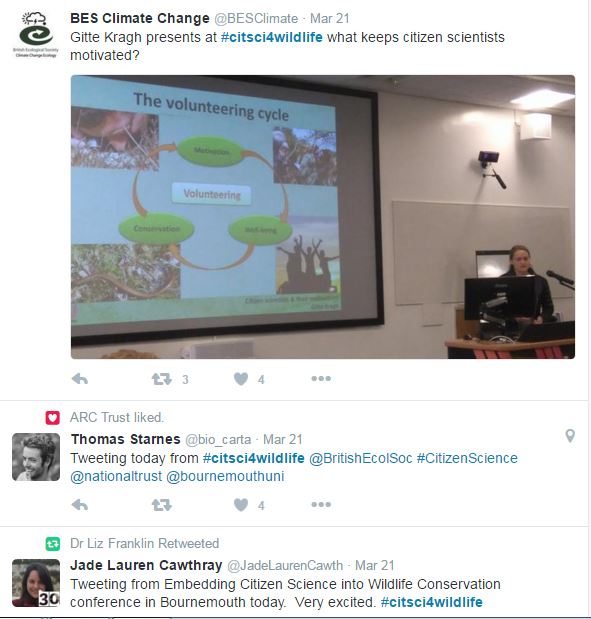
tweets on #citsci4wildlife






 When applying to become a Research Assistant for this project I expected mostly data collection and being involved in the recruitment of participants. With a background in psychology, and having worked as a voluntary Research Assistant before, I found the aim of my work slightly different. When joining the research team and the Nutrition and Dementia project in January, I got happily surprised of my part in the project. I was greatly welcomed by Dr Jane Murphy RD RNutr, Joanne Holmes RNutr and Cindy Brooks, Research Assistant.
When applying to become a Research Assistant for this project I expected mostly data collection and being involved in the recruitment of participants. With a background in psychology, and having worked as a voluntary Research Assistant before, I found the aim of my work slightly different. When joining the research team and the Nutrition and Dementia project in January, I got happily surprised of my part in the project. I was greatly welcomed by Dr Jane Murphy RD RNutr, Joanne Holmes RNutr and Cindy Brooks, Research Assistant.


 Since his arrival in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences last year postdoctoral researcher Dr. Pramod Regmi has been busy getting his publications out. Yesterday saw the latest of his articles appear in print, this time in the latest issue of the Nepal Journal of Epidemiology. The editorial, co-authored with Dr. Om Kurmi (University of Oxford) and Dr. Puspa R. Pant at the University of the West of England, addresses the growing problem air pollution in low-income countries such as Nepal. The paper is called: ‘
Since his arrival in the Faculty of Health & Social Sciences last year postdoctoral researcher Dr. Pramod Regmi has been busy getting his publications out. Yesterday saw the latest of his articles appear in print, this time in the latest issue of the Nepal Journal of Epidemiology. The editorial, co-authored with Dr. Om Kurmi (University of Oxford) and Dr. Puspa R. Pant at the University of the West of England, addresses the growing problem air pollution in low-income countries such as Nepal. The paper is called: ‘



 The April issue of the Journal of Neonatal Nursing will publish the latest article written by a combination of Faculty of Health & Social Sciences staff and Visiting Faculty. The paper ‘Experiences of fathers with babies admitted to neonatal care units: A review of the literature’
The April issue of the Journal of Neonatal Nursing will publish the latest article written by a combination of Faculty of Health & Social Sciences staff and Visiting Faculty. The paper ‘Experiences of fathers with babies admitted to neonatal care units: A review of the literature’ 









 Our latest paper in the international journal BMC Pregnancy & Childbirth published late last month was highlighted yesterday in a
Our latest paper in the international journal BMC Pregnancy & Childbirth published late last month was highlighted yesterday in a  Our paper is great example of interdisciplinary research, as celebrated at the forthcoming Interdisciplinary Research Sector Day on June 21st (
Our paper is great example of interdisciplinary research, as celebrated at the forthcoming Interdisciplinary Research Sector Day on June 21st (










 New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease