A large scale empirical and legal study on the Intellectual Property Implications of the Development of Industrial 3D Printing, funded by the European Commission and led by Professor Dinusha Mendis (FMC, Law and Co-Director CIPPM) has been published.
The report can be accessed here: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/e193a586-7f8c-11ea-aea8-01aa75ed71a1/language-en/format-PDF/source-124493516
The project was awarded to Professor Mendis in 2018 and together with academic and industry partners from UK (Dr. Julie Robson, Bournemouth University; Prof. Phill Dickens, Added Scientific Ltd), Germany (Prof. Dr. Jan Nordemann, Nordemann LLP; Hans Brorsen) Austria (Dr. Maria del Carmen Calatrava Moreno, Technopolis Group) and Finland (Dr. Rosa Ballardini, University of Lapland) the project was completed in February 2020, with the report being published in April 2020.
Ahead of the completion of the project and publication of the report, a final workshop was hosted in Brussels on 14 October 2019. The presentations from the workshop as well as the panel discussion, can be accessed here.
The project provides an overview of the past and current industrial applications of Additive Manufacturing (AM) and 3D printing in seven selected sectors (health, aerospace, automotive, consumer, energy, construction and tooling) whilst identifying potential challenges and opportunities in need of clarification. With the aim of enhancing the competitiveness of the AM sector in Europe, the Study makes policy recommendations in the field of intellectual property for businesses engaged in the AM and 3D printing field, and in the present context, is highly relevant for businesses and consumers working with 3D printers, in the fight against Covid-19.


 International Education as part of the Graduate Student Research in Progress Supplement. Contributions were made by graduate students who are currently studying in a MA, Ed.D. or Ph.D. programme from across the globe. I was very proud to have represented Bournemouth University and the UK alongside Oxford University, the other highlighted British institution. It was wonderful showcasing the impact of peer to peer employability coaching and mentoring on student confidence and awareness. With such a positive result shown by my pilot project and fieldwork where FMC students were participants, I can not wait to investigate future implementation.
International Education as part of the Graduate Student Research in Progress Supplement. Contributions were made by graduate students who are currently studying in a MA, Ed.D. or Ph.D. programme from across the globe. I was very proud to have represented Bournemouth University and the UK alongside Oxford University, the other highlighted British institution. It was wonderful showcasing the impact of peer to peer employability coaching and mentoring on student confidence and awareness. With such a positive result shown by my pilot project and fieldwork where FMC students were participants, I can not wait to investigate future implementation.





















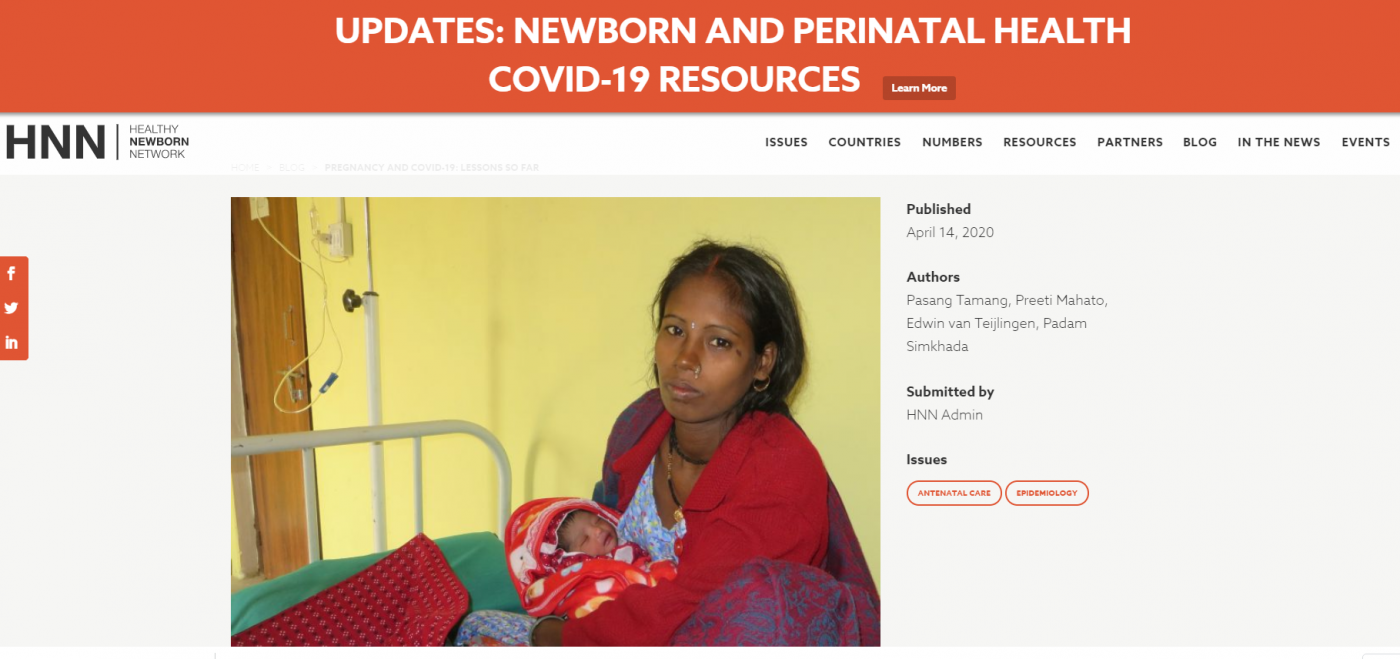
 BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease