Professors Vanora Hundley and Edwin van Teijlingen just completed their ERASMUS Plus exchange with Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (MMIHS) in Nepal. This was a very successful collaboration with colleagues in Nepal, despite the various turns of fate that were sent to challenge us. Indeed, the Profs toiled with the idea of giving this BU Research Blog the heading ‘The show must go on’ or ‘One man down….’ or even the far less punchy ‘The irony of doing a workshop by ZOOM in Nepal from a hotel 200 meters across the road’! In the end we decided that excellent collaboration requires resilience and a wee bit of ingenuity.
The trip to Nepal was marred by many little hiccups. It started at Heathrow where the airline insisted that they complete a now obsolete form about COVID-19 for the Government of Nepal, otherwise they would not let us on the flight. Arguing that Edwin had been to Nepal in April, and that no one then had asked for that particular piece of paper was fruitless. A quick online completion solved that first hurdle. The next hurdle was the flight leaving Heathrow over two hours late, which in turn meant missing the connection in Doha. Fortunately, the airline booked our academics on a replacement flight which left only hours after the original onwards flight had been scheduled to leave for Kathmandu. ingenuity. The trip to Nepal was marred by many little hiccups. It started at Heathrow where the airline insisted that they complete a now obsolete form about COVID-19 for the Government of Nepal, otherwise they would not let us on the flight. Arguing that Edwin had been to Nepal in April, and that no one then had asked for that particular piece of paper was fruitless. A quick online completion solved that first hurdle. The next hurdle was the flight leaving Heathrow over two hours late, which in turn meant missing the connection in Doha. Fortunately, the airline booked our academics on a replacement flight which left only hours after the original onwards flight had been scheduled to leave for Kathmandu.
The first five days in Kathmandu went well, apart from the to be expected tummy problems that go with monsoon in all low-income countries in South Asia. The teaching at MMIHS mainly focused on methodological issues. Our scheduled teaching sessions focused on the first-year MSc Nursing students (Vanora) and the first-year MSc Public Health students at MMIHS (Edwin).
 A more informal one-hour tutorial session was organised for the second-year MSc Public Health students who had applied to come to the UK as part of ERASMUS Plus. This question-and-answer-type session was run by both Vanora and Edwin as well as BU PhD student Sulochana Dhakal-Rai. Overall, the teaching was all organised at very short notice, but BU’s professors are flexible and had a broad range of expertise to share.
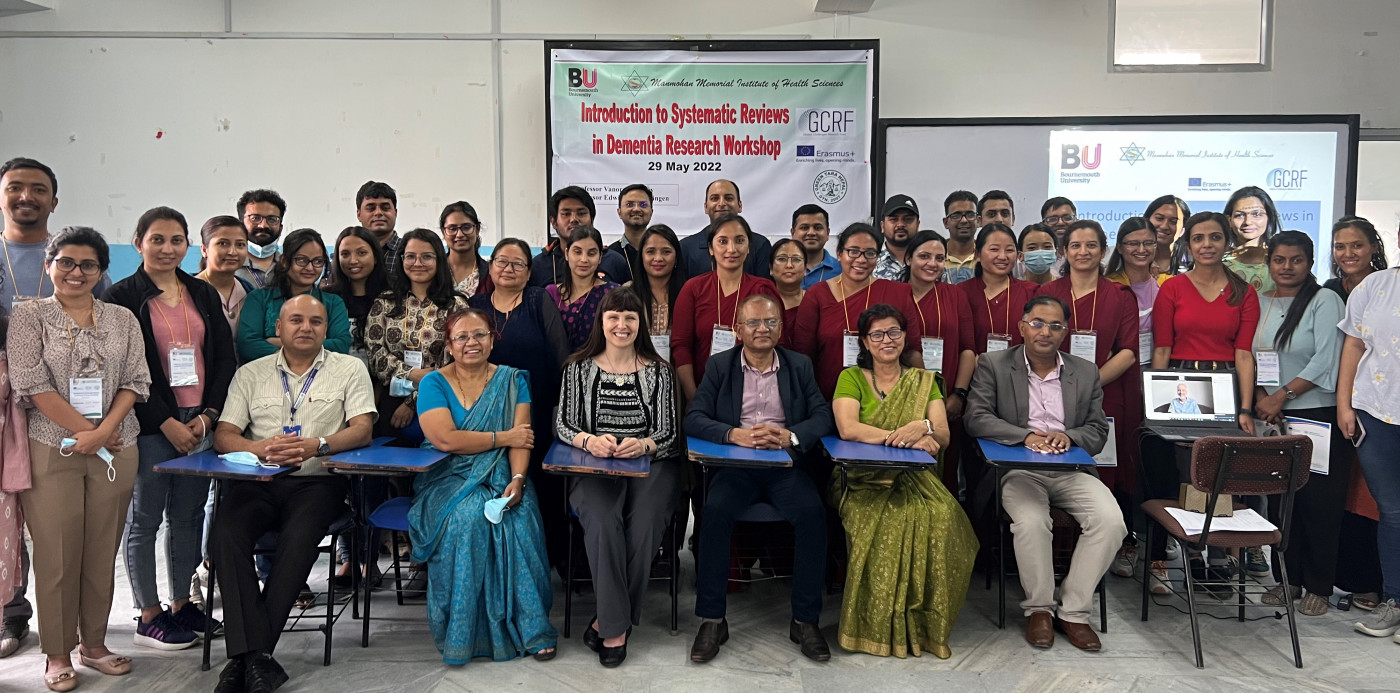
A more informal one-hour tutorial session was organised for the second-year MSc Public Health students who had applied to come to the UK as part of ERASMUS Plus. This question-and-answer-type session was run by both Vanora and Edwin as well as BU PhD student Sulochana Dhakal-Rai. Overall, the teaching was all organised at very short notice, but BU’s professors are flexible and had a broad range of expertise to share.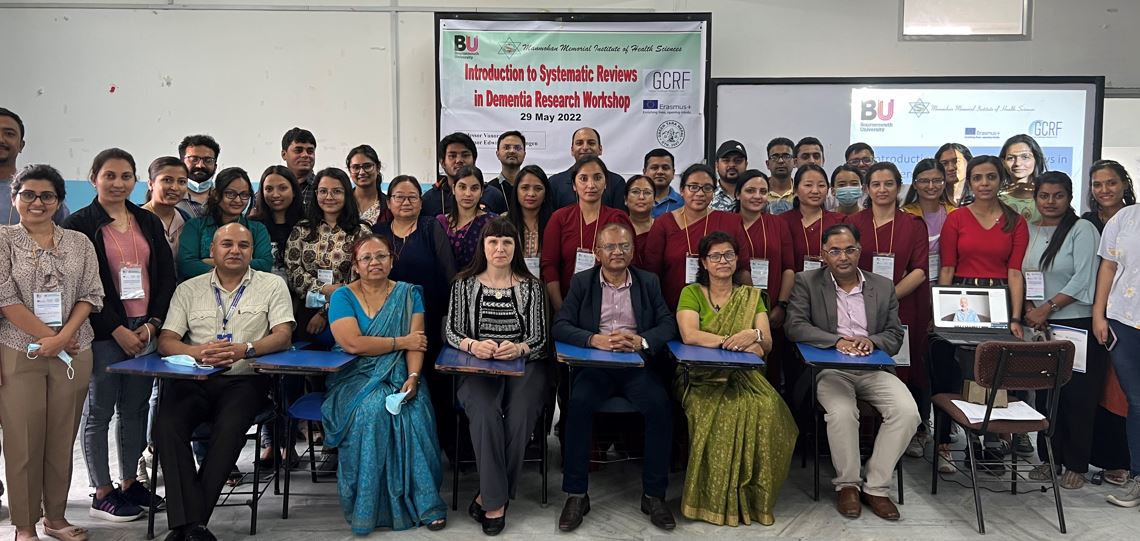
In addition, with extra funding from GCRF (Global Challenges Research Fund), Bournemouth University and MMIHS supported by the local charity Green Tara Nepal planned ran a one-day research workshop in Kathmandu. This GCRF- funded ‘Systematic Review on Dementia Research Workshop’ was very well attended. Although the workshop budgeted for 30 people the attendance register shows that nearly double (n=59) the number of people attended at least part of the workshop. However, running the workshop was not without is problems. Two-days before the workshop Prof. van Teijlingen first had a positive COVID-19 lateral flow test followed by a positive PCR test. This put the burden of running the show very much on Prof. Vanora Hundley with Edwin being called in through Zoom. This is where the potential ‘irony’ title comes in. The irony of doing a workshop by ZOOM in Nepal ….. not from halfway across the globe but from a local hotel 200 meters across the road from MMIHS! The hotel’s internet connection was not as good as most of us have grown used to in Dorset, which added to the difficulty of running the workshop smoothly.
Despite all these challenges, the result was a very successful workshop that will continue to build our collaboration with colleagues in MMIHS and more widely across Nepal.
Finally, to end the story of hiccups, MMIHS forgot to inform the hotel that Edwin would be staying four extra nights. On the day he was originally scheduled to leave Nepal he received a phone call from reception asking what time he was checking out. When he said he thought extra nights had been booked for him, there was no reply. A little later he was told he could get another night, but he would have to move to another floor, and it would be for one night only, since all 91 room of the hotel were booked for the weekend for a big Asian wedding party. Luckily MMIHS found him another hotel a bit more outside the city centre for the remaining three nights.
 We are incredibly grateful for the support of colleagues and friends in Nepal and at home in the UK, which helped smooth out some of the more interesting challenges.
We are incredibly grateful for the support of colleagues and friends in Nepal and at home in the UK, which helped smooth out some of the more interesting challenges.
Lessons learnt:
· Be ready to change and adapt to the needs of the situation.
· Strong relationships will help you deal with the unexpected.
· Keep positive when things get tough.
In the words of Steve Maraboli “Life doesn’t get easier or more forgiving, we get stronger and more resilient.”
 Some people are unsure (or unaware) of the contribution of Bournemouth University’s Visiting Faculty. At many UK universities eminent scholars (researchers, teachers and/or professionals) are offered honorary unpaid appointments to enhance the skills and knowledge of that institution’s academic staff and/or students. Unusually, these Visiting Faculty members are hosted when there already exists a well-developed professional relationship between the Visiting Faculty and the university’s staff. The Faculty of Health & Social Sciences (FHSS) has a number of Visiting Faculty members, including some local, national and international collaborators.
Some people are unsure (or unaware) of the contribution of Bournemouth University’s Visiting Faculty. At many UK universities eminent scholars (researchers, teachers and/or professionals) are offered honorary unpaid appointments to enhance the skills and knowledge of that institution’s academic staff and/or students. Unusually, these Visiting Faculty members are hosted when there already exists a well-developed professional relationship between the Visiting Faculty and the university’s staff. The Faculty of Health & Social Sciences (FHSS) has a number of Visiting Faculty members, including some local, national and international collaborators.
 Whilst last week’s publication ‘COVID-19 restrictions and psychological well-being of fathers with infants admitted to NICU (neonatal intensive care units)—an exploratory cross-sectional study‘ in the journal Acta Paediatrica [2] was co-authored by two Visiting Faculty members from University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust.
Whilst last week’s publication ‘COVID-19 restrictions and psychological well-being of fathers with infants admitted to NICU (neonatal intensive care units)—an exploratory cross-sectional study‘ in the journal Acta Paediatrica [2] was co-authored by two Visiting Faculty members from University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust.  The two clinicians, who co-authored this international paper, are both based at Poole Maternity Hospital: Prof. Minesh Khashu (Lead Consultant Neonatologist) and Ms. Jillian Ireland (Professional Midwifery Advocate).
The two clinicians, who co-authored this international paper, are both based at Poole Maternity Hospital: Prof. Minesh Khashu (Lead Consultant Neonatologist) and Ms. Jillian Ireland (Professional Midwifery Advocate).

















































 Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop
Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives
SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives BRIAN upgrade and new look
BRIAN upgrade and new look Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh
Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease