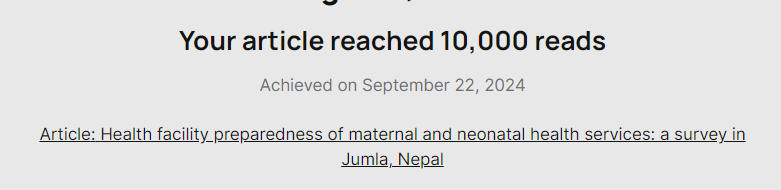
Last Sunday ResearchGate informed us that the paper ‘Health facility preparedness of maternal and neonatal health services: a survey in Jumla, Nepal‘ [1] published in the international journal BMC Health Services Research had been read 10,000 times. In this paper, which is in an Open Access journal, Pasang reports on a cross-sectional study conducted in 2019 covering all 31 state health facilities in a district of Nepal to assess the availability of maternal and neonatal health services including appropriate workforce and access to essential medicines.  Tests of association between demographic factors and the probability of a facility experiencing a shortage of essential medicine within the last 3 months were also conducted as exploratory procedures. Overall health facilities reported better availability of staff than of drugs. The authors concluded that health facilities in Nepals should be supported to meet required minimal standards such as availability of essential medicines and the provision of emergency ambulance transport for women and newborns. This paper was part of Dr. Pasang Tamang’s Ph.D. project at the University of Huddersfield, which resulted in four other related publications [2-5]. Pasang is currently working as a Lecturer in Public Health in the School of Human Sciences at the University of Greenwich.
Tests of association between demographic factors and the probability of a facility experiencing a shortage of essential medicine within the last 3 months were also conducted as exploratory procedures. Overall health facilities reported better availability of staff than of drugs. The authors concluded that health facilities in Nepals should be supported to meet required minimal standards such as availability of essential medicines and the provision of emergency ambulance transport for women and newborns. This paper was part of Dr. Pasang Tamang’s Ph.D. project at the University of Huddersfield, which resulted in four other related publications [2-5]. Pasang is currently working as a Lecturer in Public Health in the School of Human Sciences at the University of Greenwich.
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen

References:
- Tamang, P., Simkhada, P., Bissell, P., van Teijlingen, E., Khatri, R., Stephenson, J. (2021) Health facility preparedness of maternal and neonatal health services: A survey in Jumla, Nepal, BMC Health Service Research, 21:1023. https://rdcu.be/cyD01
- Tamang, P., Mahato, P., Simkhada P., Bissell, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2021) Pregnancy, Childbirth, Breastfeeding and Coronavirus Disease: What is known so far? Journal of Midwifery Association of Nepal (JMAN) 2(1): 96-101.
- Tamang, P., Simkhada, B, Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2023) Quality of care in maternal and neonatal health in Jumla, rural Nepal: Women’s perspective. Fields: Journal of Huddersfield student research, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.5920/fields.1271
- Mahato, P., Tamang, P., Simkhada, B., Wasti, S. P., Devkota, B., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E.R. (2022) Reflections on health promotion fieldwork in Nepal: Trials and tribulations. Journal of Health Promotion 10(1): 5–12. https://doi.org/10.3126/jhp.v10i1.50978
- Tamang, P., Mahato, P., Shahi, P., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E., Amgain, K. (2020) COVID-19 Quarantine: A Key Part of Prevention in Nepal. Journal of Karnali Academy of Health Sciences 3(1):1-14.


















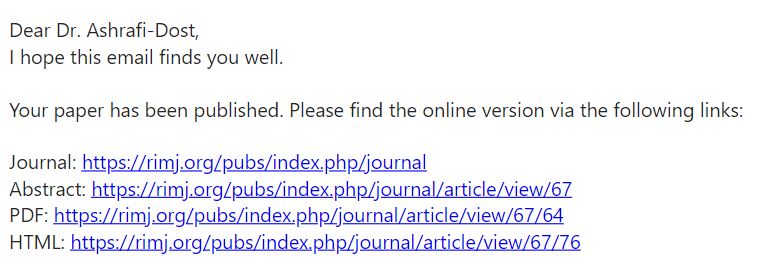




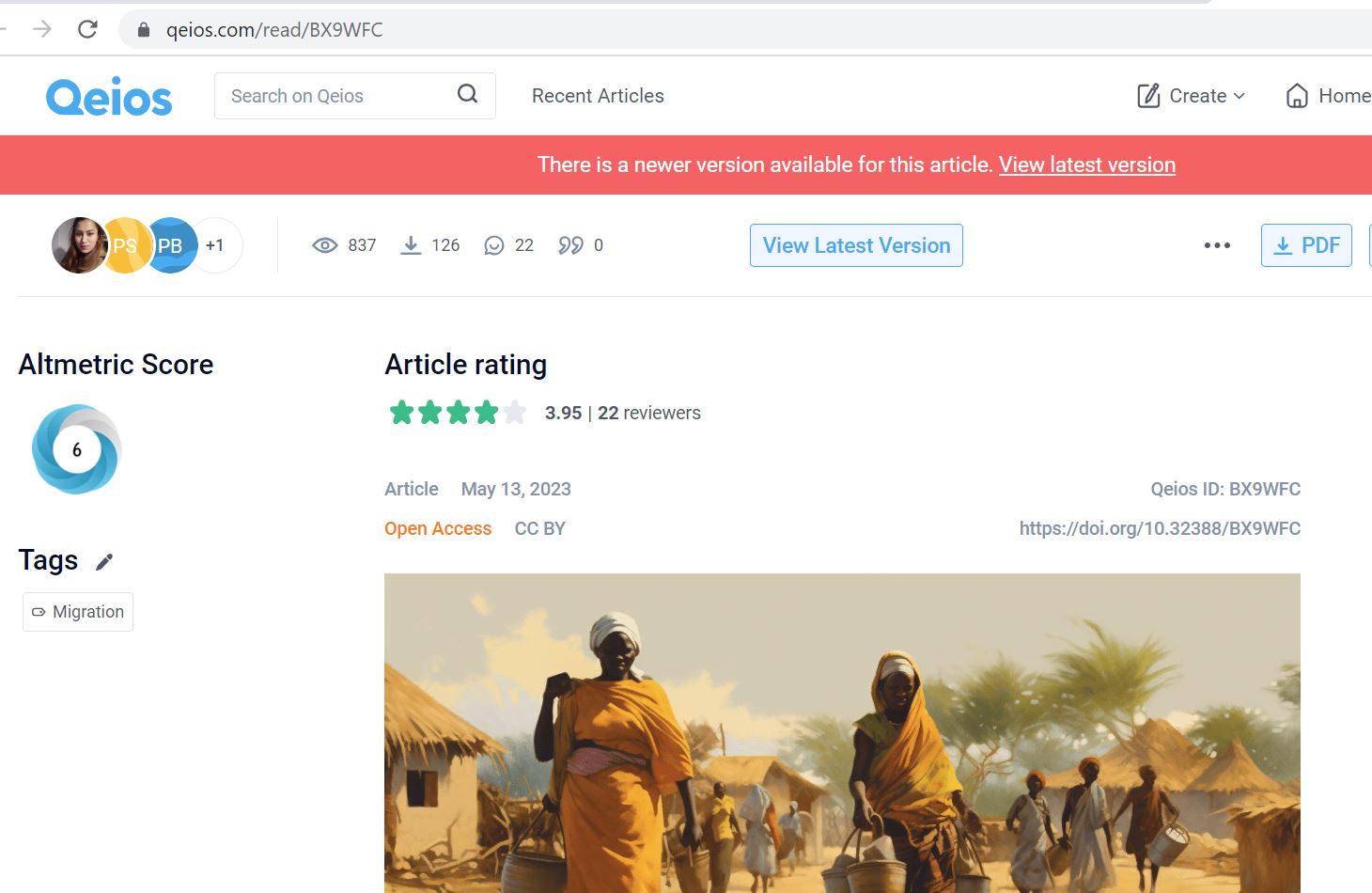

 Last we took a new step into the academic publishing by submitting a paper to Qeios. This Open Access journal publishes papers for free, more or less immediately and after the paper has appeared online peer-reviewers are being invited. The paper ‘
Last we took a new step into the academic publishing by submitting a paper to Qeios. This Open Access journal publishes papers for free, more or less immediately and after the paper has appeared online peer-reviewers are being invited. The paper ‘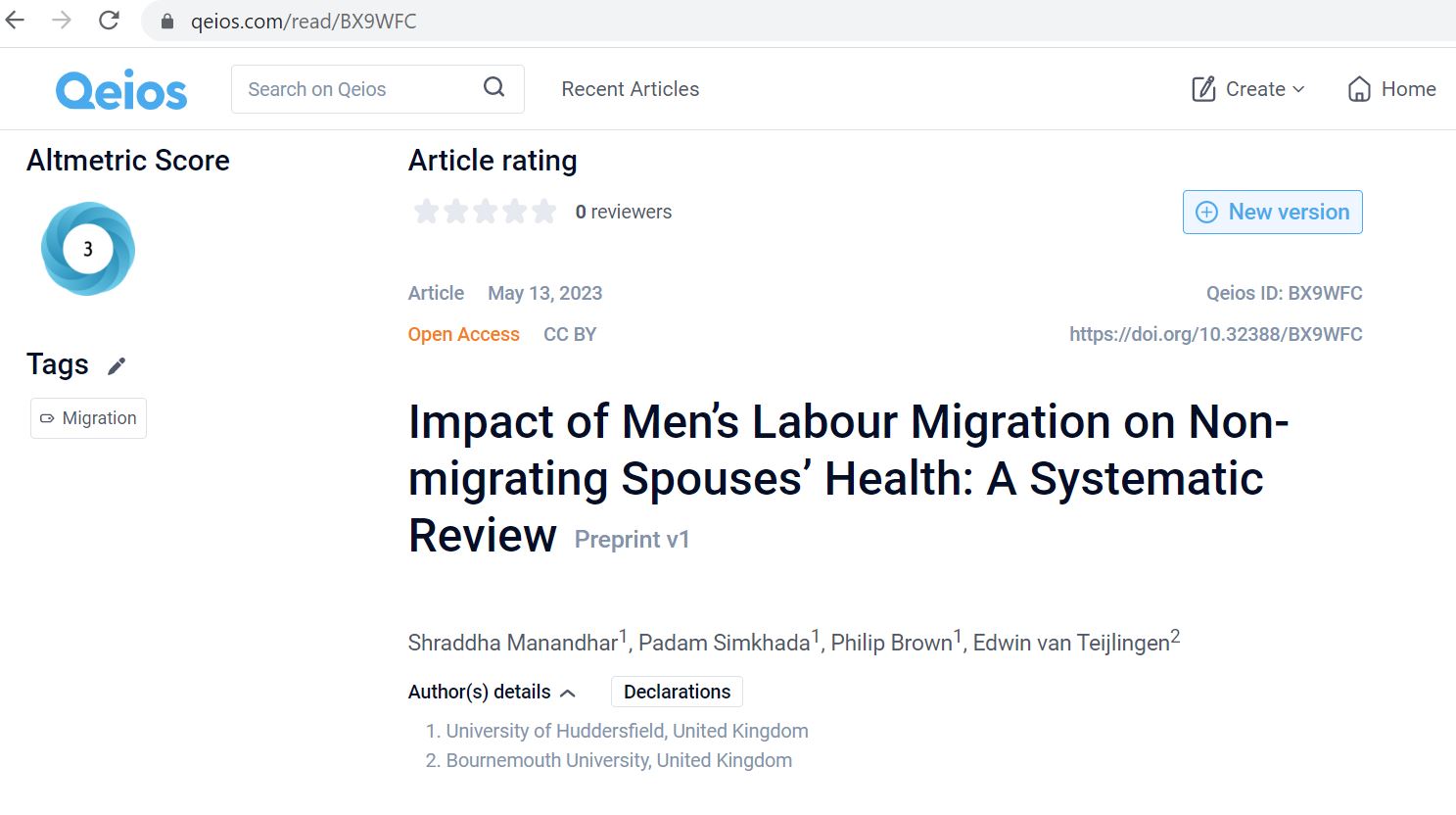













 Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU
Visiting Prof. Sujan Marahatta presenting at BU 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease