 On the day that The Sun took down an column in which Jeremy Clarkson spat vitriol at Meghan Markle, it seems odd to question what the role is of an editor in preventing material from being published. Especially since Ipso (the independent press standards organisation) received more complaints (17,500+) about the column published on Friday 16th December than the total it received in the whole of 2021.
On the day that The Sun took down an column in which Jeremy Clarkson spat vitriol at Meghan Markle, it seems odd to question what the role is of an editor in preventing material from being published. Especially since Ipso (the independent press standards organisation) received more complaints (17,500+) about the column published on Friday 16th December than the total it received in the whole of 2021.  Not publishing an article is of course censorship. Many will be calling for the column to be withdrawn and questioning why the editor accepted it in the first place. Censorship is the suppression or prohibition of any parts of a book, article, film, blog, news, etc. that are considered obscene, politically unacceptable, or a threat to security.
Not publishing an article is of course censorship. Many will be calling for the column to be withdrawn and questioning why the editor accepted it in the first place. Censorship is the suppression or prohibition of any parts of a book, article, film, blog, news, etc. that are considered obscene, politically unacceptable, or a threat to security.
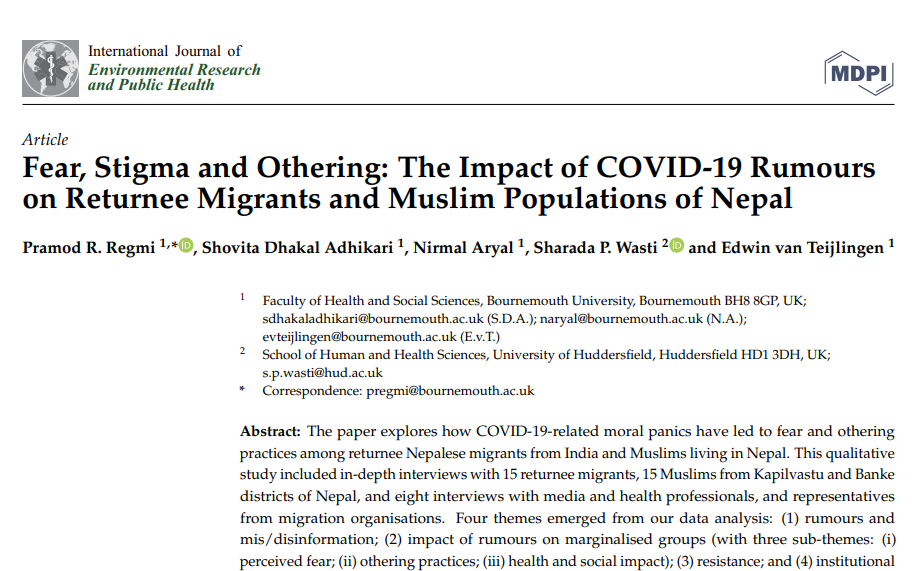
But what if you are not a Mr. Clarkson, but you are a conscientious academic, doing proper research and drafting an evidence-based paper and the editor of an academic journal refuses to publish your article, not because of academic quality, but because the “…manuscript is likely to create disharmony in society”. With the additional detail, that according to the “National Ethical Guidelines for Health Research in Nepal, 2022, section 3, article 2.2 and section 3, article 3.1, this manuscript can’t be accepted for publication.” We (Nirmal Aryal, Pramod Regmi, Shovita Dhakal Adhikari, Shreeman Sharma & Edwin van Teijlingen) had submitted a paper with the title ‘Moral panic, fear, stigma, and discrimination against returnee migrants and Muslim populations in Nepal: analyses of COVID-19 media content’ to a health journal. We don’t think the title of the journal is relevant at this stage.
In the first round of reviewing one of the reviewers questioned our focus on the Muslim population. In our resubmission we stressed that we focused on two separate population groups because the media in Nepal did. In other words, we had noticed discriminatory media coverage towards returnee migrants (particularly those from India) and Muslim populations living in Nepal. These are key populations which experienced stigmatising and ostracising behaviour and media coverage further instigated moral panic and fear. We also conducted interviews with returnee migrants, Muslims in Nepal and key stakeholders, including agencies working with these sub-populations, and these findings have already been published. [1] Image how we felt being censored or in other words ‘cancelled’.
Our paper addressed issues, explanations and allegations related to COVID-19 as portrayed in the media in Nepal, indeed some discriminatory and many very unfair. However, as researchers we were merely the ‘messenger of bad news’. If Mr. Clarkson had not been headline news we would probably have called this blog ‘Don’t shoot the messenger!”.
References:
- Regmi, P.R., Dhakal Adhikari, S., Aryal, N., Wasti, S.P. and van Teijlingen, E., 2022. Fear, Stigma and Othering: The Impact of COVID-19 Rumours on Returnee Migrants and Muslim Populations of Nepal. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19 (15). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9331294/










































 REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease