Today, Discover Public Health, published our latest academic paper on maternity and neonatal care in Nepal [1]. Our latest paper ‘A scoping review of interventions to improve maternal and neonatal care in Nepal‘ is lead by Dr. Sharada Prasad Wasti at the University of Greenwich and co-authored by Bournemouth University’s Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen. 
For this scoping review we found 418 studies, and twenty were included, which used various interventions that aimed to improve maternal and neonatal health. Five overarching interventions were identified: (1) community-based maternal health literacy; (2) health facility strengthening, including health staff training, (3) mobilisation of female community health volunteers (FCHV) for birth preparedness and identifying danger signs; (4) mobile health messaging, and (5) involving husbands in improving the uptake of maternal and neonatal care. Most interventions were a mixture of activities with a combination of interventions rather than a single intervention.
The authors note that no single intervention is sufficient on its own; indeed, a combination of approaches is needed to improve the uptake of maternal and neonatal care services.
This scientific paper in Discover Public Health is open access and, therefore, freely available worldwide to anybody with internet access. Interestingly, the journal has added an AI generated summary, despite the fact that we as authors had provided a perfectly useful abstract.

Reference:
- Wasti, S.P., van Teijlingen, E., Adhikari, N. Morgan, J. (2025) A scoping review of interventions to improve maternal and neonatal care in Nepal. Discover Public Health 22, 855 . https://doi.org/10.1186/s12982-025-01241-x






















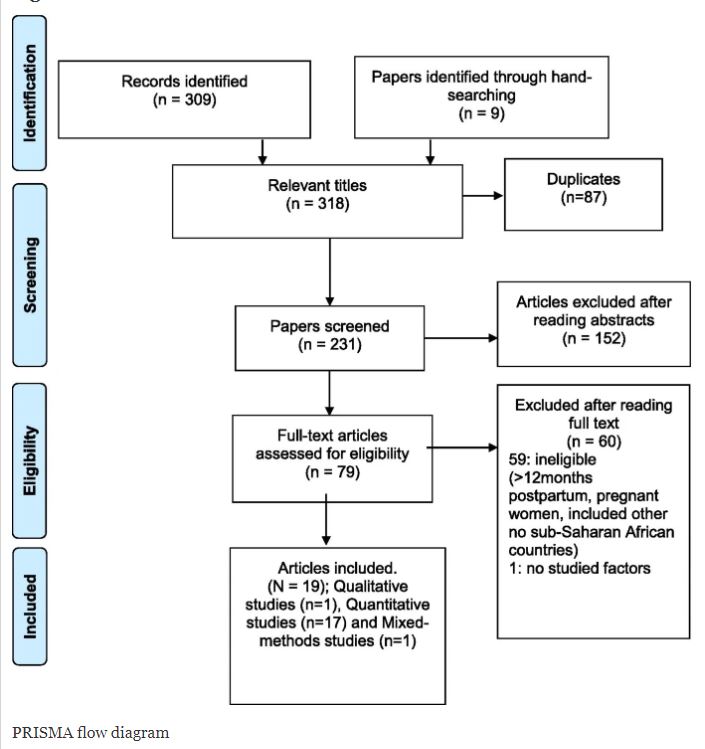







 This review covered the published literature on the epidemiology, clinical management and public health prevention aspects of pregnancy and childbirth and coronavirus (COVID-19) up until December 2020. We worked hard and fast to submit the paper as soon as possible after the end of 2020 to be able to publish up-to-date findings. We managed this and submitted the paper on March 5th, the peer-review took some months and so did the making of the revisions. As a result we resubmitted the manuscript of 29 September and we got the acceptance email within a week. We made it into the next issue of the Nepal Journal of Epidemiology which published exactly one year after the data collection period had ended for our systematic review.
This review covered the published literature on the epidemiology, clinical management and public health prevention aspects of pregnancy and childbirth and coronavirus (COVID-19) up until December 2020. We worked hard and fast to submit the paper as soon as possible after the end of 2020 to be able to publish up-to-date findings. We managed this and submitted the paper on March 5th, the peer-review took some months and so did the making of the revisions. As a result we resubmitted the manuscript of 29 September and we got the acceptance email within a week. We made it into the next issue of the Nepal Journal of Epidemiology which published exactly one year after the data collection period had ended for our systematic review.











 BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease