 On Monday 9th March Prof. Sujan Marahatta visited Bournmouth University (BU) to speak about ‘Strengthening BU-Nepal collaboration AND Nepal’s experience of competency-based health professional education’. Prof. Marahatta is the Director of the Medical Education Commission in Nepal overseeing the education of health professionals in 15 areas including Medicine, Physiotherapy, Nursing and Midwifery.
On Monday 9th March Prof. Sujan Marahatta visited Bournmouth University (BU) to speak about ‘Strengthening BU-Nepal collaboration AND Nepal’s experience of competency-based health professional education’. Prof. Marahatta is the Director of the Medical Education Commission in Nepal overseeing the education of health professionals in 15 areas including Medicine, Physiotherapy, Nursing and Midwifery.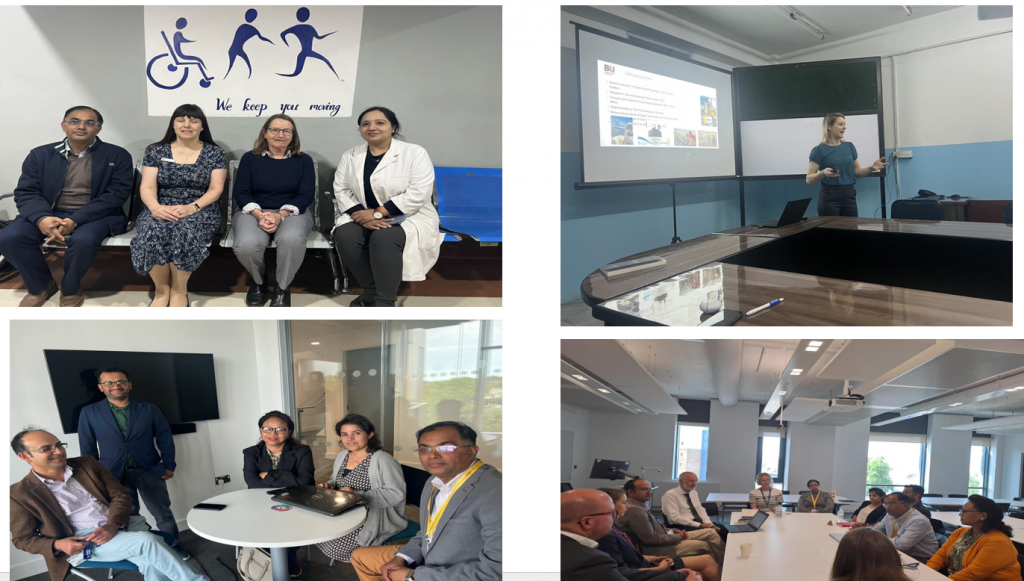  He spoke about long partnership between Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (MMIHS) and BU. This partnership is formalised in a Memoradum of Agreement (MoA) and over the years it has included joint research projects, staff-student exchanges (funded by ERASMUS+ and Turing scheme) and offering guest lectures at each others institutions.
He spoke about long partnership between Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (MMIHS) and BU. This partnership is formalised in a Memoradum of Agreement (MoA) and over the years it has included joint research projects, staff-student exchanges (funded by ERASMUS+ and Turing scheme) and offering guest lectures at each others institutions.
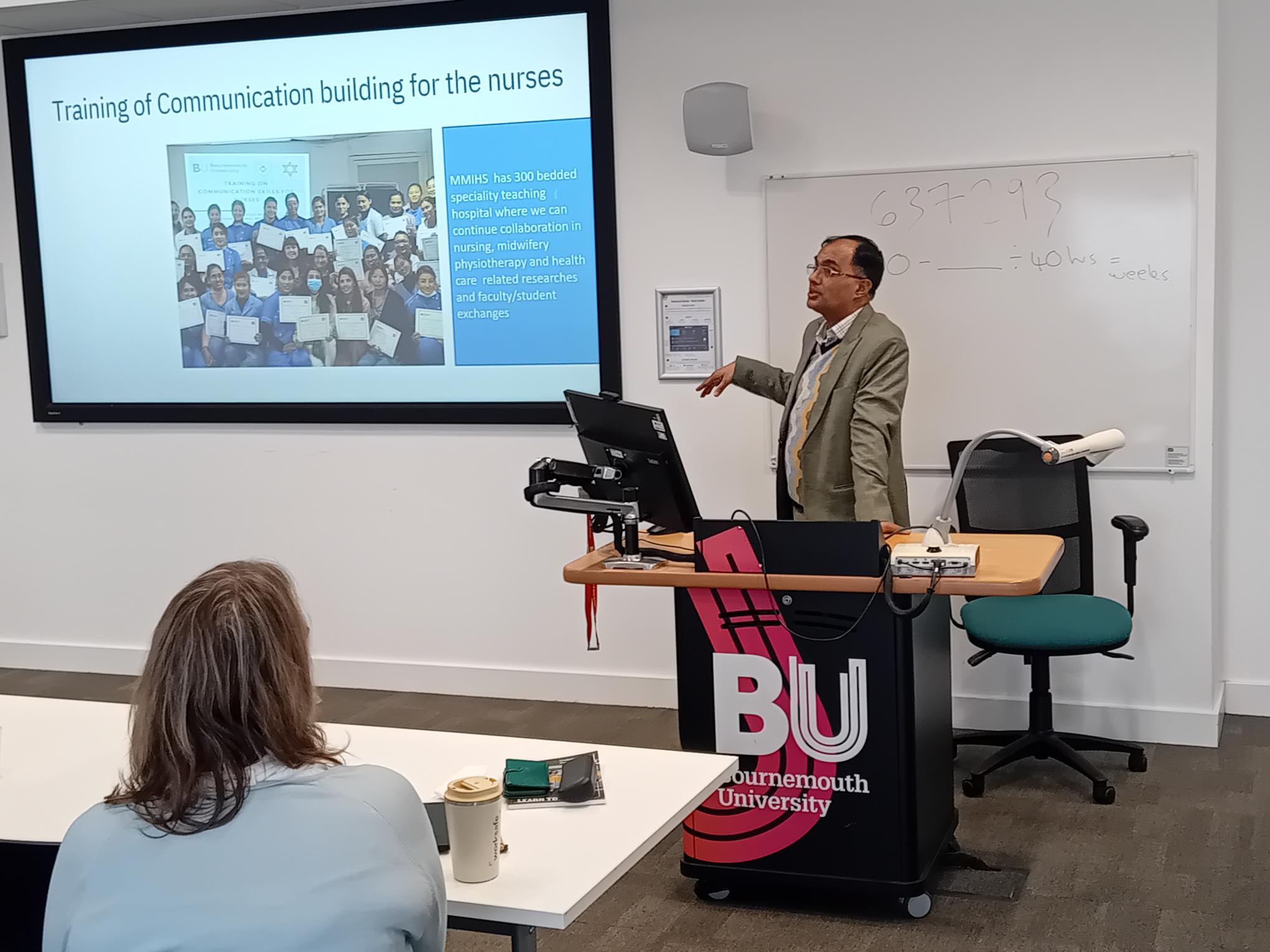
One of the jointly conducted studies which Prof. Marahatta highlighted was the work on CPD (Continuous Professional Development) in nursing and midwifery in Nepal. Research on CPD started a decade ago and culminated in several papers [1-4]. The research was combined with sustained advocacy and stakeholder engagement, and resulted in the Nepal Nursing Council (NNC) formally introduced mandatory CPD as a requirement for nursing and midwifery re-registration earlier this year (15 January 2026). The National Guideline on Continuing Nursing and Midwifery Education (CNME) CPD for Nurses and Midwives refer to our work conducted by academics based at Bournemouth University. This is the foundation for one of BU’s REF Impact Case Studies for 2029.
Amongst other studies, Prof. Marahatta also highlighted a recent publication which was jointly authored between BU’s professors Clark and Hundley and himself on pain catastrophising in nulliparous women in Nepal, the importance for childbirth [5]. Prof. Marahatta’s visit was held in the Faculty of Health, Environment & Medical Sciences (HEMS) in the Bournemouth Gateway Building.

References:
- Simkhada B, Mackay S, Khatri R, Sharma CK., Pokhrel T, Marahatta SB., Angell C, van Teijlingen E, Simkhada P. (2016) Continual Professional Development (CPD): Improving Health Prospect15 (3):1-3.
- Khatri, RJ, van Teijlingen, E, Marahatta, SB, Simkhada, P, Mackay, S and Simkhada, B. Exploring the Challenges and Opportunities for Continuing Professional Development for Nurses: A Qualitative Study with Senior Nurse Leaders in Nepal. Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences. 2021 7(1):15-29.
- Simkhada B, van Teijlingen E, Pandey A, Sharma CK, Simkhada P, Singh DR (2023) Stakeholders’ Perceptions of Continuing Professional Development among Nepalese Nurses: A Focus Group Study Nursing Open.10(5).
- Simkhada B, van Teijlingen E, Sharma C, Pandey A, Simkhada P. (2023) Nepal needs Continuing Professional Development for Re-registration in Nursing and Midwifery Journal of Nepal Health Research Council, 21(60):541-42.
- Clark CJ, Marahatta SB, Hundley VA. (2024) The prevalence of pain catastrophising in nulliparous women in Nepal; the importance for childbirth. PLoS ONE 19(8): e0308129. https://doi. org/10.1371/journal.pone.0308129.



















































 Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration
Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration 3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease