We are delighted to announce that
Bournemouth University (BU) and University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust (UHD) Clinical Match-Funded PhD researcher,
Leila Kattach, has published her first academic paper. This milestone marks an important step in Leila’s research journey and highlights the impactful work being carried out within our clinical research community.

The paper, titled
“Nurse-Led Models of Service Delivery for Skin Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review“, was published in the
Journal of Advanced Nursing yesterday (April 1, 2025)
[1]. This research consolidates evidence on nurse-led models for skin cancer detection, comparing their effectiveness to physician-led care and highlighting their potential benefits in terms of accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and patient satisfaction.

The systematic review, co-authored with
Heidi Singleton, Steven Ersser, Debbie Holley, Ian Pearson, and Abdulrahman Shadeed, rigorously analyzed studies from 1992 to 2024, assessing the role of nurses in
diagnosing, treating, and supporting skin cancer patients. The findings demonstrate that
nurse-led models can complement or even substitute traditional physician-led care, offering high
diagnostic accuracy, improved access to care, and enhanced patient education.
Key highlights from the study include:
Comparable diagnostic accuracy between nurses and ophthalmologists in skin cancer detection.
Increased accessibility and reduced waiting times for patients through community-based, nurse-led services.
Significant cost savings associated with nurse-led care delivery.
Patient preference for nurse-led models, citing convenience and enhanced education on self-examination.

The study also emphasizes the need for further research and
standardized national guidelines to scale and integrate nurse-led models effectively into healthcare systems.
Leila’s research has strong implications for policy and clinical practice, advocating for:
✅ Enhanced dermatology nursing training to equip nurses with advanced skills in assessment, diagnosis, and treatment.
✅ Development of Dermatology Nurse Consultant Training Programmes to support professional development and independent practice.
✅ Support for community-based care to enhance accessibility, particularly in underserved regions.
✅ Standardization of nurse-led models to ensure consistency and high standards across healthcare settings.
Leila Kattach’s research has a PhD studentship jointly funded by BU and UHD NHS Foundation Trust. The study was conducted in collaboration with academic dermatology experts, specialist clinicians, and a patient representative with lived experience of melanoma, ensuring a patient-centered approach. Leila’s work paves the way for further exploration into nurse-led service delivery models and their long-term impact on skin cancer care, cost-effectiveness, and healthcare workforce sustainability. We look forward to seeing how her research evolves and contributes to improving patient care in dermatology.
👏 Congratulations to Leila Kattach and the research team on this outstanding achievement!
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Reference:
- Kattach, L., Singleton, H., Ersser, S., Holley, D., Pearson, I. & Shadeed, A. (2025), Nurse-Led Models of Service Delivery for Skin Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review. Journal of Advanced Nursing.[online first] https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.16854
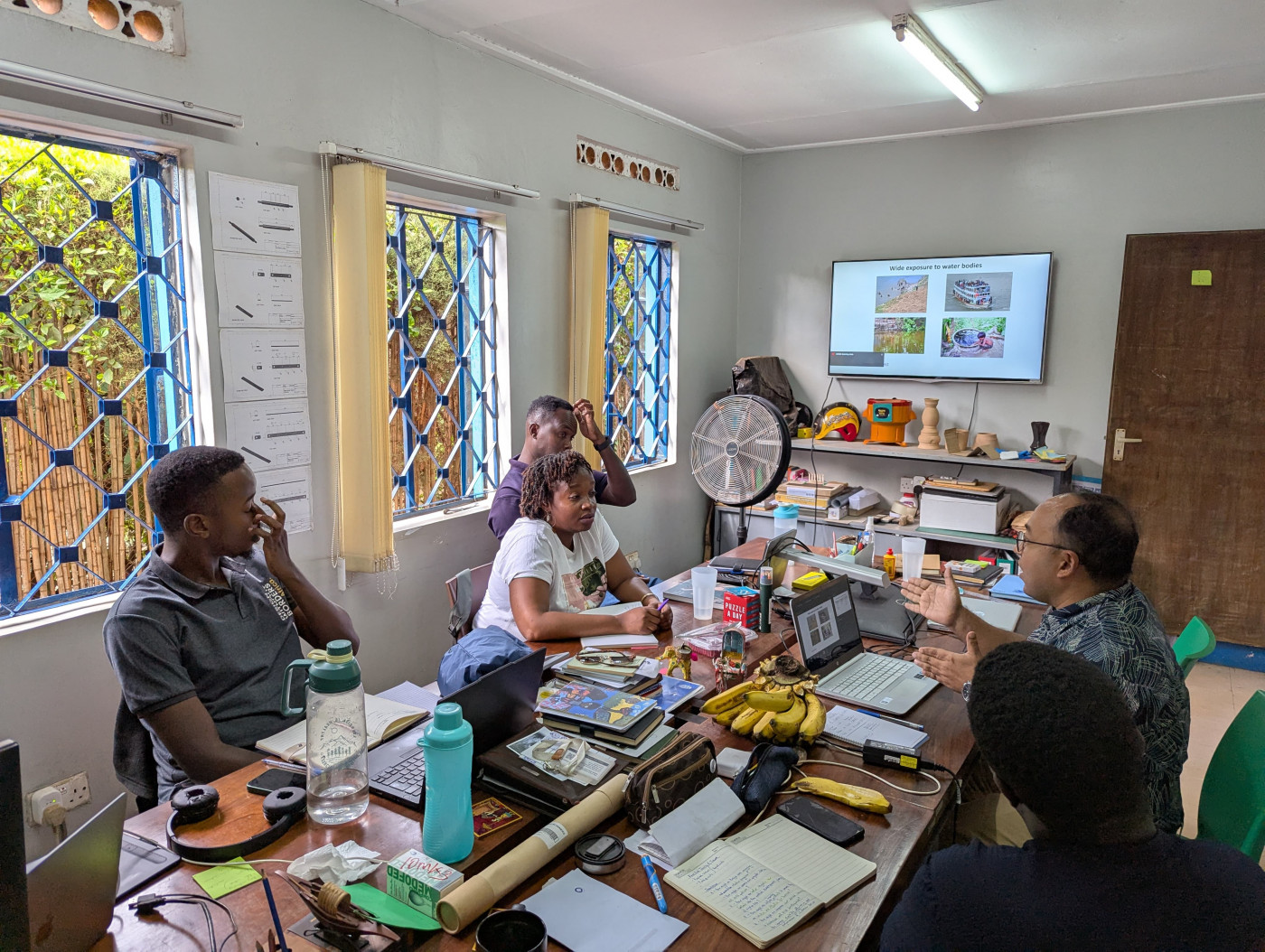
 Prof. Om Kurmi who leads the Nepal Family Cohort Study (NeFCoS) joined the Bournemouth University (BU) team today for a research planning meeting in Bournemouth today. Dr. Om Kurmi, Associate Professor Research in the Centre for Healthcare and Communities at Coventry University. The BU team comprises Dr. Pramod Regmi (Principal Academic-International Health), Prof. Carol Clark (Professor in Physiotherapy), Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen (Professor of Reproductive Health), Dr. Rebecca Neal (Principal Lecturer in Exercise Physiology) and Dr. Vanora Hundley (Professor of Midwifery).
Prof. Om Kurmi who leads the Nepal Family Cohort Study (NeFCoS) joined the Bournemouth University (BU) team today for a research planning meeting in Bournemouth today. Dr. Om Kurmi, Associate Professor Research in the Centre for Healthcare and Communities at Coventry University. The BU team comprises Dr. Pramod Regmi (Principal Academic-International Health), Prof. Carol Clark (Professor in Physiotherapy), Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen (Professor of Reproductive Health), Dr. Rebecca Neal (Principal Lecturer in Exercise Physiology) and Dr. Vanora Hundley (Professor of Midwifery). 
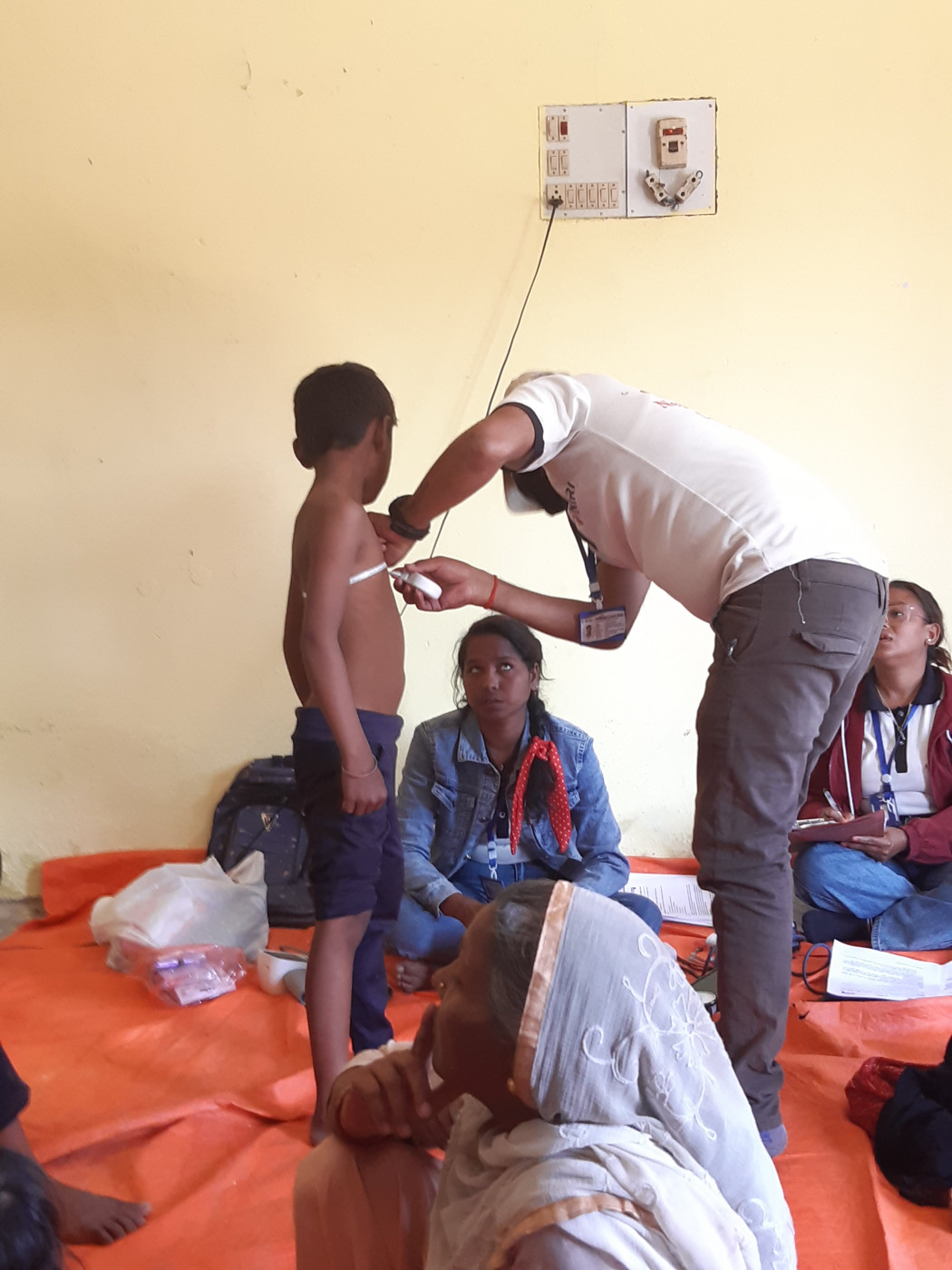 Today’s meeting was organised by Dr. Neal and supported by BU’s QR funds.
Today’s meeting was organised by Dr. Neal and supported by BU’s QR funds.


















































 New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease