Congratulations to Jane Healy and Rosslyn Dray, both in the Department of Social Sciences & Social Work on their publication today in The Journal of Adult Protection. Their paper’ Missing links: Safeguarding and disability hate crime responses’ considers the relationship between disability hate crime and safeguarding adults [1]. It critically considers whether safeguarding responses to disability hate crime have changed following the implementation of the Care Act 2014. Historically, protectionist responses to disabled people may have masked the scale of hate crime and prevented them from seeking legal recourse through the criminal justice system (CJS). This paper investigates whether agencies are working together effectively to tackle hate crime. The authors conclude that raising the profile of disability hate crime within safeguarding teams could lead to achieving more effective outcomes for adults at risk: improving confidence in reporting, identifying perpetrators of hate crimes, enabling the CJS to intervene and reducing the risk of further targeted abuse on the victim or wider community.
Well done!
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMMPH
Reference:
- Healy, J.C.,Dray, R. (2022), Missing links: safeguarding and disability hate crime responses, The Journal of Adult Protection, Online first ahead of print. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAP-09-2021-0030
Category / Sociology & Social Policy
Record 25 publications on migration & health in Nepal
 Our team of health and social science researchers reached a record 25 publications focusing on health and migration in Nepal. The team comprises members from three different departments in FHSS. Dr. Preeti Mahato, Post Doctoral Researcher, and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen are both based in the Department of Midwifery & Health Sciences, Dr. Pramod Regmi, is Senior Lecturer in International Health and Interim Global Engagement Lead in the Department of Nursing Sciences, Dr. Shovita Dhakal Adhikari is Lecturer in Criminology in the Department of Social Sciences & Social Work. Their collaborators include, among others: FHSS Visiting Faculty Prof. Padam Simkhada, Dr. Pratik Adhikary, Dr. Bibha Sinkhada, and Dr. Nirmal Aryal. The team was also instrumental in establishing the ‘‘Health Research Network for Migrant Workers in Asia’. The 25 publications are listed below [1-25].
Our team of health and social science researchers reached a record 25 publications focusing on health and migration in Nepal. The team comprises members from three different departments in FHSS. Dr. Preeti Mahato, Post Doctoral Researcher, and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen are both based in the Department of Midwifery & Health Sciences, Dr. Pramod Regmi, is Senior Lecturer in International Health and Interim Global Engagement Lead in the Department of Nursing Sciences, Dr. Shovita Dhakal Adhikari is Lecturer in Criminology in the Department of Social Sciences & Social Work. Their collaborators include, among others: FHSS Visiting Faculty Prof. Padam Simkhada, Dr. Pratik Adhikary, Dr. Bibha Sinkhada, and Dr. Nirmal Aryal. The team was also instrumental in establishing the ‘‘Health Research Network for Migrant Workers in Asia’. The 25 publications are listed below [1-25].

References:
- Khatri, R., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P. (2022) The health and well-being of female labour migrants from: A qualitative study of stakeholder views, Europasian Journal of Medical Sciences (EJMS) accepted
- Aryal, N., Sedhain, A., Regmi, P.R., KC, R.K.,& van Teijlingen, E. (2021). Risk of kidney health among returnee Nepali migrant workers: A survey of nephrologists. Asian Journal of Medical Sciences, 12(12), 126–132.
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., Sedhain, A., KC, R.K., Martinez Faller, E., Rijal, A., van Teijlingen, E. (2021) Kidney health risk of migrant workers: An issue we can no longer overlook. Health Prospect 20(1):15-7
- Simkhada, B., Vahdaninia, M., van Teijlingen, E., Blunt, H. (2021) Cultural issues on accessing mental health services in Nepali and Iranian migrants communities in the UK, International Journal of Mental Health Nursing 30(6):1610-1619.
- Khanal, S. P., van Teijlingen, E., Sharma, M. K., Acharya, J., & Sharma, S. (2021).Perceived threats towards COVID-19 pandemic among Nepali migrant workers returned from India. Journal of Health Promotion, 9(01), 87–99.
- Adhikary, P., Aryal, N., Dhungana, R.R., KC, R.K., Regmi, P.R., Wickramage, K.P., Duigan, P., Inkochasan, M., Sharma, G.N., Devkota, B., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P. (2020) Accessing health services in India: experiences of seasonal migrants returning to Nepal. BMC Health Services Research 20, 992. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05846-7
- IOM [International Organization for Migration]. (2019) Health vulnerabilities of cross-border migrants from Nepal. Kathmandu: International Organization for Migration.
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Trenoweth, S., Adhikary, P., Simkhada, P. (2020) The Impact of Spousal Migration on the Mental Health of Nepali Women: A Cross-Sectional Study, International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health 17(4), 1292.
- Regmi, P., Aryal, N., van Teijlingen, E., Adhikary, P. (2020) Nepali migrant workers and the need for pre-departure training on mental health: a qualitative study, Journal of Immigrant & Minority Health 22, 973–981.
- Adhikary, P. van Teijlingen, E. (2020) Support networks in the Middle East & Malaysia: A qualitative study of Nepali returnee migrants’ experiences, International Journal of Occupational Safety & Health (IJOSH), 9(2): 31-35.
- Vahdaninia, M., Simkhada, B., van Teijlingen, E., Blunt, H., Mercel-Sanca, A. (2020) Mental health interventions and services for Black, Asian & Minority Ethnics (BAME) in the UK: a scoping review, Mental Health & Social Inclusion 24(2): 81-95.
- Regmi, P., van Teijlingen, E., Mahato, P., Aryal, N., Jadhav, N., Simkhada, P., Syed Zahiruddin, Q., Gaidhane, A., (2019) The health of Nepali migrants in India: A qualitative study of lifestyles and risks, Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health 16(19), 3655; doi:10.3390/ijerph16193655.
- Dhungana, R.R., Aryal, N, Adhikary, P., KC, R., Regmi, P.R., Devkota, B., Sharma, G.N., Wickramage, K., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P. (2019) Psychological morbidity in Nepali cross-border migrants in India: A community-based cross-sectional, BMC Public Health 19:1534 https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-019-7881-z
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P., Mahato, P. (2019) Adolescents left behind by migrant workers: a call for community-based mental health interventions in Nepal. WHO South East Asia Journal of Public Health 8(1): 38-41.
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., Faller, E.M,, van Teijlingen, E., Khoon, C.C., Pereira, A., Simkhada, P. (2019) ‘Sudden cardiac death and kidney health related problems among Nepali migrant workers in Malaysia’ Nepal Journal of Epidemiology 9(3): 755-758. https://www.nepjol.info/index.php/NJE/article/view/25805
- Adhikary P, van Teijlingen E., Keen S. (2019) Workplace accidents among Nepali male workers in the Middle East and Malaysia: A qualitative study, Journal of Immigrant & Minority Health 21(5): 1115–1122. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10903-018-0801-y
- Simkhada, P.P., van Teijlingen, E.R., Gurung, M., Wasti, S. (2018) A survey of health problems of Nepalese female migrants workers in the Middle-East & Malaysia, BMC International Health & Human Rights 18(4): 1-7. http://rdcu.be/E3Ro
- Adhikary P, Sheppard, Z., Keen S., van Teijlingen E. (2018) Health and well-being of Nepalese migrant workers abroad, International Journal of Migration, Health & Social Care 14(1): 96-105. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJMHSC-12-2015-0052
- Adhikary, P, Sheppard, Z., Keen, S., van Teijlingen, E. (2017) Risky work: accidents among Nepalese migrant workers in Malaysia, Qatar & Saudi Arabia, Health Prospect 16(2): 3-10.
- Simkhada, P.P., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Aryal, N. (2017) Identifying the gaps in Nepalese migrant workers’ health and well-being: A review of the literature, Journal of Travel Medicine 24(4): 1-9.
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P., Adhikary, P., Bhatta, Y.K.D., Mann, S. (2016) Injury and Mortality in Young Nepalese Migrant Workers: A Call for Public Health Action. Asian-Pacific Journal of Public Health 28(8): 703-705.
- Sapkota, T., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2014) Nepalese health workers’ migration to United Kingdom: A qualitative study. Health Science Journal 8(1):57-74.
- Adhikary P, Keen S and van Teijlingen E (2011). Health Issues among Nepalese migrant workers in the Middle East. Health Science Journal.5(3):169-i75 DOI: 2-s2.0-79960420128.
- van Teijlingen E, Simkhada, P., Adhikary, P. (2009) Alcohol use among the Nepalese in the UK BMJ Rapid Response: www.bmj.com/cgi/eletters/339/oct20_1/b4028#223451
- Adhikary, P., Simkhada, P.P., van Teijlingen E., Raja, AE. (2008) Health & Lifestyle of Nepalese Migrants in the UK, BMC International Health & Human Rights 8(6). Web address: www.biomedcentral.com/1472-698X/8/6
New BU publication on academic writing
Congratulations to Dr. Orlanda Harvey in the Department of Social Sciences & Social Work, Dr. Pramod Regmi in the Department of Nursing Science and FHSS Visiting Faculty Jillian Ireland, Professional Midwifery Advocate in Poole Maternity Hospital (UHD/University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust) whose paper ‘Co-authors, colleagues, and contributors: Complexities in collaboration and sharing lessons on academic writing‘ was published today.[1] 
The paper argues that academic writing, especially in the health field, is usually an interdisciplinary team effort. It highlights some of the trials, tribulations, and benefits of working with co-authors. This includes collaborations and co-authorship between academics from different disciplines, academics of different level of careers, and authors from countries of varying economies i.e., high-income countries (HICs) and from low-and middle-income countries (LMICs). This paper also provides advice in the form of several useful tips to lead authors and co-authors to support collaborative working. Our other co-authors are: Aney Rijal, postgraduate student and Executive Editor of the journal Health Prospect based in Nepal, and Alexander van Teijlingen postgraduate student in the Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry (University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, Scotland).
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health
Reference:
- Harvey, O., van Teijlingen, A., Regmi, P.R., Ireland, J., Rijal, A., van Teijlingen, E.R. (2022) Co-authors, colleagues, and contributors: Complexities in collaboration and sharing lessons on academic writing Health Prospect 21(1):1-3.
Research papers: A game of Happy Families
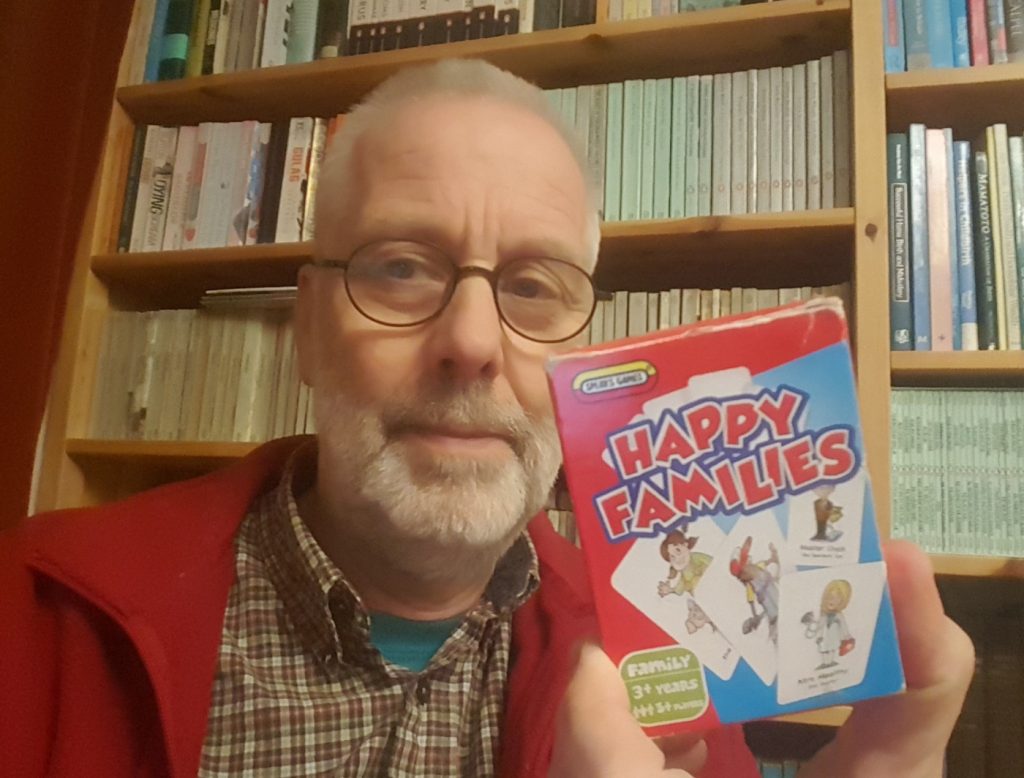 Recently I completed a game of Happy Families, to be more precise I added a paper with my fourth family member to a ‘collection’. I got the idea from Prof. Jonathan Parker and Prof. Sara Ashencaen Crabtree (both based in the Department of Social Sciences & Social Work) who published a paper with their children a few years ago [1]. When Jonathan told me about this achievement I had already published two dozen of scientific and practitioners’ papers with my partner Jilly Ireland, Professional Midwifery Advocate in University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust and FHSS Visiting Faculty (for example 2-5).
Recently I completed a game of Happy Families, to be more precise I added a paper with my fourth family member to a ‘collection’. I got the idea from Prof. Jonathan Parker and Prof. Sara Ashencaen Crabtree (both based in the Department of Social Sciences & Social Work) who published a paper with their children a few years ago [1]. When Jonathan told me about this achievement I had already published two dozen of scientific and practitioners’ papers with my partner Jilly Ireland, Professional Midwifery Advocate in University Hospitals Dorset NHS Foundation Trust and FHSS Visiting Faculty (for example 2-5).
Two years ago, Dr. Preeti Mahato (in the Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health) and I published a paper with my middle son about ‘Vaping and e-cigarettes: A public health warning or a health promotion tool?’ [6]. The following year, Prof. Hamid Bouchachia (Faculty of Science & Technology) and I co-authored a paper with my oldest son on AI and health in Nepal [7], followed by a paper this year on academic publishing with FHSS’s Dr. Shovita Dhakal Adhikari (Department of Social Sciences & Social Work , Dr. Nirmal Aryal (CMMPH) and Dr. Pramod Regmi (Department of Nursing Sciences [8]. And to complete the four family members in the Happy Families set, I published a paper late last month with my daughter under the title ‘ Understanding health education, health promotion and public health’ [9].

References:
- Parker, J., Ashencaen Crabtree, S., Crabtree Parker, M. and Crabtree Parker, I., 2019. ‘Behaving like a Jakun!’ A case study of conflict, ‘othering’ and indigenous knowledge in the Orang Asli of Tasik Chini. Journal of Sociology and Development, 3 (1): 23-45.
- Ireland, J., Bryers, H., van Teijlingen E., Hundley, V., Farmer, J., Harris, F., Tucker, J., Kiger, A., Caldow, J. (2007) Competencies and Skills for Remote & Rural Maternity Care: A Review of the Literature, Journal of Advanced Nursing, 58(2): 105-115.
- van Teijlingen E., Simkhada, P., Ireland, J. (2010) Lessons learnt from undertaking maternity-care research in developing countries. Evidence-based Midwifery 8(1): 12-6.
- Ireland, J., van Teijlingen, E, Kemp J. (2015) Twinning in Nepal: the Royal College of Midwives UK and the Midwifery Society of Nepal working in partnership, Journal of Asian Midwives 2 (1): 26-33. http://ecommons.aku.edu/jam/vol2/iss1/5/
- Ireland, J., Khashu, M., Cescutti-Butler, L., van Teijlingen, E, Hewitt-Taylor, J. (2016) Experiences of fathers with babies admitted to neonatal care units: A review of literature, Journal of Neonatal Nursing 22(4): 171–176.
- van Teijlingen, E., Mahato, P., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, C., Asim, M., & Sathian, B. (2019). Vaping and e-cigarettes: A public health warning or a health promotion tool? Nepal Journal of Epidemiology, 9(4), 792-794. https://doi.org/10.3126/nje.v9i4.26960
- van Teijlingen, A., Tuttle, T., Bouchachia, H., Sathian, B., & van Teijlingen, E. (2020). Artificial Intelligence and Health in Nepal. Nepal Journal of Epidemiology, 10(3), 915–918. https://doi.org/10.3126/nje.v10i3.31649
- van Teijlingen, E.R., Dhakal Adhikari, S., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, A., Aryal, N., Panday, S. (2021). Publishing, identifiers & metrics: Playing the numbers game. Health Prospect, 20(1). https://doi.org/10.3126/hprospect.v20i1.37391
- van Teijlingen, K., Devkota, B., Douglas, F., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2021) Understanding health education, health promotion and public health, Journal of Health Promotion 9(1):1-7. https://www.nepjol.info/index.php/jhp/article/view/40957
Expert in Health Service Accessibility
Received a lovely tweet this Sunday morning from Expertscape, an organisation in the USA, announcing that: ” As part of International Universal Health Coverage Day (Dec 12, 2021), we congratulate Dr. Edwin R van Teijlingen of Bournemouth University — Recognized as an Expertscape Expert in Health Services Accessibility”. Expertscape ranks the world’s top experts in Clinical and Research Medicine.

Two health and migration papers published in two days
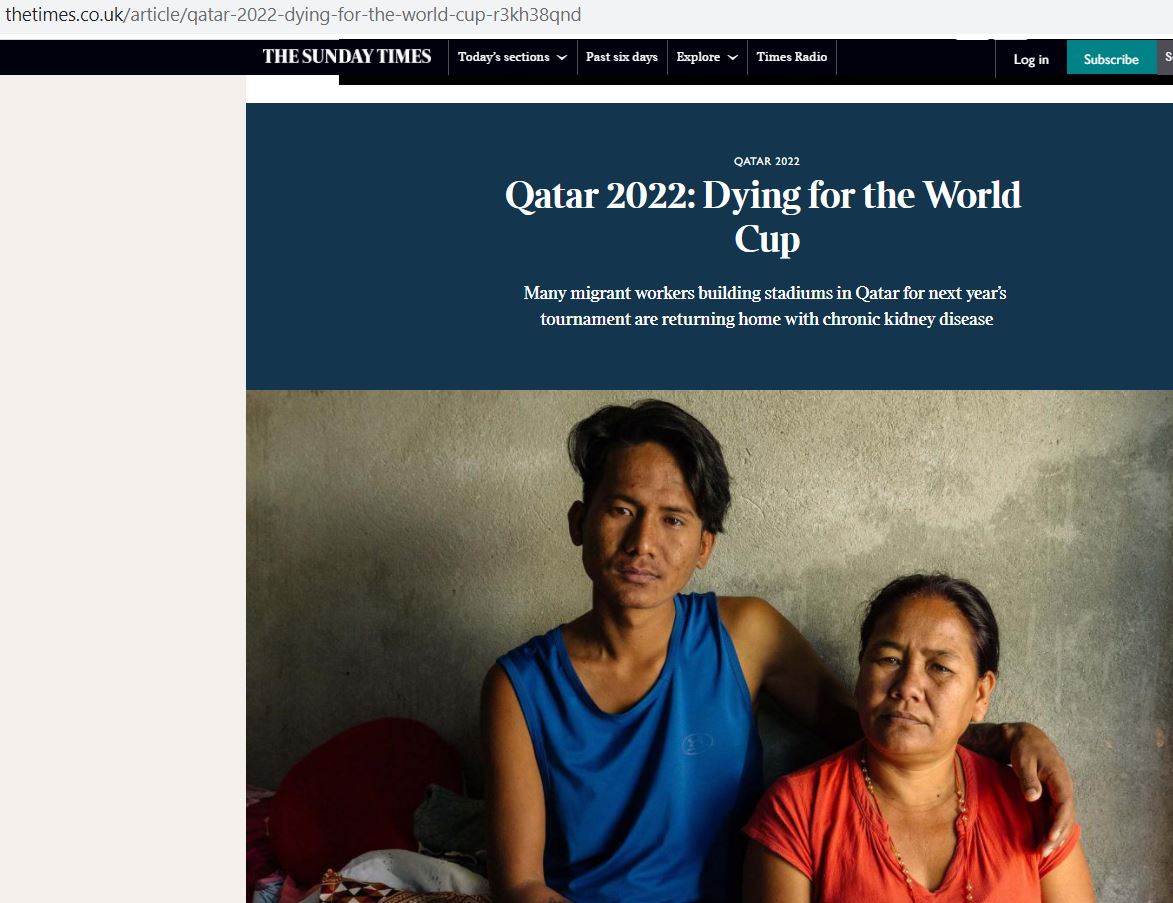
 Congratulations to dr. Pramod Regmi on the publication today of our research article ‘Risk of Kidney health among returnee Nepali migrant workers: A survey of nephrologists‘ [1]. This paper was published today in the Asian Journal of Medical Sciences. It is co-authored with a clinician (a nephrologist) and a migration and health expert in Nepal. This paper reports on the Bournemouth University-led study with kidney specialists in Nepal which was reported in The Sunday Times under the heading ‘Qatar 2022: Dying for the World Cup‘ a fortnight ago.
Congratulations to dr. Pramod Regmi on the publication today of our research article ‘Risk of Kidney health among returnee Nepali migrant workers: A survey of nephrologists‘ [1]. This paper was published today in the Asian Journal of Medical Sciences. It is co-authored with a clinician (a nephrologist) and a migration and health expert in Nepal. This paper reports on the Bournemouth University-led study with kidney specialists in Nepal which was reported in The Sunday Times under the heading ‘Qatar 2022: Dying for the World Cup‘ a fortnight ago.
 Last Saturday Dr. Nirmal Aryal (now researcher at the Greater Manchester Mental Health NHS Foundation Trust and BU Visiting Faculty) and Dr. Regmi presented this research at a webinar in Nepal which was well attended and shown on Facebook Life.
Last Saturday Dr. Nirmal Aryal (now researcher at the Greater Manchester Mental Health NHS Foundation Trust and BU Visiting Faculty) and Dr. Regmi presented this research at a webinar in Nepal which was well attended and shown on Facebook Life.
Yesterday the Journal of Health Promotion published another Bournemouth University co-authored paper on health and migration with the title ‘Perceived threats towards COVID-19 pandemic among Nepali migrant workers returned from India’. Both paper are published Open Access and, as such, freely available across the globe to anyone with internet access!
References:
- Aryal, N., Sedhain, A., Regmi, P.R., KC, R.K.,& van Teijlingen, E. (2021). Risk of kidney health among returnee Nepali migrant workers: A survey of nephrologists. Asian Journal of Medical Sciences, 12(12), 126–132.
- Khanal, S. P., van Teijlingen, E., Sharma, M. K., Acharya, J., & Sharma, S. (2021). Perceived threats towards COVID-19 pandemic among Nepali migrant workers returned from India. Journal of Health Promotion,9(01), 87–99.
Peer-reviewing ten years on
The process of peer review is widely recognised as the key element of quality control in academic publishing and the scientific community more generally. Peer review is the critical appraisal of one’s work by fellow scholars, who read and comment on your manuscript and offered a verdict on its quality, rigour, originality, style, completeness, etc. etc. 
Peer reviewers are typically experts in your field, if not your topic, or who have expertise in the methods you applied or the population or are you studied. They are also academics often with busy day jobs, who act as unpaid peer reviewers, and as journal editors for that matter. Peer reviewers are with full-time jobs who give up their free time to review for academic journals. A recent article by Aczel and colleagues (2021) reported that reviewers across the globe spent over 100 million hours on peer reviewing for free in 2020, the estimated value of this equated to nearly £300 million in the UK alone. This quantifies in some of my feelings I wrote about a decade ago now in a BU Research Blog with the title ‘Peer review and bust academics’.
However, with the ever-growing number of health and social science journals the requests for reviewing seem to grow relentlessly. This month alone (November 2021) I received twenty or 21 requests to review. I have reviewed three manuscripts for Birth, Nepal Journal of Epidemiology, and The Journal of International Development, but I had to reject or ignore many more (see Table 1). I usually do my reviews over the weekend. One weekend this month I could not review because I had to prepare materials for the external auditor who came to visit Bournemouth University for a project recently completed, and this weekend I could not find the time because I’m proof-reading two PhD chapters (and writing this blog).

I leave you with some food for thought: academics spent time applying for research funding, then apply for the ethical approval, do the research, we write up the findings, and write blogs about the process!
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH)
Reference:
Aczel, B., Szaszi, B., Holcombe, A.O. (2021) A billion-dollar donation: estimating the cost of researchers’ time spent on peer review. Res Integr Peer Rev 6, 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41073-021-00118-2.
Health & well-being of Nepal’s migrant workers
 Dr. Pramod Regmi, Senior Lecturer in International Health in the Department of Nursing Science, has been invited to speak at the forthcoming NIRI Webinar on this Saturday (27th November 2021). He will be jointly presenting with Dr. Nirmal Aryal, Visiting Faculty at the Department of Health & Social Sciences (FHSS). Pramod and Nirmal will be speaking on ‘The hidden health costs of Nepali labour migrants’, following the coverage of Bournemouth University’s research on this topic in The Sunday Times the weekend before last.
Dr. Pramod Regmi, Senior Lecturer in International Health in the Department of Nursing Science, has been invited to speak at the forthcoming NIRI Webinar on this Saturday (27th November 2021). He will be jointly presenting with Dr. Nirmal Aryal, Visiting Faculty at the Department of Health & Social Sciences (FHSS). Pramod and Nirmal will be speaking on ‘The hidden health costs of Nepali labour migrants’, following the coverage of Bournemouth University’s research on this topic in The Sunday Times the weekend before last.
NIRI (Nexus Institute of Research and Innovation) is a not-for-profit-sharing institution established by Nepalese scientists, academics, and social workers with a common goal of fostering research and innovation in Nepal. The session will be presented ‘live’ on Facebook.
Well done!
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health
Free training sessions for dementia researchers
 Bournemouth University is involved in a wider collaboration which organises the Advanced Dementia Research Conference (ADRC 2021). The conference is delivered online today and tomorrow (19th-20th November). ADRC 2021 is led by Dr. Brijesh Sathian, BU Visiting Faculty, based in the Geriatric Medicine Department, Rumailah Hospital, in Doha, Qatar. Saturday morning Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen will be delivering a session on qualitative research, preceded by a session on mixed-methods research from Prof. Padam Simkhada, also BU Visiting Faculty, from the University of Huddersfield.
Bournemouth University is involved in a wider collaboration which organises the Advanced Dementia Research Conference (ADRC 2021). The conference is delivered online today and tomorrow (19th-20th November). ADRC 2021 is led by Dr. Brijesh Sathian, BU Visiting Faculty, based in the Geriatric Medicine Department, Rumailah Hospital, in Doha, Qatar. Saturday morning Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen will be delivering a session on qualitative research, preceded by a session on mixed-methods research from Prof. Padam Simkhada, also BU Visiting Faculty, from the University of Huddersfield.
The programme shown is for Day 2 tomorrow. All sessions today and tomorrow are free to attend! You can register here! Please, note that advertised times a Qatar times which three hours ahead of the UK at the moment.

Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMMPH (Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health)
Bournemouth research cited in The Sunday Times
 Today Bournemouth University’s research on Nepali migrant workers and kidney problems was cited in The Sunday Times. In the preparation for the Qatar 2022 men’s football world cup The Sunday Times published an article under the title ‘Dying for the World Cup‘.
Today Bournemouth University’s research on Nepali migrant workers and kidney problems was cited in The Sunday Times. In the preparation for the Qatar 2022 men’s football world cup The Sunday Times published an article under the title ‘Dying for the World Cup‘.
 Dr. Pramod Regmi and Dr. Nirmal Aryal were awarded funding from GCRF (The Global Challenges Research Fund) and Bournemouth University’s QR fund. This work resulted in an editorial highlighting that low-skilled migrant workers in the Middle Wast and Malaysia are at a disproportionately higher risk of kidney problems. The working conditions are often Dirty, Dangerous and Difficult (referred at as the 3Ds) include physically demanding work, exposure to a hot environment, dehydration, chemical exposures, excessive use of pain killers, and lifestyle factors (such as restricted water intake and a high intake of alcohol/sugary drinks) which may precipitate them to acute kidney injuries and subsequent chronic kidney disease [1]. And recently, a national survey of nephrologists (kidney specialists) on their perceptions of the size of the problem of kidney health in Nepali migrant workers [2].
Dr. Pramod Regmi and Dr. Nirmal Aryal were awarded funding from GCRF (The Global Challenges Research Fund) and Bournemouth University’s QR fund. This work resulted in an editorial highlighting that low-skilled migrant workers in the Middle Wast and Malaysia are at a disproportionately higher risk of kidney problems. The working conditions are often Dirty, Dangerous and Difficult (referred at as the 3Ds) include physically demanding work, exposure to a hot environment, dehydration, chemical exposures, excessive use of pain killers, and lifestyle factors (such as restricted water intake and a high intake of alcohol/sugary drinks) which may precipitate them to acute kidney injuries and subsequent chronic kidney disease [1]. And recently, a national survey of nephrologists (kidney specialists) on their perceptions of the size of the problem of kidney health in Nepali migrant workers [2].
References:
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., Sedhain, A., KC, R.K., Martinez Faller, E., Rijal, A., van Teijlingen, E. (2021). Kidney health risk of migrant workers: An issue we can no longer overlook. Health Prospect 21(1): 15-17.
- Aryal, N., Sedhain, A., Regmi, P., KC, R. K., van Teijlingen, E. (2021). Risk of kidney health among returnee Nepali migrant workers: A survey of nephrologists. Asian Journal of Medical Sciences 12(12), 126–132.

Not going in!
 Yesterday I had the pleasure of attending the online workshop ‘500 Years of Childbirth’ together with by CMMPH (Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health) colleges Dr. Juliet Wood and Dr. Laura Iannuzzi. The session ‘500 Years of Childbirth’ was part of Being Human Festival, the UK’s national festival of the humanities which runs 11–20 November 2021. History has always been a passion of me, and the presenters, Julia Martins and Carly Lokrheim, linked early modern history with childbirth in the 21st century.
Yesterday I had the pleasure of attending the online workshop ‘500 Years of Childbirth’ together with by CMMPH (Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health) colleges Dr. Juliet Wood and Dr. Laura Iannuzzi. The session ‘500 Years of Childbirth’ was part of Being Human Festival, the UK’s national festival of the humanities which runs 11–20 November 2021. History has always been a passion of me, and the presenters, Julia Martins and Carly Lokrheim, linked early modern history with childbirth in the 21st century. 
This wonderful session reminded me of my draft chapter I wrote for my PhD thesis three decades ago. My thesis A social or medical model of childbirth? : comparing the arguments in Grampian (Scotland) and the Netherlands at the University of Aberdeen was supervised by Dr. Peter McCaffery. Peter wisely said to me: “You really needed to write this chapter to make sense of the history of midwifery in your head, but it does not really fit the thesis.” He added: “You have too many words already. You know that it is not going in?” The material of this history chapter was not lost as I used loads of text from it it in the introduction section for a textbook [1]. The section ‘History of Midwifery: Introduction’ became part of our edited volume Midwifery and the Medicalization of Childbirth: Comparative Perspectives (Nova Science Publishers, Inc., Huntington, New York, USA) [2].
It is a message I occasionally repeat to my own PhD students. Under the circumstances I may fing myself saying things like “This is something you had to get of your chest, or you had to write it to make sense of it, but as it stands do you think it fits your argument?” Or more subtly in a supervision meeting, tell us: “What does this section add to your overall story in the thesis?”
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMMPH
References:
- van Teijlingen, E. (2004) History of Midwifery: Introduction, In: van Teijlingen, E. Lowis, G., et al. (eds.), Midwifery & the Medicalization of Childbirth, NY: Nova Sci., pages: 43-52.
- van Teijlingen , E., Lowis, G., McCaffery, P. & Porter, M. (eds.) (2004) Midwifery and the Medicalization of Childbirth: Comparative Perspectives, New York: Nova Science. [Paperback ISBN: 1-59454-0314].
Two scholarships in one month for PhD student
 Congratulations to PhD student Abier Hamidi on winning two scholarships within weeks. Earlier this month Abier was awarded a scholarship from the BHIVA (British HIV Association) to pay the registration fee for BHIVA Autumn Conference. This week she was also successful in getting a scholarship covering registration for the ‘Arab Health Summit: Advancing Health Equity for Women’ to be held on October 19-21. The Arab Health Summit serves as a platform for researchers in the USA to connect with their global counterparts, including in the MENA (Middle Eastern and North African) region. This summit offers a unique opportunity for Abier to exchange ideas and develop research relationships that may support her PhD study.
Congratulations to PhD student Abier Hamidi on winning two scholarships within weeks. Earlier this month Abier was awarded a scholarship from the BHIVA (British HIV Association) to pay the registration fee for BHIVA Autumn Conference. This week she was also successful in getting a scholarship covering registration for the ‘Arab Health Summit: Advancing Health Equity for Women’ to be held on October 19-21. The Arab Health Summit serves as a platform for researchers in the USA to connect with their global counterparts, including in the MENA (Middle Eastern and North African) region. This summit offers a unique opportunity for Abier to exchange ideas and develop research relationships that may support her PhD study. 
Abier is conducting a PhD on: ‘Perceptions of the Effectiveness of Health Education Strategies in Reducing Harm from HIV in Libyan Married Women’. Recently, she had her first PhD paper “HIV epidemic in Libya: Identifying gaps” accepted for publication by the Journal of the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care (JIAPAC) published by SAGE [1]. Abier’s PhD project is supervised by Dr. Pramod Regmi (Senior Lecturer in International Health) and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen in the Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH).
Reference:
- Hamidi, A., Regmi, P., van Teijlingen, E. HIV epidemic in Libya: Identifying gaps, Journal of the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care (JIAPAC) (forthcoming)
A small or a large national survey?
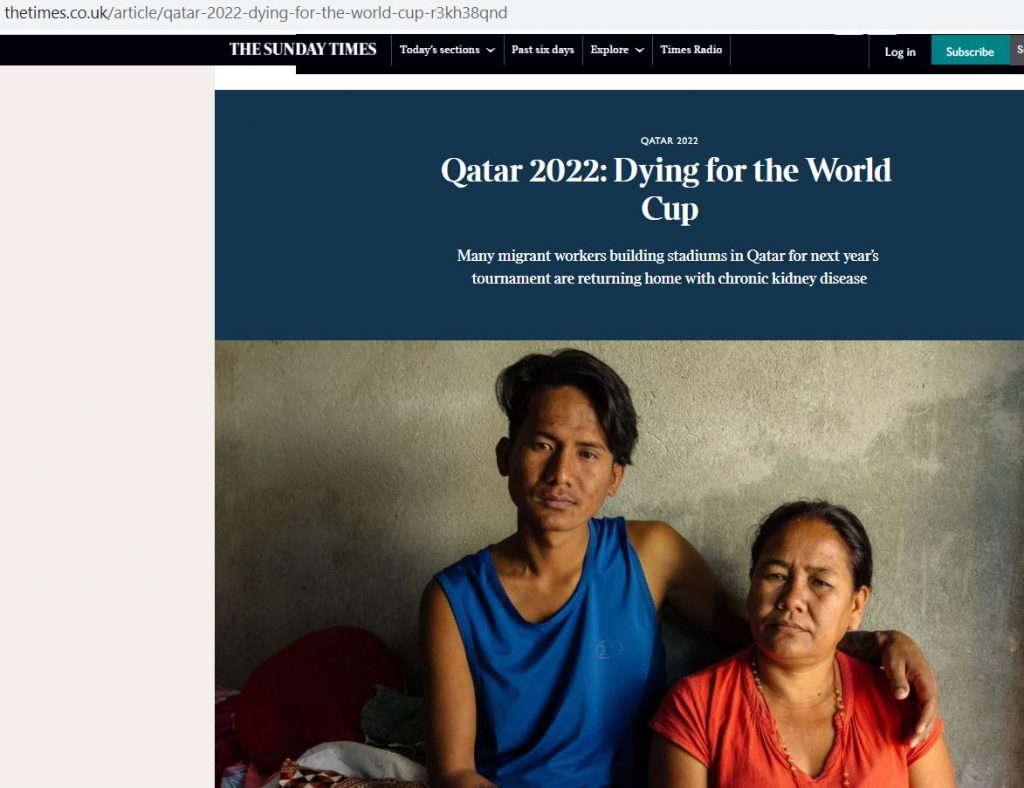
 Congratulations to Dr. Pramod Regmi and Dr. Nirmal Aryal on the acceptance of their paper ‘Risk of kidney health among returnee Nepali migrant workers: A survey of nephrologists’ [1]. This paper has been accepted by the Asian Journal of Medical Sciences, after having been rejected previous by another scientific journal . The reason for rejection was the small sample size of 38 nephrologists (=medical specialists in kidney disease). We think one of the reasons for acceptance of this research by the Asian Journal of Medical Sciences is the high proportion (74.5%) of all Nepal’s nephrologists who participated in this national study. Although the absolute number of participants is low there are only 51 kidney experts in the whole country and three-quarters took part in this study!
Congratulations to Dr. Pramod Regmi and Dr. Nirmal Aryal on the acceptance of their paper ‘Risk of kidney health among returnee Nepali migrant workers: A survey of nephrologists’ [1]. This paper has been accepted by the Asian Journal of Medical Sciences, after having been rejected previous by another scientific journal . The reason for rejection was the small sample size of 38 nephrologists (=medical specialists in kidney disease). We think one of the reasons for acceptance of this research by the Asian Journal of Medical Sciences is the high proportion (74.5%) of all Nepal’s nephrologists who participated in this national study. Although the absolute number of participants is low there are only 51 kidney experts in the whole country and three-quarters took part in this study!
 Dr. Nirmal Aryal was until recently based in the Department of Midwifery and Health Sciences and he will be starting later this month as a Research Associate at Greater Manchester Mental Health NHS Trust. Dr. Pramod Regmi is Senior Lecturer in International Health in the Department of Nursing Sciences. This paper was also co-authored with a nephrologist Dr. Arun Sedhai based in Chitwan (Nepal) and a public health expert based at the UN organisation, International Organization for Migration (IOM).
Dr. Nirmal Aryal was until recently based in the Department of Midwifery and Health Sciences and he will be starting later this month as a Research Associate at Greater Manchester Mental Health NHS Trust. Dr. Pramod Regmi is Senior Lecturer in International Health in the Department of Nursing Sciences. This paper was also co-authored with a nephrologist Dr. Arun Sedhai based in Chitwan (Nepal) and a public health expert based at the UN organisation, International Organization for Migration (IOM).
This paper which will be Open Access and hence freely available for any reader across the globe adds to the growing research evidence published by Bournemouth University’s researchers on migration and health, especially of migrants from Nepal [2-21].
Well done!
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH)
References:
- Aryal, N., Sedhain, A., Regmi, P.R., KC, R.K., van Teijlingen, E. (2021) ‘Risk of kidney health among returnee Nepali migrant workers: A survey of nephrologists’, Asian Journal of Medical Sciences (accepted).
- Simkhada, B., Vahdaninia, M., van Teijlingen, E., Blunt, H. (2021) Cultural issues on accessing mental health services in Nepali and Iranian migrants communities in the UK, International Journal of Mental Health Nursing (accepted). https://doi.org/10.1111/inm.12913
- Adhikary, P., Aryal, N., Dhungana, R.R., KC, R.K., Regmi, P.R., Wickramage, K.P., Duigan, P., Inkochasan, M., Sharma, G.N., Devkota, B., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P. (2020) Accessing health services in India: experiences of seasonal migrants returning to Nepal. BMC Health Services Research 20, 992. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05846-7
- IOM [International Organization for Migration]. (2019) Health vulnerabilities of cross-border migrants from Nepal. Kathmandu: International Organization for Migration.
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Trenoweth, S., Adhikary, P., Simkhada, P. (2020) The Impact of Spousal Migration on the Mental Health of Nepali Women: A Cross-Sectional Study, International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health 17(4), 1292; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph1704129
- Regmi, P., Aryal, N., van Teijlingen, E., Adhikary, P. (2020) Nepali migrant workers and the need for pre-departure training on mental health: a qualitative study, Journal of Immigrant & Minority Health 22, 973–981.
- Adhikary, P. van Teijlingen, E. (2020) Support networks in the Middle East & Malaysia: A qualitative study of Nepali returnee migrants’ experiences, International Journal of Occupational Safety & Health (IJOSH), 9(2): 31-35.
- Simkhada, B., Sah, R.K., Mercel-Sanca, A., van Teijlingen, E., Bhurtyal, Y.M., Regmi, P. (2020) Health and Wellbeing of the Nepali population in the UK: Perceptions and experiences of health and social care utilisation, Journal of Immigrant & Minority Health (accepted).
- Regmi, P., van Teijlingen, E., Mahato, P., Aryal, N., Jadhav, N., Simkhada, P., Syed Zahiruddin, Q., Gaidhane, A., (2019) The health of Nepali migrants in India: A qualitative study of lifestyles and risks, Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health 16(19), 3655; doi:10.3390/ijerph16193655.
- Dhungana, R.R., Aryal, N, Adhikary, P., KC, R., Regmi, P.R., Devkota, B., Sharma, G.N., Wickramage, K., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P. (2019) Psychological morbidity in Nepali cross-border migrants in India: A community-based cross-sectional, BMC Public Health 19:1534 https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-019-7881-z
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P., Mahato, P. (2019) Adolescents left behind by migrant workers: a call for community-based mental health interventions in Nepal. WHO South East Asia Journal of Public Health 8(1): 38-41.
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., Faller, E.M,, van Teijlingen, E., Khoon, C.C., Pereira, A., Simkhada, P. (2019) ‘Sudden cardiac death and kidney health related problems among Nepali migrant workers in Malaysia’ Nepal Journal of Epidemiology 9(3): 755-758. https://www.nepjol.info/index.php/NJE/article/view/25805
- Adhikary P, van Teijlingen E., Keen S. (2019) Workplace accidents among Nepali male workers in the Middle East and Malaysia: A qualitative study, Journal of Immigrant & Minority Health 21(5): 1115–1122. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10903-018-0801-y
- Simkhada, P.P., van Teijlingen, E.R., Gurung, M., Wasti, S. (2018) A survey of health problems of Nepalese female migrants workers in the Middle-East & Malaysia, BMC International Health & Human Rights 18(4): 1-7. http://rdcu.be/E3Ro
- Adhikary P, Sheppard, Z., Keen S., van Teijlingen E. (2018) Health and well-being of Nepalese migrant workers abroad, International Journal of Migration, Health & Social Care 14(1): 96-105. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJMHSC-12-2015-0052
- Adhikary, P, Sheppard, Z., Keen, S., van Teijlingen, E. (2017) Risky work: accidents among Nepalese migrant workers in Malaysia, Qatar & Saudi Arabia, Health Prospect 16(2): 3-10.
- Simkhada, P.P., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Aryal, N. (2017) Identifying the gaps in Nepalese migrant workers’ health and well-being: A review of the literature, Journal of Travel Medicine 24 (4): 1-9.
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P., Adhikary, P., Bhatta, Y.K.D., Mann, S. (2016) Injury and Mortality in Young Nepalese Migrant Workers: A Call for Public Health Action. Asian-Pacific Journal of Public Health 28(8): 703-705.
- Sapkota, T., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2014) Nepalese health workers’ migration to United Kingdom: A qualitative study. Health Science Journal 8(1):57-74.
- Adhikary P, Keen S and van Teijlingen E (2011). Health Issues among Nepalese migrant workers in the Middle East. Health Science Journal.5 (3):169-i75 DOI: 2-s2.0-79960420128.
- Adhikary, P., Simkhada, P.P., van Teijlingen E., Raja, AE. (2008) Health & Lifestyle of Nepalese Migrants in the UK, BMC International Health & Human Rights 8(6). Web address: www.biomedcentral.com/1472-698X/8/6
Nepal research published
 Yesterday saw the publication of a new scientific paper on the health care system in Nepal. The latest BU paper ‘Health facility preparedness of maternal and neonatal health services: A survey in Jumla, Nepal’ is a collaboration between academics at the University of Huddersfield, Liverpool John Moores University and the Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH) at Bournemouth University [1]. This is the third paper led by Pasang Tamang, who is currently a PhD student at the University of Huddersfield [2-3].
Yesterday saw the publication of a new scientific paper on the health care system in Nepal. The latest BU paper ‘Health facility preparedness of maternal and neonatal health services: A survey in Jumla, Nepal’ is a collaboration between academics at the University of Huddersfield, Liverpool John Moores University and the Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH) at Bournemouth University [1]. This is the third paper led by Pasang Tamang, who is currently a PhD student at the University of Huddersfield [2-3].
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMMPH
References
- Tamang, P., Simkhada, P., Bissell, P., van Teijlingen, E., Khatri, R., Stephenson, J., (2021) Health facility preparedness of maternal and neonatal health services: A survey in Jumla, Nepal, BMC Health Service Research 21:1023. https://rdcu.be/cyD01
- Tamang, P., Mahato, P., Simkhada P., Bissell, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2021) Pregnancy, Childbirth, Breastfeeding and Coronavirus Disease: What is known so far? Journal of Midwifery Association of Nepal (JMAN) 2(1): 96-101.
- Tamang, P., Mahato, P., van Teijlingen E, Simkhada, P. (2020) Pregnancy and COVID-19: Lessons so far, Healthy Newborn Network [14 April] healthynewbornnetwork.org/blog/pregnancy-and-covid-19-lessons-so-far/
Volunteers’, carers’ and home care workers’ perspectives on the pandemic
 ‘Staying Home Connecting Care’ is a British Academy funded research project exploring care provided to people at home during the Covid-19 pandemic. As society locked down, people with age-related frailties, disabilities, and certain health conditions needed to shield at home. Many relied on the support of family carers, home care workers and volunteer-run schemes to supply them with the care, companionship and essential supplies of food and medicines to stay safe and well at home.
‘Staying Home Connecting Care’ is a British Academy funded research project exploring care provided to people at home during the Covid-19 pandemic. As society locked down, people with age-related frailties, disabilities, and certain health conditions needed to shield at home. Many relied on the support of family carers, home care workers and volunteer-run schemes to supply them with the care, companionship and essential supplies of food and medicines to stay safe and well at home.
Over the past year we have been interviewing care workers, volunteers and carers from across Bournemouth, Christchurch, Poole (BCP) and Dorset, about their experiences of providing such care and support to people in their homes during the pandemic.
We recently organised an online workshop, ‘Care and Support at home in the time of Covid’. The aim of this free event was to share the interim findings of the study with a public audience, and invite feedback, reflection and discussion.
The highlight of the event was the roundtable discussion in which six speakers took part, each with extensive experience of home care work, voluntary and community pandemic activities and/or care of vulnerable adults. The round table speakers were:
Sue Warr from Prama life, Jon Sloper from Help and Kindness, Rosie Thompson from Gillingham Community Kindness, Sarah Ward from the Covid-19 Poole Community Support Group, Pam Henderson from Bournemouth University’s PIER Partnership and Andrew Davis from Right at Home and Dorset Home Care Providers’ Association.
Each round table participant spoke in fascinating and poignant detail about their activities during the pandemic. They reflected on how the ‘Staying Home’ research findings resonated with their own insights and experiences, and shared their perspectives on the priorities for future research and policy.
Several themes recurred throughout the course of the round table discussion. The dynamism and resourcefulness of the voluntary and community sector response to the pandemic was evident from many of the talks, which detailed how people in communities across BCP and Dorset rapidly and creatively devised practical schemes for getting help and support to people at home. The innovative use of telephone and web-based technologies to build new infrastructures to connect people was also a key area of discussion.
Speakers highlighted important shifts over the course of the pandemic. As one remarked, it is easy to forget the public uncertainty about how coronavirus was transmitted in the early days, when an effective vaccine seemed a distant prospect. This made close-contact caring for adults vulnerable to Covid-19 acutely stressful and challenging for carers and care workers.
Over time, as needs of people at home for basic supplies of food and medicines eased from summer 2020, other needs became apparent, not least many people’s poor mental health and loneliness. The isolation and loss of services had a profound impact on (family) carers. The pandemic has stretched to breaking point the fragile support networks on which many carers continue to depend. The phase of clapping for care workers and carers is over, but for some, the challenges to daily existence posed by the pandemic are more acute than ever.
Speakers highlighted several important questions for future research and policy. How can the hugely positive innovations within the voluntary organisations and communities be best supported and transformed as society reopens? How can that project be harnessed to the transformation of the social care system to make it fairer and fit for purpose, with appropriate levels of public investment? How can the rights and needs of people who still need to shield, and their carers, be protected, as wider society reopens?
Evaluation
20-25 people attended the event, and, 15 of them anonymously completed the evaluation survey at the end of the workshop. All agreed that the presentation of interim findings was clear, accessible, interesting and informative, and that the roundtable furthered their understanding of care during Covid-19. All except one agreed that research on social care needs to take account of unwaged forms of support, such as that provided by carers and volunteers, as well as that provided by workers within social care services. One commented “This is a really important need as I don’t think people realise the scope of unpaid care that is happening”, whilst another remarked, “I feel the total focus is always around residential care, and other areas…including homecare and voluntary, get forgotten”.
Survey respondents highlighted several areas for further research.
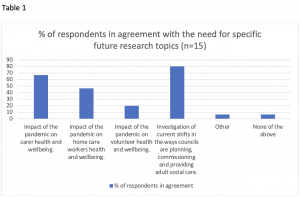
The event was recorded and a link to it can be found here.
Dr Rosie Read, Principal Investigator
Erica Ferris, Research Assistant
Faculty of Health and Social Sciences
Bournemouth University
Email for correspondence: rread@bournemouth.ac.uk
And the publication date is….

You may have seen the BU Research Blog two years ago congratulating Bournemouth University’s MSc Public Health graduate Hana Dinh on the acceptance of her paper ‘‘Factors influencing engagement in premarital sex among Vietnamese young adults: a qualitative study’ [1]. 
In April 2019 this paper was published ‘online first’ in the International Journal of Adolescent Medicine & He alth. Last month, two years later, her paper finally appeared in print. Hana’s paper had originally been accepted by this journal in 2018, it was put online in 2019 and now it has been formally published. It can still be a long process for an academic paper to get into print as we have discussed elsewhere [2]. Hence the title of this blog, the question to me is ‘What is the appropriate publication date for this article on my CV?
alth. Last month, two years later, her paper finally appeared in print. Hana’s paper had originally been accepted by this journal in 2018, it was put online in 2019 and now it has been formally published. It can still be a long process for an academic paper to get into print as we have discussed elsewhere [2]. Hence the title of this blog, the question to me is ‘What is the appropriate publication date for this article on my CV?
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMMPH (Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health)
References:
- Dinh, T., van Teijlingen, E. (2021) Factors influencing engagement in premarital sex among Vietnamese young adults: a qualitative study, International Journal of Adolescent Medicine & Health, 33(4), 20180201. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijamh-2018-0201
- van Teijlingen E., P.P., Simkhada, B., Ireland, J. (2012) The long & winding road to publication, Nepal Journal Epidemiology 2(4): 213-215
BU contribution to development of Nepali academics
 Yesterday we had the pleasure of running an Academic Writing Workshop for academics and postgraduate students in the Department of Health & Physical Education based at the Sanothimi campus of Tribhuvan University. Tribhuvan University is the oldest and largest university of Nepal. We base these training session on our various publications on academic publishing, [1-14] and we used the opportunity to advertise our forthcoming textbook on the matter [15].
Yesterday we had the pleasure of running an Academic Writing Workshop for academics and postgraduate students in the Department of Health & Physical Education based at the Sanothimi campus of Tribhuvan University. Tribhuvan University is the oldest and largest university of Nepal. We base these training session on our various publications on academic publishing, [1-14] and we used the opportunity to advertise our forthcoming textbook on the matter [15].
Prof. Padam Simkhada, Professor of Global Health and Associate Dean International at the School of Human and Health Sciences at the University of Huddersfield and FHSS Visiting Professor.
&
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen, Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH)
References

- Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen E., Hundley, V., Simkhada, BD. (2013) Writing an Abstract for a Scientific Conference, Kathmandu Univ Med J 11(3): 262-65. http://www.kumj.com.np/issue/43/262-265.pdf
- van Teijlingen, E, Hundley, V. (2002) Getting your paper to the right journal: a case study of an academic paper, J Advanced Nurs 37(6): 506-11.
- Pitchforth, E, Porter M, Teijlingen van E, Keenan Forrest, K. (2005) Writing up & presenting qualitative research in family planning & reproductive health care, J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 31(2): 132-135.
- van Teijlingen, E, Simkhada, PP, Rizyal A (2012) Submitting a paper to an academic peer-reviewed journal, where to start? (Guest Editorial) Health Renaissance 10(1): 1-4.
- van Teijlingen, E, Simkhada. PP, Simkhada, B, Ireland J. (2012) The long & winding road to publication, Nepal J Epidemiol 2(4): 213-215 http://nepjol.info/index.php/NJE/article/view/7093/6388
- Hundley, V, van Teijlingen, E, SimkhadP (2013) Academic authorship: who, why and in what order? Health Renaissance 11(2):98-101 www.healthrenaissance.org.np/uploads/Download/vol-11-2/Page_99_101_Editorial.pdf
- Simkhada P, van Teijlingen E, Hundley V. (2013) Writing an academic paper for publication, Health Renaissance 11(1):1-5. www.healthrenaissance.org.np/uploads/Pp_1_5_Guest_Editorial.pdf
- van Teijlingen, E., Ireland, J., Hundley, V., Simkhada, P., Sathian, B. (2014) Finding the right title for your article: Advice for academic authors, Nepal J Epidemiol 4(1): 344-347.
- van Teijlingen E., Hundley, V., Bick, D. (2014) Who should be an author on your academic paper? Midwifery 30: 385-386.
- Hall, J., Hundley, V., van Teijlingen, E. (2015) The journal editor: friend or foe? Women & Birth 28(2): e26-e29.
- Sathian, B., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E., Roy, B, Banerjee, I. (2016) Grant writing for innovative medical research: Time to rethink. Med Sci 4(3):332-33.
- Adhikari, S. D., van Teijlingen, E. R., Regmi, P. R., Mahato, P., Simkhada, B., & Simkhada, P. P. (2020). The Presentation of Academic Self in The Digital Age: The Role of Electronic Databases. International J Soc Sci Management, 7(1), 38-41. https://doi.org/10.3126/ijssm.v7i1.27405
- Pradhan, AK, van Teijlingen, ER. (2017) Predatory publishing: a great concern for authors, Med Sci 5(4): 43.
- van Teijlingen, E (2004), Why I can’t get any academic writing done, Medical Sociol News 30(3): 62-63. britsoc.co.uk/media/26334/MSN_Nov_2004.pd
- Wasti, S.P., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P., Hundley, V. with Shreesh, K. Writing and Publishing Academic Work, Kathmandu, Nepal: Himal Books
Risk of kidney problems in migrant workers
 Congratulations to Dr. Pramod Regmi, Lecturer in International Health & Global Engagement Lead, Department of Nursing Sciences, and Dr. Nirmal Aryal, formerly of the Centre of Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH), whose editorial “Kidney health risk of migrant workers: An issue we can no longer overlook” has been published today in Health Prospect [1]. Further co-authors (Arun Sedhain, Radheshyam Krishna KC, Erwin Martinez Faller, Aney Rijal, and Edwin van Teijlingen) work in India, Nepal, the Philippines and at BU. The study was funded by GCRF.
Congratulations to Dr. Pramod Regmi, Lecturer in International Health & Global Engagement Lead, Department of Nursing Sciences, and Dr. Nirmal Aryal, formerly of the Centre of Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health (CMMPH), whose editorial “Kidney health risk of migrant workers: An issue we can no longer overlook” has been published today in Health Prospect [1]. Further co-authors (Arun Sedhain, Radheshyam Krishna KC, Erwin Martinez Faller, Aney Rijal, and Edwin van Teijlingen) work in India, Nepal, the Philippines and at BU. The study was funded by GCRF. 
This editorial highlights that low-skilled migrant workers in the countries of the Gulf and Malaysia are at a disproportionately higher risk of kidney health problems. The working conditions are often Dirty, Dangerous and Difficult (referred at as the 3Ds) include physically demanding work, exposure to a hot environment, dehydration, chemical exposures, excessive use of pain killers, and lifestyle factors (such as restricted water intake and a high intake of alcohol/sugary drinks) which may precipitate them to acute kidney injuries and subsequent chronic kidney disease.

References
- Aryal, N., Regmi, P.R., Sedhain, A., KC, R.K., Martinez Faller, E., Rijal, A., van Teijlingen, E., (2021) Kidney health risk of migrant workers: An issue we can no longer overlook. Health Prospect 21(1): 15-17.











 Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration
Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration 3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease