Congratulations to Emeritus Prof. Jonathan Parker, Faculty of Health & Social Sciences Visiting Faculty Prof. Vanessa Heaslip and Dr. Kirsty Marshall, the latter two co-authors are based at the University of Salford, on their latest paper ‘Promoting equity in community nursing’ [1].  This paper links to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) published by the United Nations (UN) in 2015 in order to promote health, well-being and economic security for all. Bournemouth University, of course, is among the best universities worldwide for its sustainability, according to the new Times Higher Education (THE) Impact Rankings. BU was ranked 39th out of 1,963 universities measured against the UN Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs) internationally in June 2024.
This paper links to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) published by the United Nations (UN) in 2015 in order to promote health, well-being and economic security for all. Bournemouth University, of course, is among the best universities worldwide for its sustainability, according to the new Times Higher Education (THE) Impact Rankings. BU was ranked 39th out of 1,963 universities measured against the UN Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs) internationally in June 2024.
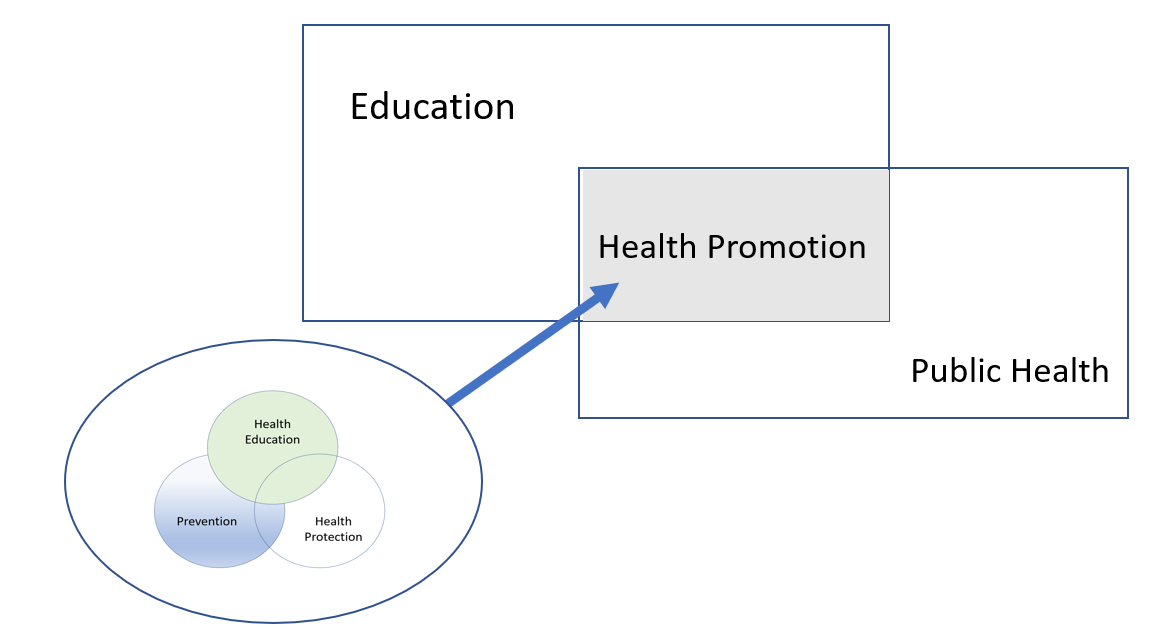
 Heaslip and colleagues remind us that is worth considering the degree to which these influence one’s professional practice. They offer a reflective activity on the issue, see Box 1 ‘Community nurses and the SDGs’ .
Heaslip and colleagues remind us that is worth considering the degree to which these influence one’s professional practice. They offer a reflective activity on the issue, see Box 1 ‘Community nurses and the SDGs’ .

Congratulations!
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Reference:





 This edition includes news items and stories related the successes of CMWH staff and students. For example, about Drs. Dominique Mylod and Daisy Wiggins who both secured innovative NIHR funding for undergraduate student internships. Or about the recently awarded National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) funding for ‘INSIGHT: Inspiring Students into Research’. This innovative three-year programme started this summer as part of the NIHR Academy’s portfolio of career support for health and social care professionals. The programme supports the NIHR aim to develop a highly skilled research workforce capable of advancing the best research which improves health and care, and benefits society and the economy.
This edition includes news items and stories related the successes of CMWH staff and students. For example, about Drs. Dominique Mylod and Daisy Wiggins who both secured innovative NIHR funding for undergraduate student internships. Or about the recently awarded National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) funding for ‘INSIGHT: Inspiring Students into Research’. This innovative three-year programme started this summer as part of the NIHR Academy’s portfolio of career support for health and social care professionals. The programme supports the NIHR aim to develop a highly skilled research workforce capable of advancing the best research which improves health and care, and benefits society and the economy.
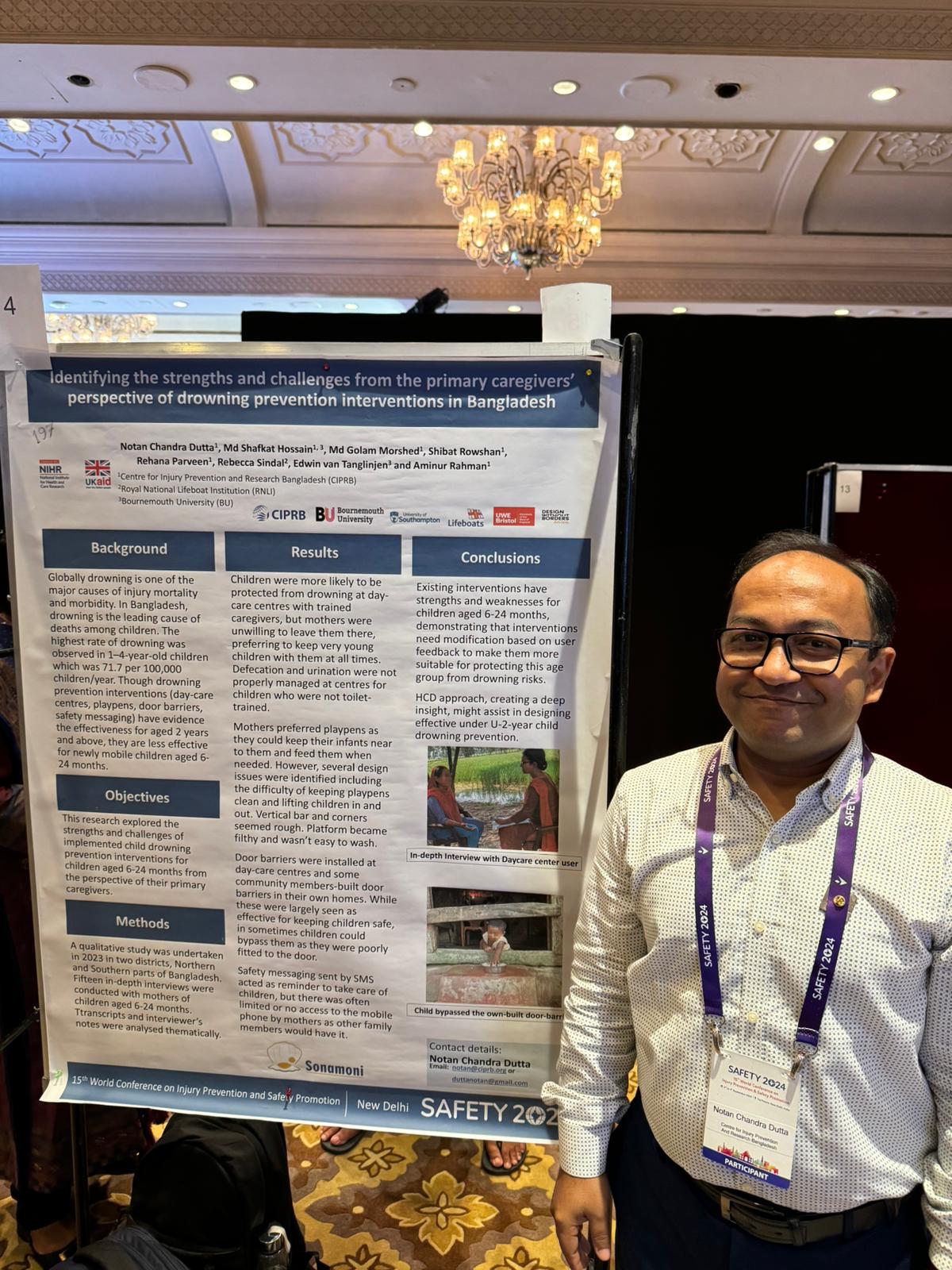
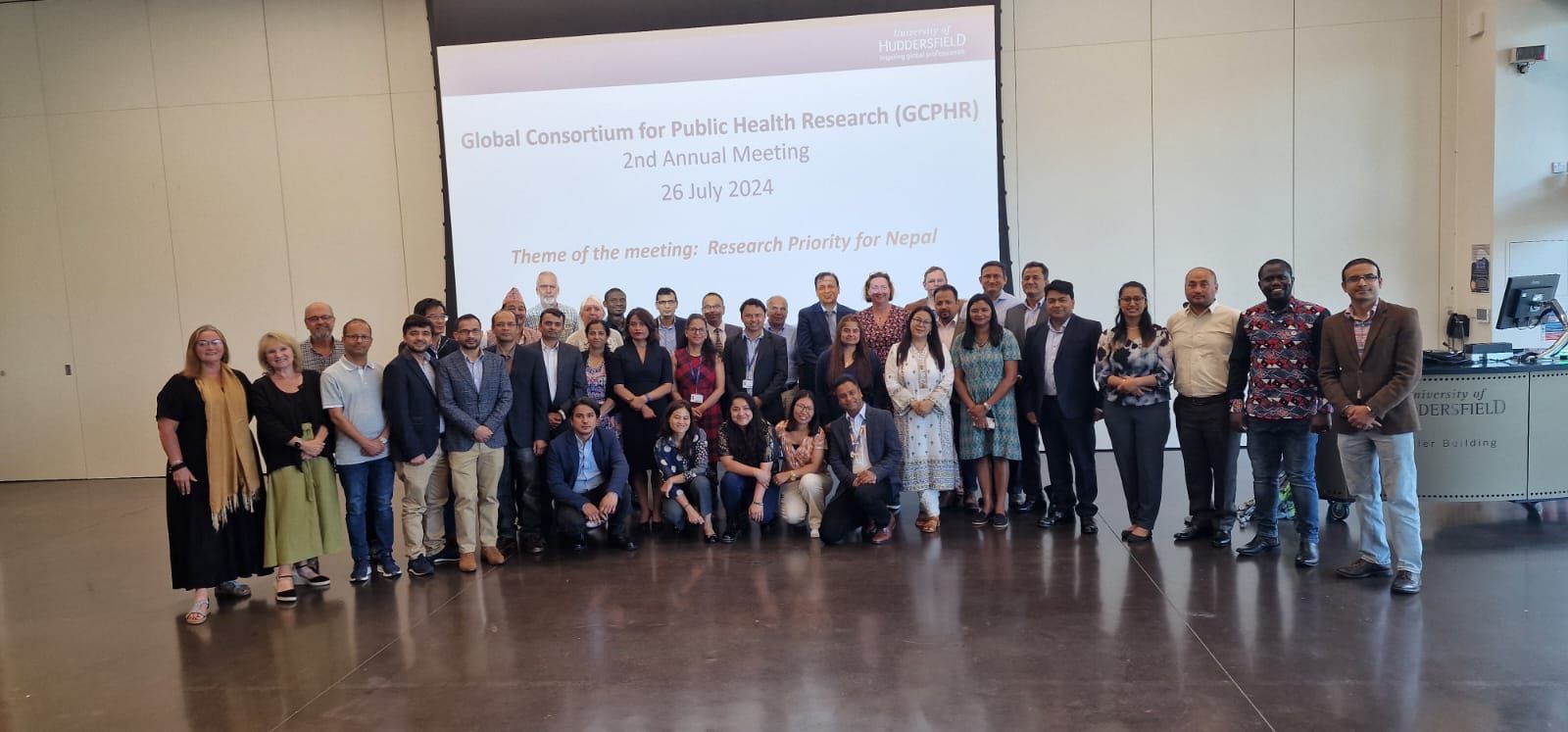



































 BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease