
The Faculty of Health and Social Sciences is holding a Writing Week between 4th-8th January 2016 aimed at supporting staff to find time in their busy academic diaries to prioritise writing grant applications and papers for publication.
The Bournemouth University Clinical Research Unit offers methodological and statistical collaboration for all healthcare researchers in the area. It supports researchers in improving the quality, quantity and efficiency of research across Bournemouth University and local National Health Service (NHS) Trusts. It incorporates the Dorset office of the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Research Design Service who offer free methodological support to researchers who are developing research ideas in the field of health and social care.
BUCRU will be supporting Writing Week in HSS by holding two drop-in sessions on Tuesday 5th January and Thursday 7th January 12-2pm in R508 Royal London House. We would also like to extend the invitation across the other Faculties for anyone who feels we may be able to support them. For those unable to attend the drop-in sessions, we would be delighted to arrange an alternative appointment.
Please see further information here, contact our adminstrator Louise Ward on 01202 961939 / bucru@bournemouth.ac.uk or visit our website. We look forward to seeing you!
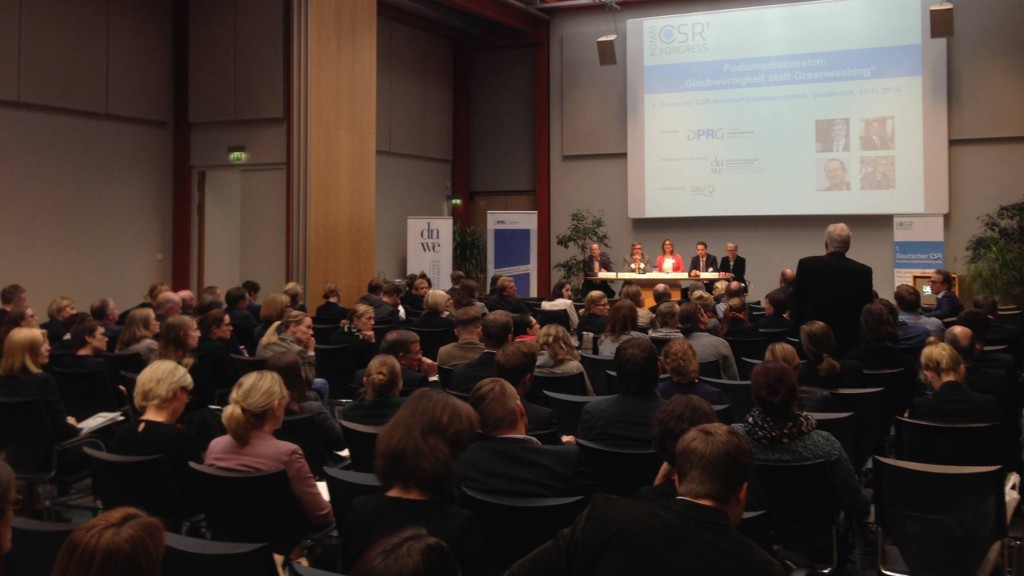
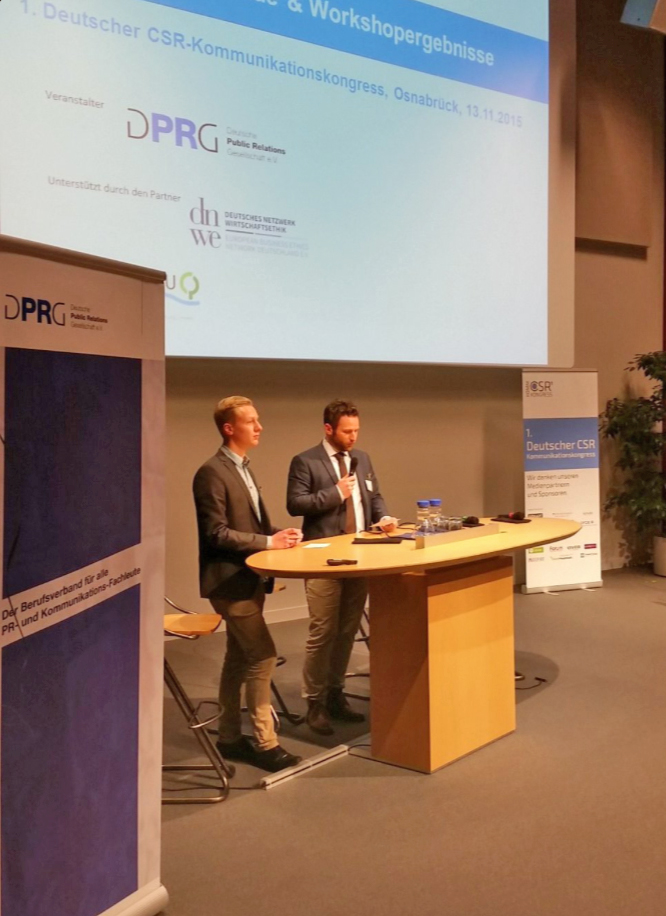
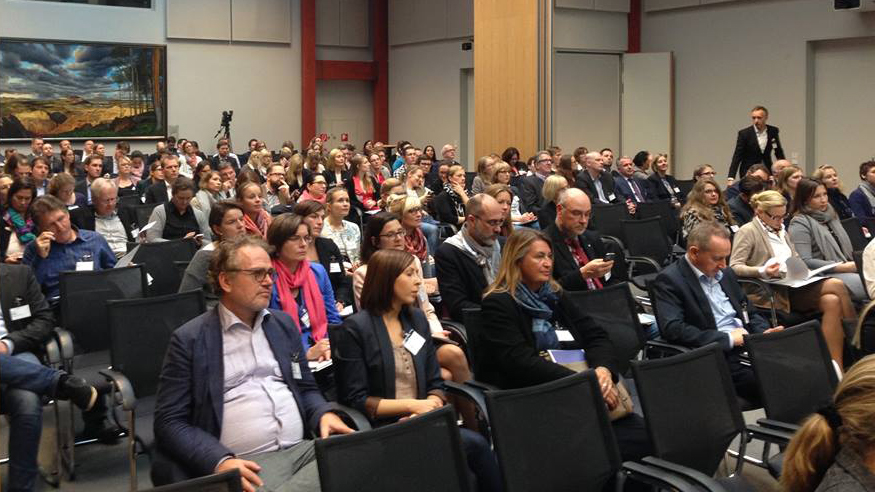














 This afternoon Prof. Jonathan Parker introduced the final of three session in the Executive Business Centre under the title ‘Enhancing social life through global social research: Part 3. Social science research in diverse communities’. This session was well attended and coveredwas a wide-range of interesting social science research topics.
This afternoon Prof. Jonathan Parker introduced the final of three session in the Executive Business Centre under the title ‘Enhancing social life through global social research: Part 3. Social science research in diverse communities’. This session was well attended and coveredwas a wide-range of interesting social science research topics.





 Carol Richardson, joint Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust and CMMPH’s PhD student, published her latest article ‘On running for supervisor’ in the most recent edition of The Practising Midwife. Carol as Clinical Academic Doctoral Midwife is conducting her thesis research on the topic of pregnancy and obesity. Her PhD is supervised by FHSS Prof. Vanora Hundley, Dr. Carol Wilkins & Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen.
Carol Richardson, joint Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust and CMMPH’s PhD student, published her latest article ‘On running for supervisor’ in the most recent edition of The Practising Midwife. Carol as Clinical Academic Doctoral Midwife is conducting her thesis research on the topic of pregnancy and obesity. Her PhD is supervised by FHSS Prof. Vanora Hundley, Dr. Carol Wilkins & Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen.














 Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease