I am delighted to share that our most recent methods paper in the International Journal of Qualitative Methods entitled “Most Significant Change Approach: A Guide to Assess the Programmatic Effects” [1] is now published and is available online (click here!). This paper is co-authored by Mohan K. Sharma, Shanti P. Khanal and Edwin R.van Teijlingen.
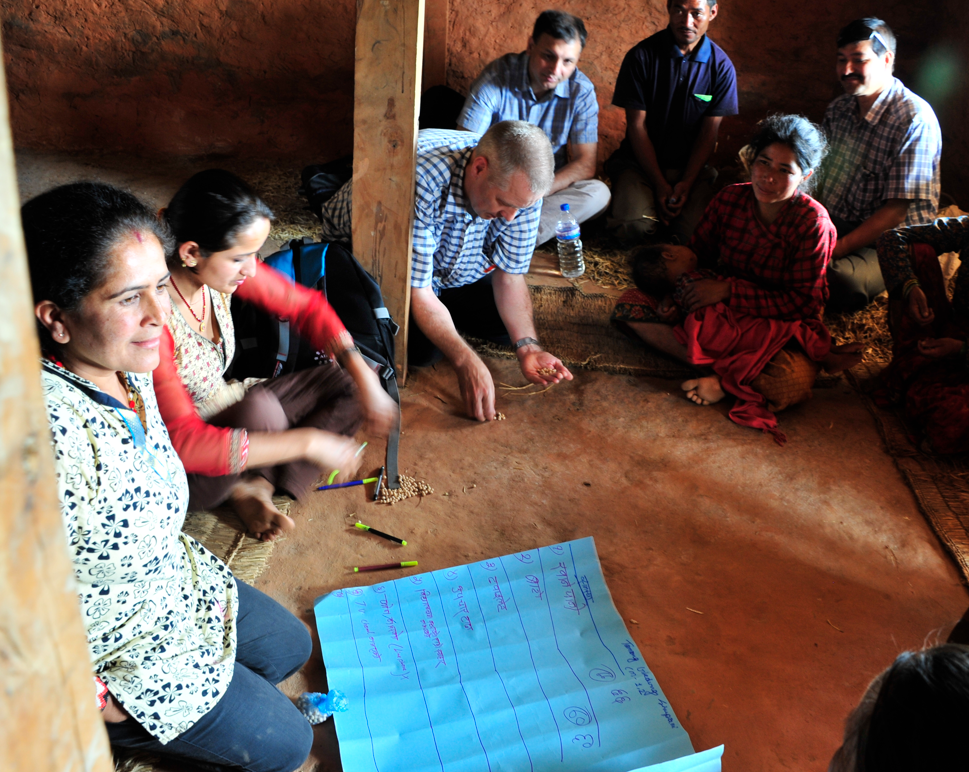
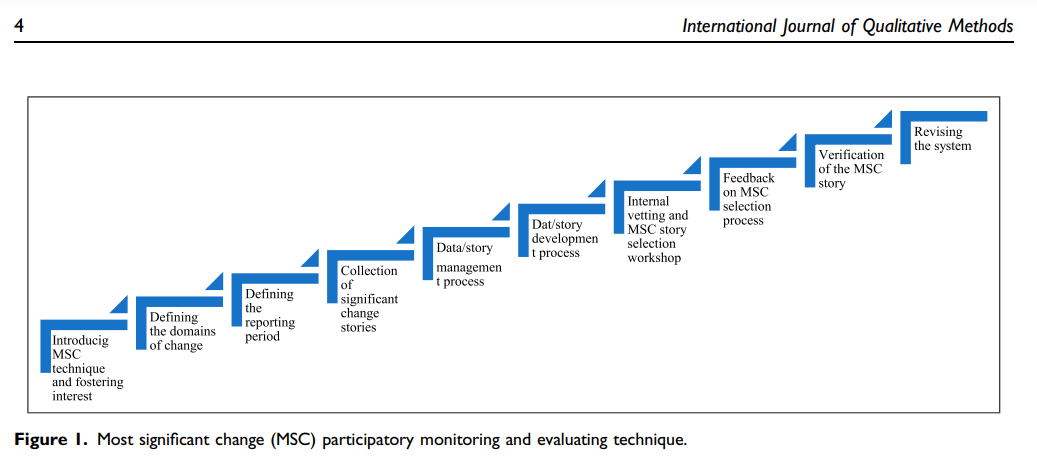
 The paper outlines the so-called ‘Most Significant Change’ (MSC) participatory technique to monitor and evaluate programmatic effects. MSC is a form of monitoring that can be applied throughout the programme cycle and it provides information to help manage the programme. Furthermore, MSC as an evaluation method, provides stories from which programmes’ overall impact can be assessed. However, MSC, as a participatory evaluation technique using qualitative approaches, is often neglected by many evaluators.
The paper outlines the so-called ‘Most Significant Change’ (MSC) participatory technique to monitor and evaluate programmatic effects. MSC is a form of monitoring that can be applied throughout the programme cycle and it provides information to help manage the programme. Furthermore, MSC as an evaluation method, provides stories from which programmes’ overall impact can be assessed. However, MSC, as a participatory evaluation technique using qualitative approaches, is often neglected by many evaluators.
 This is the latest in a series of papers describing the strengths and weaknesses of applying specific research approaches. Other recent methods papers included two on positionality [2-3], a paper on interview methods [4], reflections on conducting participatory policy analysis in Nepal [5], some considerations about the selection of study localities in health research [6], distinguishing between methods and methodology [7], the use of the appreciative inquiry methods [8], reflections on interdisciplinary research [9], and patient and public involvement in research in Bangladesh and Nepal [10].
This is the latest in a series of papers describing the strengths and weaknesses of applying specific research approaches. Other recent methods papers included two on positionality [2-3], a paper on interview methods [4], reflections on conducting participatory policy analysis in Nepal [5], some considerations about the selection of study localities in health research [6], distinguishing between methods and methodology [7], the use of the appreciative inquiry methods [8], reflections on interdisciplinary research [9], and patient and public involvement in research in Bangladesh and Nepal [10].
Whilst older methods papers published Faculty of Health & Social Sciences academics include topics such as focus group discussions, working with translators, conducting pilot studies, the Delphi Method, comparative studies, and qualitative interviews [11-22].
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMWH
References:
- Sharma, M.K., Khanal, S.P., van Teijlingen E. (2024) Most Significant Change Approach: A Guide to Assess the Programmatic Effects, International Journal of Qualitative Methods, https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/16094069241272143
- Gurr, H., Oliver, L., Harvey, O., Subedi, M., van Teijlingen, E. (2024) Positionality in Qualitative Research, Dhaulagiri Journal of Sociology & Anthropology 18(1): 48-54. https://doi.org/10.3126/dsaj.v18i01.67553
- Thapa, R., Regmi, P., van Teijlingen, E., Heaslip, V. (2023) Researching Dalits and health care: Considering positionality, Health Prospect 21(1): 6-8.
- Harvey, O., van Teijlingen, E., Parrish, M. (2024) Using a range of communication tools to interview a hard-to-reach population, Sociological Research Online 29(1): 221–232 https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/13607804221142212
- Sapkota, S., Rushton, S., van Teijlingen, E., Subedi, M., Balen, J., Gautam, S., Adhikary, P., Simkhada, P., Wasti,SP., Karki, JK., Panday, S., Karki, A., Rijal, B., Joshi, S., Basnet, S., Marahatta, SB. (2024) Participatory policy analysis in health policy and systems research: reflections from a study in Nepal. Health Research & Policy Systems, 22(7) https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-023-01092-5 .
- Wasti, S.P., van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P., Rushton, S., Balen, J., Subedi, M., Karki, J., Adhikary, P., Sapkota, S., Gautam, S., Marahatta, S., Panday, S., Bajracharya, B., Vaidya, A. for the Nepal Federal Health System Team (2023) Selection of Study Sites and Participants for Research into Nepal’s Federal Health System, WHO South-East Asia Journal of Public Health
- Harvey, O., Regmi, P.R., Mahato, P., Dhakal Adhikari, S., Dhital, R., van Teijlingen E. (2023) Methods or Methodology: Terms That Are Too Often Confused. Journal of Education & Research, 13(2): 94-105. https://doi.org/10.51474/jer.v13i2.716
- Arnold, R., Gordon, C., Way, S., Mahato, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2022) Why use Appreciative Inquiry? Lessons learned during COVID-19 in a UK maternity service, European Journal of Midwifery 6 (May): 1-7. https://doi.org/10.18332/ejm/147444
- Shanker, S., Wasti, S.P., Ireland, J., Regmi, P., Simkhada, P., van Teijlingen, E. (2021) The Interdisciplinary Team Not the Interdisciplinarist: Reflections on Interdisciplinary Research, Europasian Journal of Medical Sciences 3(2): 1-5. https://doi.org/10.46405/ejms.v3i2.317
- Simkhada, B., van Teijlingen, E., Nadeem, A., Green, S., Warren A. (2021) Importance of involving patients and public in health research in Bangladesh and Nepal. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 37: e10. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0266462320000811
- Kirkpatrick, P., van Teijlingen E. (2009) Lost in Translation: Reflecting on a Model to Reduce Translation and Interpretation Bias, The Open Nursing Journal, 3(8): 25-32 web address: bentham.org/open/tonursj/openaccess2.htm
- van Teijlingen E, Hundley, V. (2005) Pilot studies in family planning & reproductive health care, Journal of Family Planning & Reproductive Health Care 31(3): 219-21.
- van Teijlingen E, Pitchforth E. (2006) Focus Group Research Family Planning & Reproductive Health Care, Journal of Family Planning & Reproductive Health Care 32(1): 30-2
- van Teijlingen E, Pitchforth, E., Bishop, C., Russell, E.M. (2006) Delphi method and nominal group techniques in family planning and reproductive health research, Journal of Family Planning & Reproductive Health Care 32(4): 249-252.
- Pitchforth, E, van Teijlingen E, Ireland, J. (2007) Focusing the group, RCM Midwives Journal 10(2): 78-80.
- Pitchforth, E., van Teijlingen E. (2005) International Public Health Research involving interpreters: a case study approach from Bangladesh, BMC Public Health, 5: 71 Web address: http://www.biomedcentral.com/content/pdf/1471-2458-5-71.pdf
- Forrest Keenan, K., Teijlingen van, E., Pitchforth, E. (2005) Analysis of qualitative research data in family planning & reproductive health care, Journal of Family Planning & Reproductive Health Care 31(1): 40-43.
- Brindle S, Douglas, F, van Teijlingen E., Hundley V. (2005) Midwifery Research: Questionnaire surveys, RCM Midwives Journal 8 (4): 156-158.
- Douglas, F, van Teijlingen E, Brindle S, Hundley, V, Bruce, J., Torrance, N. (2005) Designing Questionnaires for Midwifery Research, RCM Midwives Journal 8: 212-215.
- van Teijlingen E Ireland, J. (2003) Research interviews in midwifery RCM Midwives Journal 6: 260-63. http://www.midwives.co.uk/default.asp?chid=439&editorial_id=13768
- van Teijlingen E, Sandall, J., Wrede, S., Benoit, C., DeVries, R., Bourgeault, I. (2003) Comparative studies in maternity care RCM Midwives Journal 6: 338-40.
- van Teijlingen E, Hundley, V. (2002) ‘The importance of pilot studies’ Nursing Standard 16(40): 33-36. Web: nursing-standard.co.uk/archives/vol16-40/pdfs/vol16w40p3336.pdf
 Profs. Vanora Hundley and Edwin van Teijlingen, both in BU’s Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) have published several methods papers [1-6] on the importance of (a) conducting pilot studies, but also (b) reporting on their outcomes and lessons learnt. It started more than two decades ago with lessons learnt from the Scottish Birth study [2]. Followed by a methods paper in a sociology journal [3], one in a midwifery journal [4] and one in a family planning journal [5]. The icing on the pudding was an encyclopedia entry in 2003 [6].
Profs. Vanora Hundley and Edwin van Teijlingen, both in BU’s Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) have published several methods papers [1-6] on the importance of (a) conducting pilot studies, but also (b) reporting on their outcomes and lessons learnt. It started more than two decades ago with lessons learnt from the Scottish Birth study [2]. Followed by a methods paper in a sociology journal [3], one in a midwifery journal [4] and one in a family planning journal [5]. The icing on the pudding was an encyclopedia entry in 2003 [6].





























 New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event
From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives: Reflections from the SPROUT Network Event REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease