Entrepreneurship often begins with a deceptively simple act: reaching out to someone you do not know.
During the first week of our MBA Technology Entrepreneurship unit at Bournemouth University, a final year engineering student entrepreneur, Atanas Burmov, spoke to the class about building his venture from scratch. He arrived in Bournemouth at 18 to study software engineering. Within months he had established a mathematics and programming society to create peer support for students navigating the demands of their degree. Soon afterwards, he began contacting academics, technologists and organisations—sometimes completely cold—seeking advice and collaboration for a technology idea he was developing.
At that stage he had no venture capital, no established network, and no formal ecosystem behind him. What he had instead was something more fundamental: the belief that he could learn, build, and navigate uncertainty. He simply started reaching out to people. Those early emails and conversations eventually became the foundations of the collaborations that now support the growth of his venture. But at the beginning, it was not about partnerships or strategic alliances. It was about initiative.
His story is simply an illustration which shows a much larger phenomenon in entrepreneurship research: the role of entrepreneurial self-efficacy in enabling individuals to act under conditions of uncertainty and constraint ( McGee et al., 2009; Zhao et al., 2005).
The concept of self-efficacy originates in Albert Bandura’s social cognitive theory. Bandura defines self-efficacy as an individual’s belief in their capability to organise and execute the actions required to manage prospective situations (Bandura, 1977; Bandura, 1997). In other words, it is not simply about possessing knowledge or skills. It is about believing that those capabilities can be applied effectively in uncertain circumstances. Entrepreneurship is inherently uncertain. New ventures rarely begin with stable structures, predictable markets or guaranteed resources. In such environments, internal judgements of capability become critically important. A substantial body of research shows that entrepreneurial self-efficacy is strongly associated with entrepreneurial intention, persistence and opportunity pursuit (Chen et al., 1998; Zhao et al., 2005; McGee et al., 2009).
Individuals who believe they can navigate uncertainty are more likely to act despite incomplete information. They are more willing to experiment, to approach new contacts, to persist after rejection and to mobilise resources creatively when conventional pathways are unavailable. This becomes particularly relevant when entrepreneurs begin under conditions of constraint. Many founders start without financial capital, established networks or institutional legitimacy. Research on entrepreneurial bricolage shows how entrepreneurs often respond by recombining the resources already available to them in creative ways (Baker & Nelson, 2005). Similarly, the theory of effectuation highlights how entrepreneurs begin with the means they already possess—who they are, what they know and whom they know—and gradually build ventures through partnerships and experimentation (Sarasvathy, 2001).
Technical expertise can reinforce this process. Founders with deep domain knowledge, particularly in technology-based ventures, often possess greater confidence in their ability to solve problems. This confidence can strengthen entrepreneurial self-efficacy and increase the likelihood that individuals will attempt to translate ideas into ventures (Marvel et al., 2016). Yet confidence does not emerge in isolation. Bandura himself emphasised that self-efficacy develops through interaction with social environments. Mastery experiences, encouragement from others, observing peers succeed and working within supportive communities all contribute to the strengthening of self-efficacy beliefs (Bandura, 1997).
This is one reason why institutional environments such as universities can play such an important role in the entrepreneurial journey. Universities increasingly operate as entrepreneurial institutions, supporting venture creation alongside their traditional roles in research and teaching (Etzkowitz, 2003; Guerrero et al., 2016). For students, universities offer more than academic instruction. They provide access to laboratories, intellectual property expertise, mentoring networks, entrepreneurship societies, careers services and communities of peers who are also experimenting with ideas. These infrastructures matter because they help transform tentative initiative into sustained entrepreneurial action. When students know that expertise, resources and encouragement exist around them, their willingness to act increases.
The role of place also deserves attention. Entrepreneurship discourse often focuses heavily on global innovation hubs such as London or Silicon Valley, where capital and talent are highly concentrated. These ecosystems undoubtedly provide significant advantages. Yet they also involve intense competition and high barriers to visibility for early-stage founders.
Research on entrepreneurial ecosystems suggests that smaller regions can offer different but equally important advantages. In regional contexts, social networks are often more visible and accessible, and relationships between ecosystem actors may form more quickly (Stam, 2015; Spigel, 2017). Studies of regional entrepreneurial networks show that such environments frequently display dense relational ties and higher levels of trust, which can lower barriers for new entrepreneurs seeking advice, introductions or collaboration (Granovetter, 1985; Feldman & Zoller, 2012). In these ecosystems, universities frequently function as anchor institutions. They concentrate knowledge, talent, infrastructure and legitimacy within a particular place, often acting as catalysts for regional innovation and venture creation (Goddard & Kempton, 2016).
For student entrepreneurs, this combination of place-based networks and institutional support can be powerful. Access to mentors, academics, laboratories and peer communities can enable ideas to move more quickly from concept to experimentation.
Returning to the story that opened this article, the venture did not begin with a fully formed ecosystem. It began with initiative: sending emails, asking questions and seeking conversations. Over time those conversations developed into collaborations that now support the growth of the business.
What began as individual initiative gradually evolved into a network. Entrepreneurship research often focuses on funding, scaling and investment. Yet the earliest stages of venture creation frequently occur long before these elements appear. They occur in moments that are almost invisible: an email written, a conversation initiated, a question asked despite uncertainty.
Self-efficacy plays a critical role in these moments. It allows individuals to act before legitimacy, capital or networks are fully in place. But sustaining entrepreneurial action requires more than individual belief. It requires environments that recognise initiative and respond to it. Universities, mentors, regional ecosystems and institutional infrastructures all contribute to creating contexts where entrepreneurial action becomes possible.
Sometimes the most important entrepreneurial resource is not capital or connections. It is the quiet confidence to begin.





References
Baker, T., & Nelson, R. (2005). Creating something from nothing: Resource construction through entrepreneurial bricolage. Administrative Science Quarterly, 50(3), 329–366. https://doi.org/10.2189/asqu.2005.50.3.329
Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioural change. Psychological Review, 84(2), 191–215. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.84.2.191
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York: W.H. Freeman.
Chen, C., Greene, P., & Crick, A. (1998). Does entrepreneurial self-efficacy distinguish entrepreneurs from managers? Journal of Business Venturing, 13(4), 295–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-9026(97)00029-3
Etzkowitz, H. (2003). Research groups as ‘quasi-firms’: The invention of the entrepreneurial university. Research Policy, 32(1), 109–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-7333(02)00009-4
Feldman, M., & Zoller, T. D. (2012). Dealmakers in Place: Social Capital Connections in Regional Entrepreneurial Economies. Regional Studies, 46(1), 23–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2011.607808
Goddard, J., & Kempton, L. (2016). The civic university: Universities in leadership and management of place. Available from https://www.ncl.ac.uk/mediav8/centre-for-urban-and-regional-development-studies/files/the-Civic-University.pdf
Granovetter, M. (1985). Economic action and social structure: The problem of embeddedness. American Journal of Sociology, 91(3), 481–510. https://doi.org/10.1086/228311
Guerrero, M., Urbano, D., & Fayolle, A. (2016). Entrepreneurial activity and regional competitiveness: Evidence from European entrepreneurial universities. Journal of Technology Transfer, 41, 105–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-014-9377-4
Marvel, M., Davis, J., & Sproul, C. (2016). Human capital and entrepreneurship research: A critical review. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 40(3), 599–626. https://doi.org/10.1111/etap.12136
McGee, J., Peterson, M., Mueller, S., & Sequeira, J. (2009). Entrepreneurial self-efficacy: Refining the measure. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 33(4), 965–988. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6520.2009.00304.x
Sarasvathy, S. (2001). Causation and effectuation: Toward a theoretical shift from economic inevitability to entrepreneurial contingency. Academy of Management Review, 26(2), 243–263. https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.2001.4378020
Spigel, B. (2017). The relational organization of entrepreneurial ecosystems. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 41(1), 49–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/etap.12167
Stam, E. (2015). Entrepreneurial ecosystems and regional policy: A sympathetic critique. European Planning Studies, 23(9), 1759–1769. https://doi.org/10.1080/09654313.2015.1061484
Zhao, H., Seibert, S., & Hills, G. (2005). The mediating role of self-efficacy in the development of entrepreneurial intentions. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(6), 1265–1272. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.90.6.1265
 On Monday 9th March Prof. Sujan Marahatta visited Bournmouth University (BU) to speak about ‘Strengthening BU-Nepal collaboration AND Nepal’s experience of competency-based health professional education’. Prof. Marahatta is the Director of the Medical Education Commission in Nepal overseeing the education of health professionals in 15 areas including Medicine, Physiotherapy, Nursing and Midwifery.
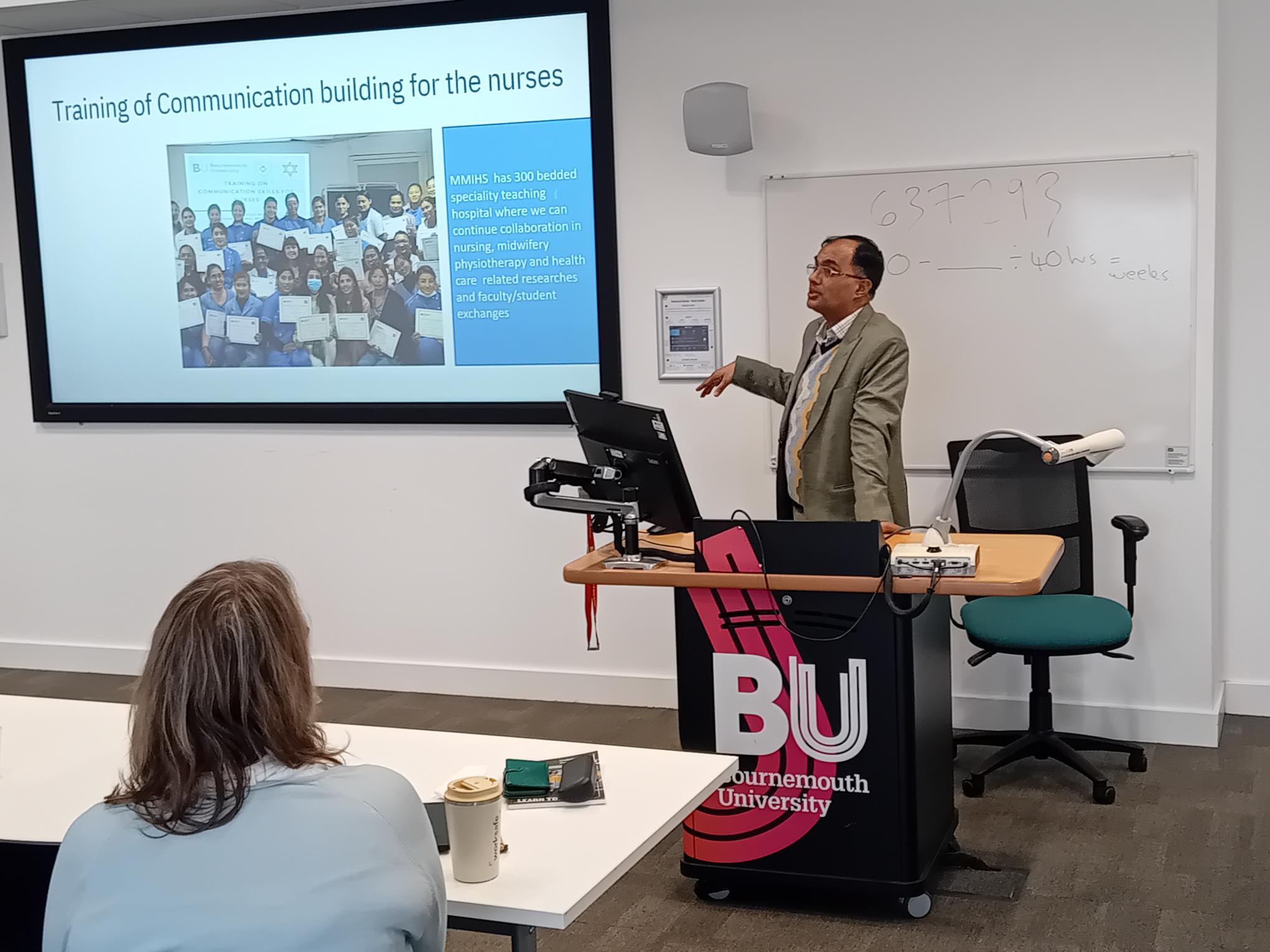
On Monday 9th March Prof. Sujan Marahatta visited Bournmouth University (BU) to speak about ‘Strengthening BU-Nepal collaboration AND Nepal’s experience of competency-based health professional education’. Prof. Marahatta is the Director of the Medical Education Commission in Nepal overseeing the education of health professionals in 15 areas including Medicine, Physiotherapy, Nursing and Midwifery.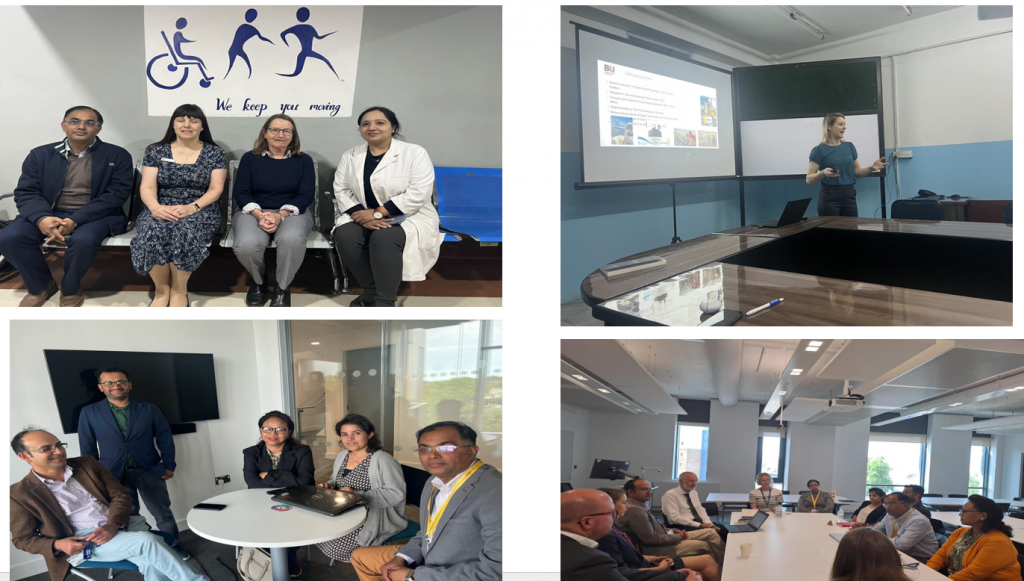  He spoke about long partnership between Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (MMIHS) and BU. This partnership is formalised in a Memoradum of Agreement (MoA) and over the years it has included joint research projects, staff-student exchanges (funded by ERASMUS+ and Turing scheme) and offering guest lectures at each others institutions.
He spoke about long partnership between Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (MMIHS) and BU. This partnership is formalised in a Memoradum of Agreement (MoA) and over the years it has included joint research projects, staff-student exchanges (funded by ERASMUS+ and Turing scheme) and offering guest lectures at each others institutions.
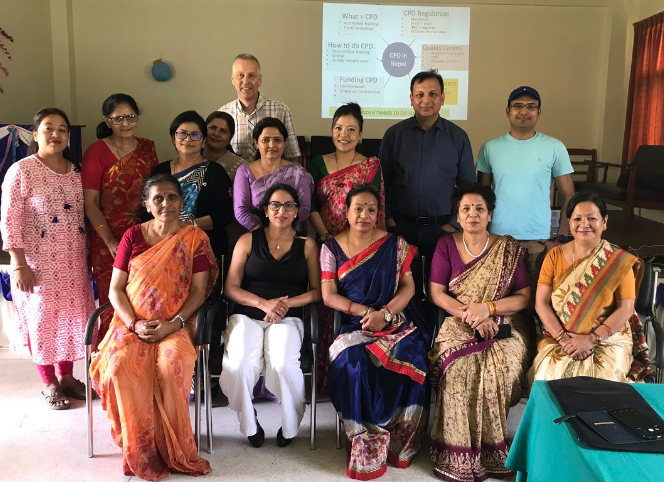

















































 Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration
Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration 3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease