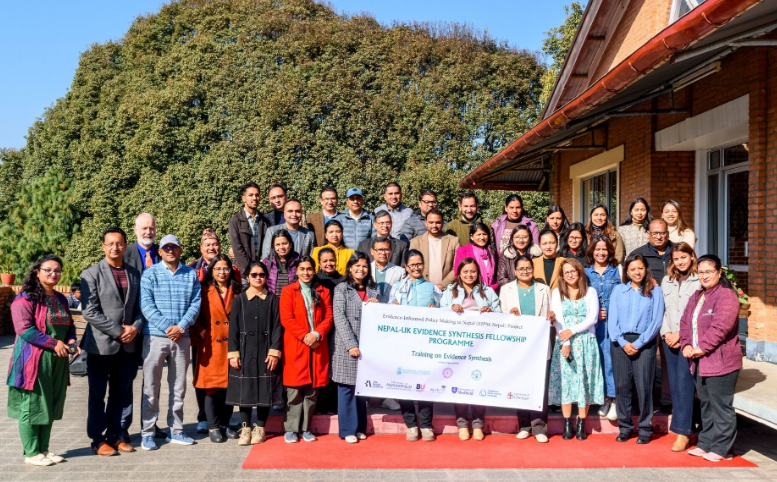
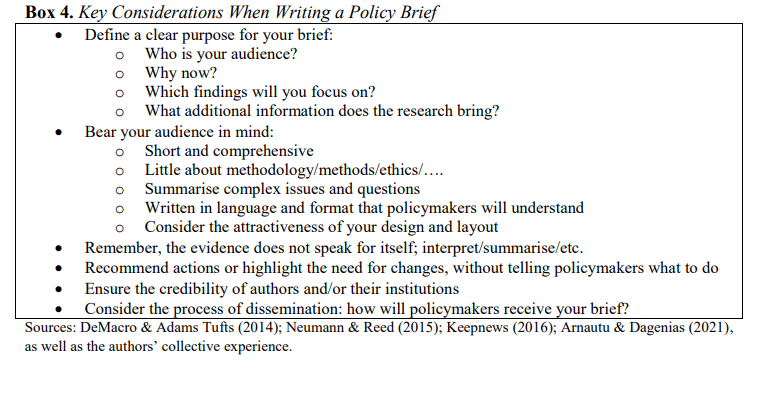
 Last week we opened the Evidence Synthesis Centre in the School of Medical Sciences at Kathmandu University in Nepal. The centre is part of a wider initiative is funded by The British Academy and supported in the field by Green Tara Nepal. Earlier parts of this initiative included online workshop on systematic reviewing and evidence synthesis as well as face-to-face training in Nepal late last year. The project involved Bournemouth University’s Dr. Pramod Regmi and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen both in the Faculty of Health, Environment & Medical Sciences.
Last week we opened the Evidence Synthesis Centre in the School of Medical Sciences at Kathmandu University in Nepal. The centre is part of a wider initiative is funded by The British Academy and supported in the field by Green Tara Nepal. Earlier parts of this initiative included online workshop on systematic reviewing and evidence synthesis as well as face-to-face training in Nepal late last year. The project involved Bournemouth University’s Dr. Pramod Regmi and Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen both in the Faculty of Health, Environment & Medical Sciences. 
This capacity-building project is led by Prof. Padam Simkhada from the University of Huddersfield and takes place at Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences (KUSMS). This new Fellowship scheme is an international collaboration led by the University of Huddersfield in the UK, in close collaboration with Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences (in Nepal), the Nepal Health Research Council, and several UK universities: Bournemouth University, the University of Sheffield, Canterbury Christ Church University, Keele University and the University of Chester. The Evidence Synthesis Centre and The British Academy grant grew out of an editorial written four years ago and published in the Journal of the Nepal Health Research Council [1]. The wider British Academy funded project on strengthening evidence synthesis for health policy-making in Nepal has been described in two recent publications [2-3].
References:
-
Simkhada, P., Dhimal, M., van Teijlingen, E., Gyanwali, P. (2022) Nepal Urgently Needs a National Evidence Synthesis Centre, Journal of Nepal Health Research Council, 20 (3): i-ii.
-
Simkhada, P., Vaidya, A., Regmi, P. P., Paudyal, P., van Teijlingen, E., Dhimal, M., Kiorala, B., Shrestha, A., Simkhada, B. (2025). Strengthening Evidence Synthesis for Health Policymaking in Nepal: A New Fellowship Initiative. Nepal Journal of Epidemiology, 15(2), 1379–1380. https://doi.org/10.3126/nje.v15i2.88516
- Vaidya, A., Simkhada, P., Silwal, R. C., Paudyal, P., Dhimal, M., Simkhada, B., van Teijlingen, E. (2025). Progress of the Unique Fellowship in Health Research Evidence Synthesis in Nepal. Nepal Journal of Epidemiology, 15(4), 1397–1398. https://doi.org/10.3126/nje.v15i4.88535


































 Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration
Prof Marahatta promoting BU-Nepal collaboration 3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm
3C Online Social: Research Culture, Community & Can you Guess Who? Thursday 26 March 1-2pm Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
Explore our work, meet our partners, and find out how you can collaborate with us by clicking here! MIHERC is led by Sheffield Hallam University, with Bournemouth University as a key partner and the important funding coming from NIHR (National Institute for Health and Care Research) Maternity Challenge Initiative. The BU key academics are: Huseyin Dogan, Vanora Hundley, Edwin van Teijlingen, and Deniz Çetinkaya. Please share with all who may be interested.