Professor Andy Phippen answers some key questions for The Conversation about giving children mobile devices, based on his research into young people and the internet…
When to give your child their first mobile phone – and how to keep them safe

Andy Phippen, Bournemouth University
I spend my career researching young people and the internet: what they do online, what they think about it and how their views differ to those of their parents.
I often get questions from parents about their children’s internet use. One of the most common is when to get their child a mobile phone, as well as how to keep them safe when they have one. Here are my answers to some key questions.
How old should my child be when they get their first phone?
I’m afraid I often disappoint parents in my answer to this question by not giving them a definite number. But the key here is what your child is going to use the phone for – and when might be suitable for that individual child.
According to a 2023 report by UK communications regulator Ofcom, 20% of three year olds now own a mobile phone. But this phone may just be used for taking pictures, playing simple games and supervised video calls with family.
The more pertinent question is when children should have their own fully-connected phone, which they can use unsupervised to contact others online.
When a child is primary school age, it’s highly likely that they will be used to adult supervision in most aspects of their life. They will either be at school, at home, with friends and trusted adults or with other family members.
Their need to contact a distant adult may not be that great – but you will want to think about what the specific needs of your own child might be.
Typically the transition from primary school to secondary is when children might be more distant from home, or be involved in school activities or socialising with friends where being able to contact home becomes more important. I have spoken to plenty of young people who talk about starting secondary school as the point where they first had their own phone.
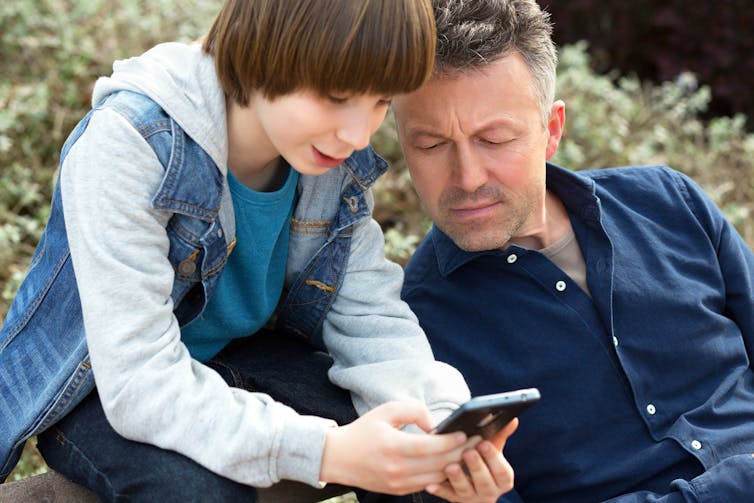
How do I make sure they use a phone safely?
First of all, it’s important that if your child is going online – at whatever age and regardless of the device they’re using – you have a conversation with them about online safety.
Parents have a role to play in educating their children and making them aware of the risks that come with being online, as well as being mindful that most online experiences are not harmful.
I have carried out extensive research with young people on online harms. As part of this research, I and colleagues developed a number of resources for parents, put together with the help of over 1,000 young people.
What these young people say the most is they want to know who to turn to when they need help. They want to be confident they will receive support, not a telling off or confiscation of their phone. This means that a key first step is to reassure your child that they can come to you with any problems they encounter and you will help them without judgment.
It’s also important to discuss with your child what they can and can’t do with their device. This could mean, for instance, setting ground rules about which apps they can have installed on their phone, and when they should stop using their phone at the end of the day.
You should also explore the privacy settings for the apps that your child uses, in order to ensure that they cannot be contacted by strangers or access inappropriate content. The NSPCC has resources for parents on how to use privacy settings.
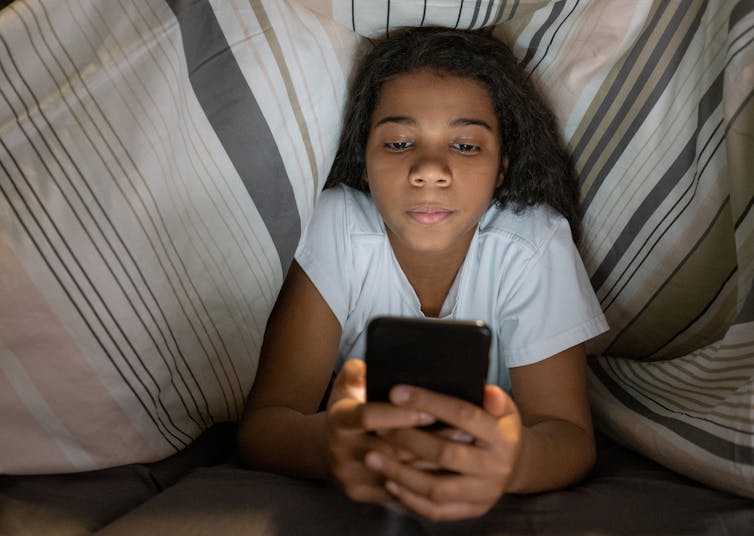
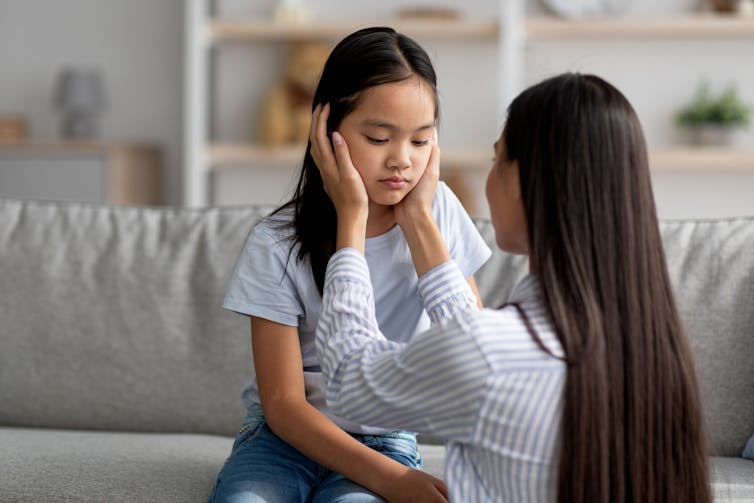
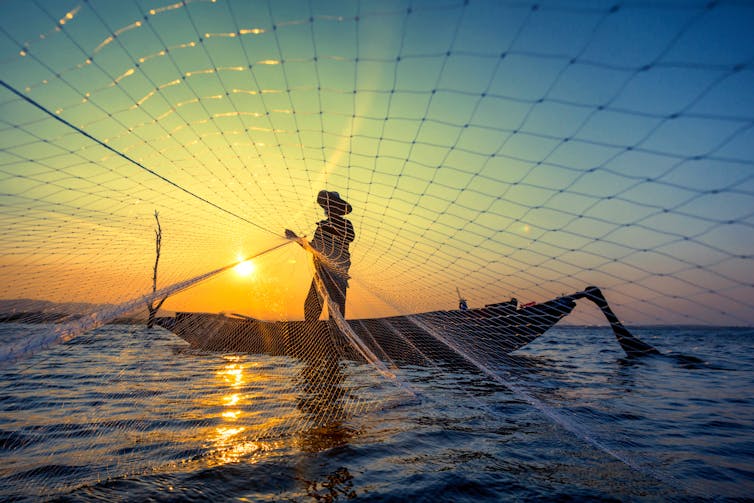
Should I check my child’s phone?
Sometimes parents ask me about whether they should be able to check a child’s device – either by physically looking at the phone or by using “safetytech”, software on another device that can access the communications on the child’s phone.

Khorzhevska/Shutterstock
I believe it’s important that this is also something you discuss with your child. Trust is important to ensure that your child comes to you with any online issues, so if you want to monitor their phone, talk to them about it rather than doing so covertly.
It seems reasonable parental supervision to be accessing a child’s device when they are of primary age, in the same way a parent would check with another child’s parent before agreeing to let them visit their home.
However, as your child gets older, they might not want their parent to see all of their messages and online interactions. The UN Convention on the Rights of the Child clearly states that a child does have a right to privacy.
Should I track my child’s location through their phone?
I have spoken to some families that track each other’s devices in an open and transparent manner, and this is a decision for the family. However, I have also spoken to children who find it very creepy that a teenage friend is tracked by their parents.
The question here is whether parents are reassuring themselves that their child is safe – or whether they want to know what they are doing without them knowing. I had a particularly memorable conversation with someone who told me their friend was extremely upset because their daughter had changed device and so they could no longer track her. When I asked how old the daughter was, they said she was 22.
It’s also worth considering whether tech like this actually provides false reassurance. It may allow parents to know where their child is, but not necessarily whether they are safe.
As with monitoring a child’s phone, it is worth reflecting upon whether a surveillance approach creates the ideal conditions for them to come to you with problems, or whether this is more likely to be fostered by open conversations and an environment of mutual trust.![]()
Andy Phippen, Professor of IT Ethics and Digital Rights, Bournemouth University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.







 The award demonstrates BU’s commitment to aligning process and practice to the
The award demonstrates BU’s commitment to aligning process and practice to the 







 The initiative brings together four universities:
The initiative brings together four universities:  Session 1, led by
Session 1, led by  Session 2, led by
Session 2, led by  Session 3, presented by
Session 3, presented by  The closing session, led by the
The closing session, led by the 











 Read and sign up to BU’s Policy Influence Digest
Read and sign up to BU’s Policy Influence Digest Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally
Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant
BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant New COVID-19 publication
New COVID-19 publication MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024 Horizon Europe News – December 2023
Horizon Europe News – December 2023