This week the Nepal Federal Health System Team published its latest paper the international journal Health Research Policy & Systems [1]. This Open Access paper ‘Overcoming the challenges facing Nepal’s health system during federalisation: an analysis of health system building blocks‘ reports on two separate methods: interviews and participatory policy analysis workshops, to offer an in-depth understanding of stakeholders’ practical learning, experiences, and opinions. Participants included policymakers, health service providers, local elected members, and other local stakeholders. All interviews were audio-recorded, transcribed, translated into English, and analysed thematically using the six WHO (World Health Organization) health system building blocks [2] as its theoretical framework. 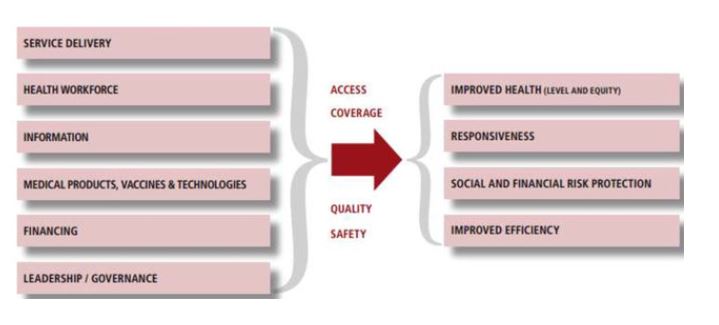
Wasti et al. found that participants noted both opportunities and challenges around each building block. Identified opportunities were: (a) tailored local health policies and plans, (b) improved health governance at the municipality level, (c) improved health infrastructure and service capacity, (d) improved outreach services, (e) increased resources (health budgets, staffing, and supplies), and (f) improved real-time data reporting from health facilities. At the same time, several challenges were identified including: (a) poor coordination between the tiers of government, (b) delayed release of funds, (c) maldistribution of staff, (d) problems over procurement, and (e) limited monitoring and supervision of the quality of service delivery and data reporting.
The paper concludes that since federalisation, Nepal’s health system performance is improving, although much remains to be accomplished. For Nepal to succeed in its federalisation process, understanding the challenges and opportunities is vital to improving each level of the health system in terms of (a) leadership and governance, (b) service delivery, (c) health financing, (d) health workforce, (e) access to essential medicines and technologies and (f) health information system.
This publication is the fourth one originating from our Nepal Federal Health System Project, our major collaborative project examining the consequences for the health system of Nepal’s move to a federal government structure [2-5]. This is a joint project (2020-2024) led by the University of Sheffield and in collaboration with Bournemouth University, the University of Huddersfield, Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences (MMIHS) and PHASE Nepal. This longitudinal interdisciplinary study is funded by the UK Health Systems Research Initiative [Grant ref. MR/T023554/1].
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH)
References:
- Wasti, S.P., van Teijlingen, E.,Rushton, S., Subedi, M., Simkhada, P., Balen, J. for the Nepal Federal Health System Team (2023) Overcoming the Challenges Facing Nepal’s Health System During Federalisation: An Analysis of Health System Building Blocks, Health Research Policy & Systems 21(117) https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-023-01033-2
- World Health Organization (2007) Everybody’s business: strengthening health systems to improve health outcomes. WHO’s Framework for Action. Geneva: World Health Organization.
- Sapkota, S., Panday, S., Wasti, S.P., Lee, A., Balen, J., van Teijlingen, E., Rushton, S., Subedi, M., Gautam, S., Karki., J., Adhikary, P., Marahatta, S., Simkhada, P., for the Nepal Federal Health System Team (2022) Health System Strengthening: The Role of Public Health in Federal Nepal, Journal of the Nepal Public Health Association 7(1):36-42.
- Adhikary, P., Balen, J., Gautam, S., Ghimire, S., Karki, J., Lee, A.C.K., Marahatta, S.B., Panday, S., Pohl, G., Rushton, S., Sapkota, S., Simkhada, P.P., Subedi, M., van Teijlingen, E. for the Nepal Federal Health System team (2020) The COVID-19 pandemic in Nepal: Emerging evidence on the effectiveness of action by, and cooperation between, different levels of government in a federal system, Journal of Karnali Academy of Health Sciences 3 (3): 1-11.
- Rushton, S., Pandey, S., van Teijlingen, E., Subedi, M., Balen, J., Karki, J., Simkhada, P. on behalf of the Nepal Federal Health System Team (2021) An Investigation into the Impact of Decentralization on the Health System of Nepal. Journal of Manmohan Memorial Institute of Health Sciences, 7(1): 3–14. https://doi.org/10.3126/jmmihs.v7i1.43146
 The paper in the Journal of Asian Midwives highlights that during the COVID-19 pandemic, OOHBs were a way to avoid Public Health regulations and lock-down constraints, and to guarantee the presence of a partner at the birth. The authors argue, however, that the pandemic is not at the origin of the trend, but more of a catalyst. Advocacy groups, maternity-service users’ groups, the media, and midwifery organisations in several high-income countries have in recent years underlined the growing criticism of existing maternity care and midwifery services and a long-term shortage of midwives. This is in addition to a longstanding trend in the United Kingdom of closing community-based hospitals, including small, free-standing midwife-led units.
The paper in the Journal of Asian Midwives highlights that during the COVID-19 pandemic, OOHBs were a way to avoid Public Health regulations and lock-down constraints, and to guarantee the presence of a partner at the birth. The authors argue, however, that the pandemic is not at the origin of the trend, but more of a catalyst. Advocacy groups, maternity-service users’ groups, the media, and midwifery organisations in several high-income countries have in recent years underlined the growing criticism of existing maternity care and midwifery services and a long-term shortage of midwives. This is in addition to a longstanding trend in the United Kingdom of closing community-based hospitals, including small, free-standing midwife-led units.




 Today we received notice that our paper ‘The impacts of decentralisation on health systems: a systematic review of reviews’ has been accepted by the international journal BMJ Global Health. [1] This review of reviews was produced as part of the Nepal Federal Health System Project, examining the consequences for the health system of Nepal’s move to a federal government structure. This is a joint project (2020-2024) led by the University of Sheffield and in collaboration with Bournemouth University, the University of Huddersfield,
Today we received notice that our paper ‘The impacts of decentralisation on health systems: a systematic review of reviews’ has been accepted by the international journal BMJ Global Health. [1] This review of reviews was produced as part of the Nepal Federal Health System Project, examining the consequences for the health system of Nepal’s move to a federal government structure. This is a joint project (2020-2024) led by the University of Sheffield and in collaboration with Bournemouth University, the University of Huddersfield, 






 Professor Edwin van Teijlingen in the Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) has been invited to speak at Royal Holloway, University of London, about writing an academic paper. His public lecture will be coming Tuesday lunch time in the appropriately named ‘Bourne Lecture Theatre’ at Royal Holloway. Prof. van Teijlingen, together with several Bournemouth University (BU) colleagues, has published a text book [1], several book chapters [2-18] and a large number of papers [19-38] about a wide-range of aspects of academic writing and publishing. One of former BU academics, who co-authored a book chapter [10], and two papers [21, 25], is Dr. Preeti Mahato. She is Lecturer in Global Health at Royal Holloway as well as Visiting Faculty in BU’s Faculty of Health & Social Sciences.
Professor Edwin van Teijlingen in the Centre for Midwifery & Women’s Health (CMWH) has been invited to speak at Royal Holloway, University of London, about writing an academic paper. His public lecture will be coming Tuesday lunch time in the appropriately named ‘Bourne Lecture Theatre’ at Royal Holloway. Prof. van Teijlingen, together with several Bournemouth University (BU) colleagues, has published a text book [1], several book chapters [2-18] and a large number of papers [19-38] about a wide-range of aspects of academic writing and publishing. One of former BU academics, who co-authored a book chapter [10], and two papers [21, 25], is Dr. Preeti Mahato. She is Lecturer in Global Health at Royal Holloway as well as Visiting Faculty in BU’s Faculty of Health & Social Sciences.

























 Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation
Fourth INRC Symposium: From Clinical Applications to Neuro-Inspired Computation ESRC Festival of Social Science 2025 – Reflecting back and looking ahead to 2026
ESRC Festival of Social Science 2025 – Reflecting back and looking ahead to 2026 3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Cookies – Tuesday 13 January 10-11am
3C Event: Research Culture, Community & Cookies – Tuesday 13 January 10-11am Dr. Chloe Casey on Sky News
Dr. Chloe Casey on Sky News Final Bournemouth University publication of 2025
Final Bournemouth University publication of 2025 ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published
Horizon Europe Work Programme 2025 Published Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease