Hardly ever does a research trip go smoothly and completely to plan. Our latest trip to Nepal was no different. It started really with a delay, I had the money for a flight in the spring, but I really could not find the time to leave Bournemouth University for a three-week trip.
 The first little hiccup of this summer’s fieldwork trip, during the monsoon, occurred on arrival at Kathmandu Airport on 23 July. I normally bring three bottles of whisky as a present for my PhD former students and fellow researchers in Nepal. These are bought during my stop-over in the Middle East and this always worked well until this year. This time I was stopped on arrival by a very apologetic customs officer who informed me that the rules for bringing alcohol into Nepal had changed since the beginning of this year and that I could only bring in one bottle. I received a lovely certificate for the two bottles I had to leave behind (see photo).
The first little hiccup of this summer’s fieldwork trip, during the monsoon, occurred on arrival at Kathmandu Airport on 23 July. I normally bring three bottles of whisky as a present for my PhD former students and fellow researchers in Nepal. These are bought during my stop-over in the Middle East and this always worked well until this year. This time I was stopped on arrival by a very apologetic customs officer who informed me that the rules for bringing alcohol into Nepal had changed since the beginning of this year and that I could only bring in one bottle. I received a lovely certificate for the two bottles I had to leave behind (see photo).
The second little hiccup was that one of the three research dissemination meetings we had hoped to organise in Kathmandu could not take place. Unfortunately, the organisation we had been collaborating with had not managed to finalise the research report on time. We had also hoped to meet up with staff at Social Science Baha. We have submitted the final draft manuscript for our next book to them and wanted to discuss progress, but the director was unfortunately out of the country.
Further little hiccups were more mundane, such as the electricity going off twice (for perhaps five minutes each time) during one of my teaching sessions on Introduction to Qualitative Research. This meant trying to start a slow laptop as back-up, whilst restarting a still warm overhead projector, etc. But the Nepali audience, being used this, took it all in its stride. And I’ll spare you the details of my day of diarrhoea (either weather or food-hygiene related, probably both).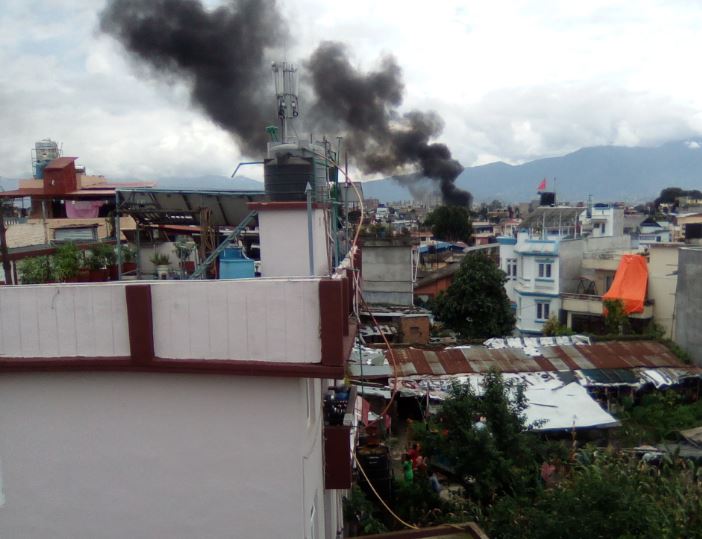
The biggest problem this time was much more unexpected. Two days ago there was a big fire not too far from in Kathmandu (see picture taken from my bed room). A little later after the photo was taken, we got stuck in traffic because several roads were blocked around the burning building on our way to Tribhuvan University. Later I found out that the fire had destroyed the head office of a national internet provider, which is also the provider for the charity Green Tara Nepal, which we are working with. So I have had hardly any internet for a few days which is really difficult for a 21st century academic.

However, this fieldwork trip has been very successful to date. We have co-organised two well attended meetings, one on the introduction of CPD in Nursing led by Dr. Bibha Simkhada (see previous BU blog here) and one Consultation meeting on migration and health research led by Dr. Pramod Regmi, both run in collaboration with BU’s Visiting Professor Padam Simkhada. Moreover, I was invited to speak at an international sociology conference last Sunday here in Kathmandu which I did not even know was going on till two days before. I had to pleasure of meeting our midwifery friends in Nepal as well as a representative of the German Aid Agency GIZ. We managed to have dinner in Kathmandu with loads of colleagues and friends who work with BU in one form or another, including one of my recent co-authors from the University of Tokyo who happened to be in Nepal.
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMMPH




































 Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop
Beyond Academia: Exploring Career Options for Early Career Researchers – Online Workshop UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching
UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme: Deadline Approaching SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives
SPROUT: From Sustainable Research to Sustainable Research Lives BRIAN upgrade and new look
BRIAN upgrade and new look Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh
Seeing the fruits of your labour in Bangladesh ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease