There’s something for everyone in this final policy update of 2022. Although things have calmed down a bit as we approach the festive period there is still lots of news. We’ve kept matters as light as possible for you with links to more information for those that wish to read more. Here’s wishing you all a relaxing break, happy Christmas and a good start to the New Year.
Parliamentary News
Parliamentary session to continue: It’s been confirmed that the King’s Speech (and therefore, the State Opening of Parliament in 2023) will be delayed allowing more time for the Government to pass its legislative agenda. This is because when the Parliamentary session is closed any outstanding legislation drops away automatically unless a carry-over motion is passed to enable it to continue. (You’ll recall the Freedom of Speech (HE) Bill was carried over from the previous session because the Government is determined to get it on the statute books). The monarch then re-opens parliament with a speech setting out the Government’s legislative plans for the coming months. The Government indicated they plan to dissolve Parliament in Autumn 2023 meaning the new parliamentary session may begin in November 2023. The Prime Minister’s spokesperson said: “The programme is very full and to make sure we have the time we need to get through the packed agenda the Prime Minister wants to deliver, the session will run until autumn 2023.” A cynic might mention it’s also getting awfully close to the next general election. Both Houses will return from recess on the 9 January.
HE priorities: Education Select Committee session: HE Minister Robert Halfon was examined by the Education select committee and HE received a brief mention. Miriam Cates MP queried whether HE funded provided value for money considering the lower funding settlement received by FE institutions. Halfon stated he welcomed the impact and successes of both sectors and suggested that he wanted the sector to focus on social justice and bringing the most disadvantaged the opportunities to get enter higher or further education. This is a personal agenda for Halfon and he has been very open about his interest in social justice, social mobility and accessibility/performance of HE institutions in supporting disadvantage. Cates was unimpressed with Halfon’s response and pressed for a full review of joined up education post-16, not just 16 to 18, stating that the investment in HE did pay off in terms of jobs and prosperity.
Spring budget announced: Chancellor Jeremy Hunt will deliver the Spring Budget on 15 March 2023. This fulfils the obligation to produce two forecasts in a financial year (required by law).
HERA – the Christmas edition
The DfE published their policy paper assessing the Higher Education and Research Act 2017: post-legislative scrutiny. HERA was a major change to HE operations and was pushed through the Commons (against substantial Lords backlash) by Jo Johnson in 2017. It established the OfS and UKRI in their current form.
Although the paper seems to have come out of the blue the DfE are expected to do this for each major piece of legislation within their remit after the first 5 years. As the paper is written for the Education select committee we may well see a new inquiry in this field in the new year.
Even if you’re not interested in the paper per se it has an interesting synopsis of the sector from page 8 onwards. And what is a Christmas edition of anything without a review of the major occurrences over the last (5) years? Here are the ‘high’lights we’ve contended with:
- Left EU
- Global pandemic and all that implied: changed social and economic environment and remote/hybrid/blended learning
- New regulatory and funding system
- Revolving door for ministers each with their own stamp on specific priorities (printing and accommodation costs, free speech, antisemitism, university advertising, post qualification admissions, the role of universities in school performance
- All the big things: disadvantage, quality and outcomes, Lifelong Loan Entitlements, degree apprenticeships, T levels, broader structural HE reform. Cue the adverts… phew!
On the paper Wonkhe say: It is meant to properly reflect on the act – what has worked, what hasn’t, and what needs to change, with a view to making sure we have the best law we can. The publication we got made a start – and there are some eyebrow-raising lines in there about the way the underlying assumptions and government policy have shifted, often quite radically. They have a blog for those who enjoy Wonkhe’s analyses: David Kernohan wonders if we really have the system that was asked for.
HEPI have a related blog: Have the Higher Education & Research Act and the Office for Students delivered for new and ‘challenger’ providers?
Regulatory & Free Speech
HE (Freedom of Speech) Bill
The HE (Freedom of Speech) Bill received its third reading in the House of Lords. The Lords made more amendments and have passed it back to the House of Commons. So we are now in the final stage of ‘ping pong’ where the Commons and Lords tussle over the ultimate wording before the Bill passes to the King for Royal Assent.
The Third Reading was a calm affair but the Lords didn’t roll over. Minister for the School System and Student Finance, Baroness Barran, stated she was pleased to have introduced a definition of “freedom of speech” to the Bill and that this was one of the many important clarifications as a result of their discussions in the House (during Report Stage). She also confirmed they had avoided inadvertently giving alumni the same protections as current students and had clarified that the new power given to the OfS to give guidance on supporting freedom of speech was not related to the duty on higher education providers and their constituent colleges to promote the importance of freedom of speech and academic freedom. She recognised as a breakthrough the banning of non-disclosure agreements in cases of sexual misconduct, abuse or harassment, or other forms of bullying. However, the proposed right to bring a civil claim in the courts against universities remains a big bone of contention. The Peers voted to remove it during the Report Stage and Baroness Barran said the Government would “reflect on this verdict and the arguments advanced to support it very carefully indeed.”
Lord Wallace spoke about the appointment of the new OfS free speech director. He asked the Government to “take particular care in finding a candidate for that position who will be accepted—possibly even welcomed—by the sector he or she sets out to regulate.” This reminds us of the controversy of partisan appointments that dogged Boris Johnson’s premiership.
Lord Wallace also drew attention to the outstanding question of the degree of overlap between this Bill, the recent National Security and Investment Act and the current National Security Bill, all of which imposed new duties and reporting requirements on universities. This has still not been fully resolved.
Baroness Thornton, Shadow Equalities Spokesperson, said “the jury it still out” on whether the Bill was necessary at all, but she was confident the legislation was being sent back to the Commons in an improved state. She drew attention to other outstanding matters, such as the role of the students’ unions. She also agreed with concerns around the risk of duplicating security regulations, and the risk that the Bill might pose to the business community, the commercial relations and the trading futures of universities.
Baroness Fox of Buckley (Non-Affiliated) said she hoped the Commons would “restore some version of Clause 4 and material remedies for victims of cancel culture on campus”.
OfS Annual Review: The OfS published its annual review. In her commentary of the report, OfS Chief Executive Susan Lapworth, sets out the key OfS priorities for 2023 including how tackling poor quality provision, ensuring students from all backgrounds are able to enter higher education and succeed in their studies, and protecting freedom of speech on campus are the key priorities for the OfS in 2023.
Parliamentary Questions: Regulatory
Matt Western (Shadow Universities Minister) asked some interesting questions regarding OfS funding:
In response to a parliamentary question Robert Halfon (Universities Minister) confirmed that the department’s priorities for higher education are consistent with those set out in guidance to the Office for Students (OfS) earlier this year. This includes a continued focus on delivering the government’s skills mission, driving up quality and ensuring equality of opportunity and real social mobility for students. The Government will only issue the OfS with new guidance for the current financial year if new issues or priorities emerge.
Matt Western also asked: whether a review of the potential changes required to the admissions system for HE course in advance of the delivery of the Lifelong Learning Entitlement (2024/25) has been conducted. Robert Halfon responded:
- To support the design and delivery of the Lifelong Loan Entitlement (LLE) from 2025, the department will continue to engage with sector bodies across both further education and higher education, as well as the Student Loans Company and regulatory bodies.
- On admissions, the department is continuing to work with UCAS and sector bodies to improve transparency, reduce the use of unconditional offers, and reform the personal statement to improve fairness for applicants of all backgrounds.
- The LLE consultation and other ongoing engagements are an important part of delivering a transformation of student finance. The department is carefully considering the contributions and will publish a response in due course.
Research
Pro-innovation regulation
The Treasury published a policy paper: Pro-Innovation Regulation of Technologies Project: Terms of Reference which announces a review considering how to regulate emerging technologies.
Pro-innovation regulation focuses on ensuring that we can safely and ethically accelerate the development, testing, route to market and uptake of new technology products. It should give confidence to innovators. This is key to making the UK an attractive destination for R&D projects, manufacturing and investment, and ensuring we can realise the economic and social benefits of new technologies as quickly as possible.
The Treasury also announced the appointment of five industry experts to help accelerate the development and deployment of emerging technologies in the following key UK growth sectors:
- digital technology
- green industries
- life sciences
- advanced manufacturing
- creative industries.
Experts will collaborate with industry and Sir Patrick Vallance to advise on new rules that use regulatory freedom to promote innovation. The aim of the review is to establish the UK as the best regulated economy ensuring that industry and investors have the certainty needed to drive innovation, investment and growth through anticipating new developments in emerging technologies. The experts are:
Matt Clifford, Chair of the new Advanced Research and Invention Agency (ARIA), and Priya Lakhani OBE, a member of the AI Council, have been appointed to support work to harness new digital technology such as artificial intelligence.
Sir John Bell, sits on Genomics England’s board of directors, and Camilla Fleetcroft, Eclevar UK’s Vice-President of Clinical and Regulatory Affairs, will work on cultivating the life sciences sector and help drive the next generation of discoveries, such as delivering genomics-enabled clinical trials.
Jane Toogood, Chief Executive of Catalyst Technologies at Johnson Matthey, will take forward work on building green industries like hydrogen and battery development in the UK.
Future Research Assessment Programme
UKRI/Research England published three reports on the Future Research Assessment Programme (FRAP). Taken together the reports speak out against a fully metricised system for the next REF but do suggest ways in which AI might support low risk areas of the exercise. The reports are:
- Harnessing the metric tide: indicators, infrastructures and priorities for responsible research assessment in the UK
- Responsible use of technology in research assessment
- REF outputs analysis: maximising the use of REF data
Quick news:
Horizon Europe extension: The Government announced an extension to the support provided to UK Horizon Europe applicants, originally launched in November 2021. The extension will ensure that eligible, successful UK applicants will continue to be guaranteed funding. The guarantee will be in place to cover all Horizon Europe calls that close on or before 31 March 2023. Eligible, successful applicants to Horizon Europe will receive the full value of their funding at their UK host institution for the lifetime of their grant. Successful awardees do not need to leave the UK to receive this funding, which will provide reassurance for future collaborations, and support UK researchers whether association is confirmed, or otherwise.
Science Minister, George Freeman, has been busy recently:
Wonkhe blog: The International Science Partnerships Fund is out, and James Coe thinks it has implications for UK research post Horizon.
The Lords Science and Technology Committee wrote to the Minister for Science, Research and Innovation George Freeman with the findings of its inquiry into people and skills in UK STEM. And THE has a blog on the topic: Academic careers: Teetering progress: A House of Lords committee has warned that the precarity of academic careers is exacerbating the UK’s growing skills gap in STEM.
HEPI blog: Research Leadership Matters: Agility, Alignment, Ambition
Graduate outcomes and employment
Sir John Holman, Independent Strategic Adviser on Careers Guidance wrote to DfE and DWP Minister regarding England’s careers guidance system.The letter summarises his recommendations for the future of the careers guidance system. It draws upon 18 months’ of consultation and conversations with careers practitioners and sector representatives, employers, schools, colleges, local bodies and a range of other interested parties, as well as a review of available evidence from the DfE, the Department for Work and Pensions (DWP) and the wider sector. You can read Holman’s recommendations (9 Strategic Principles) here. It’s worth a read, put it on your January list! HE and Skills Minister Robert Halfon welcomed the recommendations and stated he will consider them carefully – and that the Department will publish more information on future plans for the careers guidance system “in due course”.
Graduate employment: A catch up on the news that graduate employers aren’t focussed on degree outcome grade. The Times broke the story. Quickly followed up by Research Professional: The Times reports that fewer than half of graduate employers asked recruits for a 2:1 this year, according to a report by the Institute of Student Employers. And by Wonkhe: For the first time, less than half of graduate employers require a 2:1, new findings from the Institute for Student Employers suggest. The data from its 2022 student recruitment survey – drawn from 168 responses covering 32,110 hires, with larger organisations somewhat overrepresented – saw only 48% of responding employers having such a stipulation for graduate roles, down from 57% in 2021.
Data: The DfE released a new type of LEO data dashboard (and a report) looking at the earnings of individuals post GCSE over a 15 year period. Socioeconomic, demographic and education factors are within the data providing a granular picture. It isn’t directly comparable with the Graduate Outcomes data the HE sector routinely uses as there are small methodological differences, not least the inclusion of non-graduates. The box on page 23 explains the differences. However, it provides a comparator for graduate and non-graduates of the same age (rather than mixed ages with all of the same graduation cohort). For the data buffs page 22 onwards explains the graduate/non-graduate comparators re: the value of a degree.
Key points:
- People have diverse employment pathways in their 15 years. Taking into account the 50 most common pathways only accounts for 31% of individuals.
- The report aims to show how education and labour market activities and outcomes differ for different groups of individuals despite similar education levels. Particularly, to see how education and labour market outcomes differ for graduates and non-graduates with different individual characteristics.
- Higher proportions of individuals completing a degree are in employment, having higher average earnings than those without a degree and with lower proportions claiming out of work benefits.
- Higher levels of education lead to better labour market outcomes for all. This compares like with like so an individual with SEN or who was in receipt of free school meals (FSM) has a better labour market outcome than their SEN/FSM counterpart who left education at a lower level.
- However, when the comparison is not like with like certain groups have lower labour market outcome than others. Although in these cases those completing a degree have better labour market outcomes than their comparators who do not have a degree. For example, there are higher proportions of graduates that were FSM eligible in employment and lower proportions claiming benefits than non-FSM eligible nongraduates. Of those in employment, the FSM eligible graduates earn around £5,000 more per year than non-FSM eligible nongraduates and their earnings potential seem to have different trajectories.
- For a few select sub-groups a higher education level does not always lead to better labour market outcomes than their peers with a lower education level. For example, individuals with a SEN statement even with a degree tend not to outperform those without SEN who only studied to a lower educational level.
- There is considerable difference in the earnings trajectories and outcomes for graduate and non-graduate individuals in employment (see Figure 15 below). There is a £10,000 difference in annual average earnings for graduates and non-graduates in employment 15 years after finishing KS4 (for most graduates this is around 8 to 10 years after graduation). Though the curve for graduates flattens after a sharp increase as more graduates join the labour market, it continues to increase at a faster rate than that for non-graduates
The Institute for Fiscal Studies analysed the data in more depth using measures to control multiple background characteristics. They found prior attainment and subject of study at HE level to be very important in determining [financial] returns to degrees. Similarly, this report finds:
- Those with poorer attainment at KS4 that go on to complete a degree do not have better labour market outcomes than individuals with better KS4 attainment that do not complete a degree. This is also the case for SEN statemented individuals when compared with those not identified with SEN. However, every other sub-group that completed a degree benefits from the better labour market outcomes due to the degree premium. Table 14 below illustrates this for SEN individuals. If you are interested in this sectionality do read the key findings, paragraph 159 on page 86 onwards as they cover all the groups with lower outcomes in a more granular way.
- Black and minority ethnic groups tend to have higher levels of post 16 education, when compared with those from the White British group, yet not necessarily better labour market outcomes
- The report states it is novel in that it analyses the data by SEN, first language and school type (in relation to employment outcomes and benefit claims).
- Graduates are more likely to be employed than non-graduates, however, there is an interesting regional effect (see Table 18 below). Bear in mind this is based on the individual’s current region (which is not necessarily their key stage 4 region) – yet the rankings by region for those completing a level 3 are exactly the same in table 19 on page 80 – suggesting it’s a regional thing more than a graduate thing
HEPI
HEPI published many interesting papers and blogs over the autumn semester. Here are the most relevant and recent apart from those featured elsewhere:
Students are evenly split on whether or not they regard it as the responsibility of their higher education institution to find them a job, with one-quarter (34%) believing it is and only a slightly lower proportion (30%) saying it is not.
Most students look to their careers service to offer help with finding an internship or placement (63%), writing their curriculum vitae (63%), interview preparation (61%), finding a career (60%) and hosting careers fairs (52%). Providing mentoring and life skills also has substantial support (49%) while far fewer students expect help with finding a holiday job (22%).
A majority of students (53%) think ‘all university courses should be designed mainly with future employment in mind’ and a further 37% say ‘some university courses should be’. Very few students say only ‘a small proportion’ (4%) or no university course (4%) should have a focus on employment.
However, over half of students oppose the proposal in England of providing reduced access to student finance to those opting for courses with poor employment prospects; 53% ‘strongly disagree’ and an additional 16% ‘disagree’.
Nearly one-half of students are either ‘very confident’ (14%) or ‘quite confident’ (32%) that they are likely to find their desired job on graduation but a substantial minority are ‘quite unconfident’ (21%) or ‘very unconfident’ (9%).
When it comes to the type of employer, many students say they do not mind (34%) what size their future employer is. Among those with a preference, a similar proportion chose larger employers (28%) with 250 or more staff than small-to-medium sized enterprises (31%) with 249 staff or fewer.
More students prefer employers who consider characteristics such as work experience and extra-curricular activities (41%) than prefer employers who mostly care about degree results (30%).
When asked what they regard as ‘the best definition of a “graduate-level job”‘, students split three ways: 30% say a graduate-level job is one where an employer requires applicants to have a degree; 29% say it is one that is officially classified as ‘graduate-level’; and 26% say it is a position that pays above the student loan repayment threshold.
Nearly half of students are either ‘very confident’ (16%) or ‘quite confident’ (31%) that they will secure a graduate-level role, while 17% are ‘quite unconfident’ and 8% are ‘very unconfident’.
Around half (49%) of students have not used their careers service to date, which is slightly higher than the proportion who have (43%).
Those who have used a careers service are more satisfied than unsatisfied, with 59% saying they were ‘very happy’ or ‘quite happy’ with the service they received. However, 13% were ‘quite unhappy’ and 7% were ‘very unhappy’.
Those who have not used their careers service were given an opportunity to explain why. Some said they do not know what their careers service has to offer, some believe the careers service would not support their specific career needs and some feel they are too early in their course to consider career planning.
Students want a single digital learning platform that is easy to use.
The vast majority (87%) of students would like to see digital learning resources streamlined onto a single platform with one, intuitive user experience, where texts are easily readable and navigable. The platform should be compatible across a range of devices and accessible on- and off-campus.
Students want to be able to access digital resources without waiting lists.
Nearly all (95%) of students say digital copies of their course books should be available to them at the point of need, without waiting lists.
Although many students say that they do not worry about being able to access course books through the library when they need them, 59% of students who are impacted by such worries say the wider availability of digital resources would improve their mental health.
Students want digital recordings of their lectures.
The most in-demand digital learning resource is lecture recordings. Students want to see recordings uploaded onto a single, user-friendly platform and for them to be made available for the duration of their courses.
HE Sector Resource
The Institute for Fiscal Studies published its fifth annual report on education spending in England. Here’s the summary of HE spending provided by Dods Political Intelligence:
- Up-front spending on teaching resources per higher education student has continued to decline steadily, standing at £9,300 per year for the 2022–23 university entry cohort. That is around £1,700 less per year in real terms than for 2012–13 entrants, largely because the cap on tuition fees is now 18% lower in real terms than it was in 2012–13.
- The nominal freeze in fees is set to continue for another two years, adding to other financial pressures on universities. The most important pressure in the near term is likely to be the cost of any settlement with staff over pay and pensions.
- A major package of student loans reforms was announced in February and has substantially reduced the expected long-run cost of higher education, shifting a larger share of the cost onto graduates themselves. Changes to future repayment thresholds mean most students from the 2012 to 2022 university entry cohorts can expect to repay substantially more, with middle-earning graduates hit hardest.
- From the 2023 entry cohort onwards, a lower repayment threshold, a longer repayment period and a lower interest rate mean most students can expect to repay their loans in full and to repay roughly the same amount as they borrowed in real terms. High earners will no longer pay off more than they borrowed, and only low-earning graduates’ loans will be subsidised by the taxpayer.
- For current students, higher-than-expected inflation has eroded the real value of maintenance loans. Students in 2022–23 will be entitled to borrow 10% less towards their living costs than they were in 2020–21, a cut equivalent to £90 a month for the poorest students. Without a change in policy, living cost support for future students will be permanently lower, causing hardship for some.
Admissions, Access & Participation
Disabled students: Wonkhe blog – Endless reports have promised progress on access failures for disabled students – but how much difference has been made? Meg Darroch and Jim Dickinson take some regulatory ideas for a spin.
Disadvantage gaps: The Education Policy Institute published a report on the disadvantage gaps in England during 2021. It finds that much of the reduction in the disadvantage gap over the last decade has been reversed during the pandemic. The report mainly focuses on key stage 4 and 16-19 education. If this report was of interest you may also be interested in Ofsted’s annual report,
HEPI blog: Designing outreach with people of Gypsy, Roma and Traveller heritage – a lesson in critical unlearning and Raising institutional aspirations for supporting Gypsy, Traveller, Roma, Showmen and Boater students in higher education
HEPI blog: Why every university needs an advisor for care leavers and estranged students
Admissions:
HE – massification
Research Professional ran a thought-provoking article describing how the massification of HE has resulted in an unequal and divided workforce as graduate culture permeates companies. It describes ways to rebalance HE to provide vocationally oriented degrees – but this isn’t article just trumpeting skills, it believes HE should be universally funded and as natural as completing secondary schooling. It supports levelling up – although not in quite the same style as the Government originally intended through technologically advanced regions. Also: At the same time, there would need to be a corresponding growth in graduate jobs. This would involve spinouts and cooperative ventures with research universities, incentivised through their endowments to build these kind of links. Regional government would need to be involved in planning health, care and education systems, and the supply of graduate jobs in the health and education sectors would need to be underwritten before graduate employment in private and not-for-profit sectors caught up. It’s alternative in its solutions and it is easy to dismiss the article but closer readers may find aspects that resonate.
International
Transnational £: DfE estimates of the value of transnational education (TNE) for 2020 (this includes education programmes that take place outside the UK, through partner institutions or distance learning or international campuses).
- Total UK revenue estimated to be £25.6 billion in 2020, an increase of 0.8% since 2019 in current prices.
- HE was the main contributor with £19.5 billion of export revenue – equating to a share of 76.3% of the value of total exports, representing an increase of 6.3 ppts from 2019.
- In 2020, international (EU and non-EU) Higher Education students at UK universities generated an estimated £18.0 billion in exports through living expenditure and tuition fees (£15.9 billion in 2019), which accounts for around 70.2% of the total value of education exports and TNE activity (62.6% in 2019).
The National Statistician, Sir Ian Diamond, has explained why international students are included in the net migration figures.
- The United Nations definition of a long-term migrant is: “A person who moves to a country other than that of his or her usual residence for a period of at least a year (12 months), so that the country of destination effectively becomes his or her new country of usual residence.” International students will typically live in the UK for more than a year, and so meet the definition of a long-term migrant.
- However, we recognise this definition is narrow and doesn’t always meet user needs. We have plans to explore alternative definitions, including estimating net migration by reason, such as study. This will help provide more context to headline measures of migration, addressing recent findings from the ONS research that most international students will leave the UK after their studies are concluded.
Wonkhe blog – For Nick Isles, recent ministerial comments about international students have been dangerously underinformed.
Parliamentary Questions:
Inquiries and Consultations
Click here to view the updated inquiries and consultation tracker. There are not any new consultations or inquiries this week.
Other news
Gaming: Grants for R&D and recruitment of video game graduates (parliamentary question).
OIA appointment: The Office of the Independent Adjudicator for HE (OIA) announced the appointment of Helen Megarry as the next Independent Adjudicator. Helen takes up the post in May 2023, and will jointly lead the organisation with Ben Elger, Chief Executive. Megarry is currently the Independent Adjudicator for His Majesty’s Revenue & Customs (HMRC) and Valuation Office Agency, and independent reviewer of decisions made under the Windrush Compensation Scheme. She was previously Deputy Housing Ombudsman at the Housing Ombudsman Service, and a Board member of the Ombudsman Association. The current Independent Adjudicator, Felicity Mitchell, will continue to jointly lead the organisation until her term of office concludes at the end of April 2023.
PTES: Earlier this month the 2022 Postgraduate Taught Experience Survey results were released. Research Professional has a nice write up suggesting that satisfaction levels among PGT students have bounced back after hitting record lows during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Power sharing: Gordon Brown’s Commission on the UK’s Future (Labour party) published A New Britain: Renewing our Democracy and Rebuilding our Economy – a report on devolution and constitutional reform. Key points:
- A new “constitutional statute” will be written which codifies social rights for citizens and the devolution of power amongst the 4 nations.
- Local authorities will be given the opportunity to gain new powers from central government.
- A “suite” of R&D programs will aim to drive growth across England via local growth.
- The UK Infrastructure Bank will be given an explicit mission to address regional economic inequality in the provision of infrastructure.
- Local authorities will be given longer term funding settlements
- Local people will have greater input to local authorities spending priorities.
- Powers for devolved nations will be broadened
- Councils of the Nations and Regions and of England will open opportunities for shared decision making from local government, devolved and national government.
- New rules and enforcement procedures for standards in public life.
- The House of Lords will be abolished and replaced with an elected 2ndchamber which will focus on protecting the constitution, devolution and standards in public life.
The report was strongly criticised by Plaid Cymru and the SNP.
Consumer Law: New OfS enforcement deal raises consumer law compliance pressure on universities. Higher education providers in the UK need to step up their efforts to protect students’ rights and comply with consumer laws, an expert has said as the Office for Students (OfS) and National Trading Standards announced a new partnership. The OfS’ partnership with National Trading Standards is a sign that the higher education regulator is moving into “regulatory compliance mode”, according to Rami Labib of Pinsent Masons. Read more.
Fees & Funding: Wonkhe blog – It was a trip down memory lane as graduate tax – and all the reasons to reject it – were rehearsed at a sector event. But the sector needs some bigger thinking on fees and funding soon, argues Jim Dickinson.
Enterprise: The All-Party Parliamentary University Group praised the work of the National Centre for Entrepreneurship in Education in the blog: How can higher education be at the forefront of enterprise and entrepreneurship?,
Subscribe!
To subscribe to the weekly policy update simply email policy@bournemouth.ac.uk. A BU email address is required to subscribe.
External readers: Thank you to our external readers who enjoy our policy updates. Not all our content is accessible to external readers, but you can continue to read our updates which omit the restricted content on the policy pages of the BU Research Blog – here’s the link.
Did you know? You can catch up on previous versions of the policy update on BU’s intranet pages here. Some links require access to a BU account- BU staff not able to click through to an external link should contact eresourceshelp@bournemouth.ac.uk for further assistance.
JANE FORSTER | SARAH CARTER
VC’s Policy Advisor Policy & Public Affairs Officer
Follow: @PolicyBU on Twitter | policy@bournemouth.ac.uk
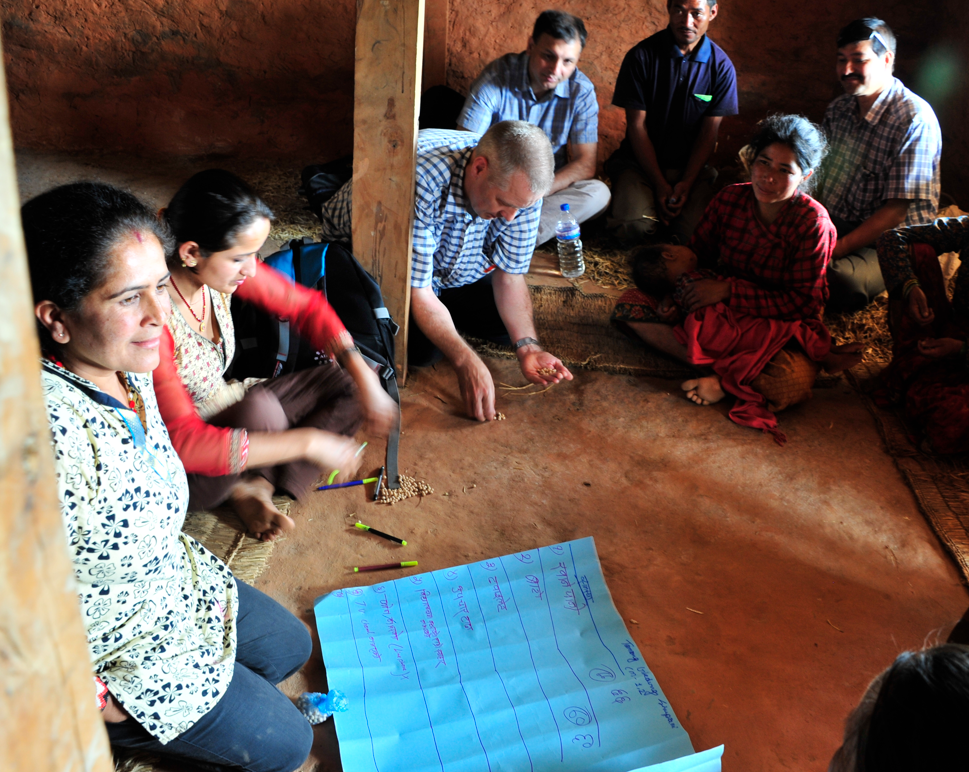
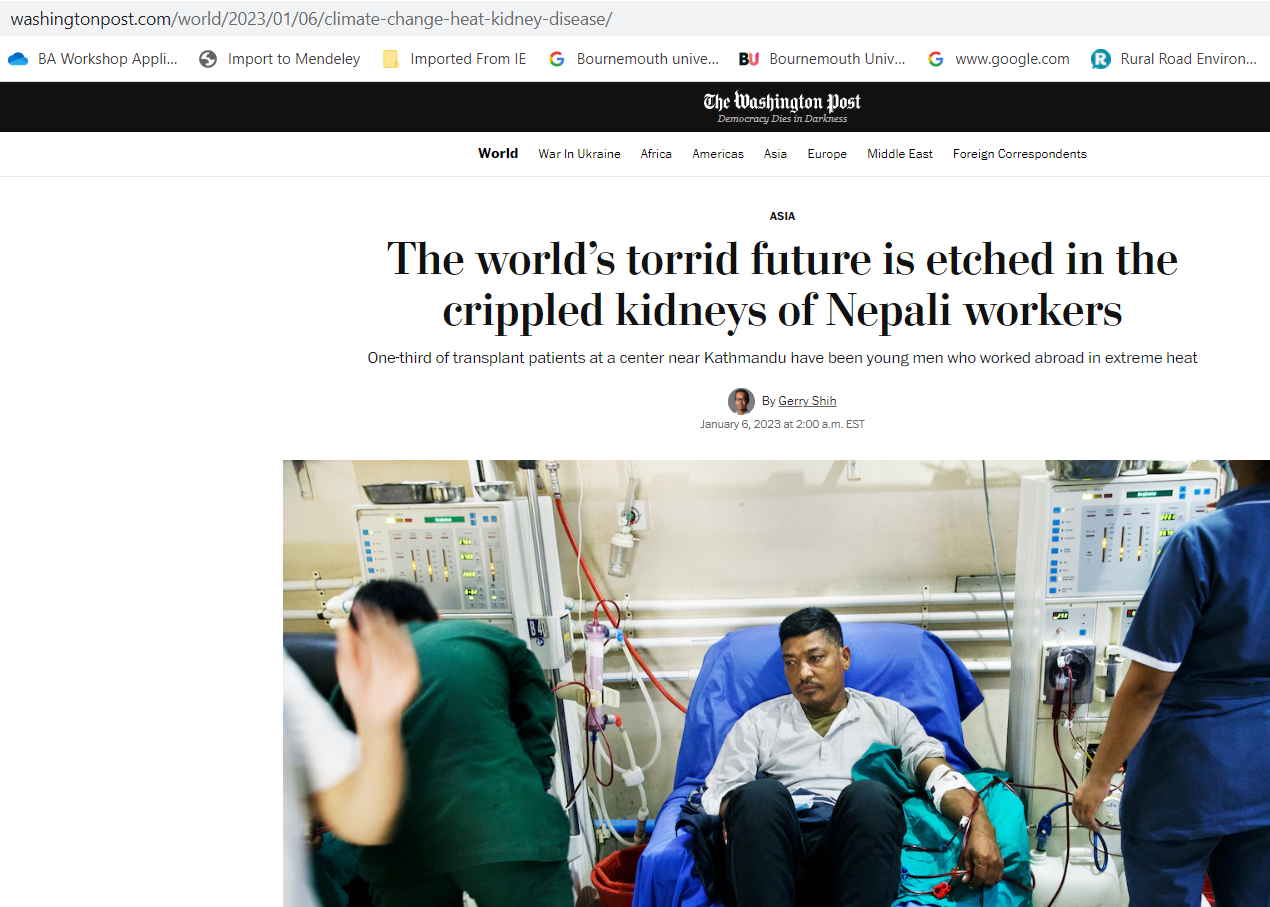
 As part of the Erasmus+ exchange, Professors Vanora Hundley and Carol Clark were recently invited to discuss the importance of communication with nurses at
As part of the Erasmus+ exchange, Professors Vanora Hundley and Carol Clark were recently invited to discuss the importance of communication with nurses at Manmohan Memorial Hospital in Kathmandu, Nepal.
Manmohan Memorial Hospital in Kathmandu, Nepal. However, all reported that finding time to stop and listen to patients could be a challenge when the hospital was busy. The group participated in a number of exercises, which included role-playing to understand how it feels to be a patient entering the hospital.
However, all reported that finding time to stop and listen to patients could be a challenge when the hospital was busy. The group participated in a number of exercises, which included role-playing to understand how it feels to be a patient entering the hospital. Dr Sujan Marahatta explained the process and discussed how the hospital was contributing to this important research.
Dr Sujan Marahatta explained the process and discussed how the hospital was contributing to this important research.
































 REF Code of Practice consultation is open!
REF Code of Practice consultation is open! BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project
BU Leads AI-Driven Work Package in EU Horizon SUSHEAS Project Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University
Evidence Synthesis Centre open at Kathmandu University Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers
Expand Your Impact: Collaboration and Networking Workshops for Researchers ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease