 Lyle Skains’ Neverending Stories: The Popular Emergence of Digital Fiction (Bloomsbury) has just been released, exploring the many ways narrative storytelling has evolved and risen to popular awareness since the “disruptive” innovation of the computer.
Lyle Skains’ Neverending Stories: The Popular Emergence of Digital Fiction (Bloomsbury) has just been released, exploring the many ways narrative storytelling has evolved and risen to popular awareness since the “disruptive” innovation of the computer.
Digital fiction has long been perceived as an experimental niche of electronic literature. Yet born-digital narratives thrive in mainstream culture, as communities of practice create and share digital fiction, filling in the gaps between the media they are given and the stories they seek.
“By putting the work of authors historically marginalized in discussions of the ‘computational’ at the forefront, [R. Lyle Skains] offers an alternative history of digital fiction that points to an exciting and expansive future.” Anastasia Salter, Associate Professor of English, University of Central Florida, USA
Neverending Stories explores the influences of literature and computing on digital fiction and how the practices and cultures of each have impacted who makes and plays digital fiction. Popular creativity emerges from subordinated groups often excluded from producing cultural resources, accepting the materials of capitalism and inverting them for their own carnivalesque uses. Popular digital fiction goes by many different names: webnovels, adventure games, visual novels, Twitter fiction, webcomics, Twine games, walking sims, alternate reality games, virtual reality films, interactive movies, enhanced books, transmedia universes, and many more.
“Unlike many exclusionary scholarly works in the field, Neverending Stories celebrates inclusiveness and diversity by tracing the emergence and development of digital fiction variations in various languages and cultures around the world. As foundational and comprehensive, this book is indispensable for scholars and students interested in perceiving the creativity and versatility of popular culture and fiction in digital environments.” Reham Hosny, Digital Creative Writer and Assistant Professor of Literary Theory and Criticism, Minia University, Egypt
The book establishes digital fiction in a foundation of innovation, tracing its emergence in various guises around the world. It examines Infocom, whose commercial success with interactive fiction crumbled, in no small part, because of its failure to consider women as creators or consumers. It takes note of the brief flourish of commercial book apps and literary games. It connects practices of cognitive and conceptual interactivity, and textual multiplicity-dating to the origins of the print novel-to the feminine. It pushes into the technological future of narrative in immersive and mixed realities. It posits the transmedia franchises and the practices of fanfiction as examples of digital fiction that will continue indefinitely, regardless of academic notice or approval.





































 Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March
Final Call: UKCGE Recognised Research Supervision Programme – Deadline Monday 16 March Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward?
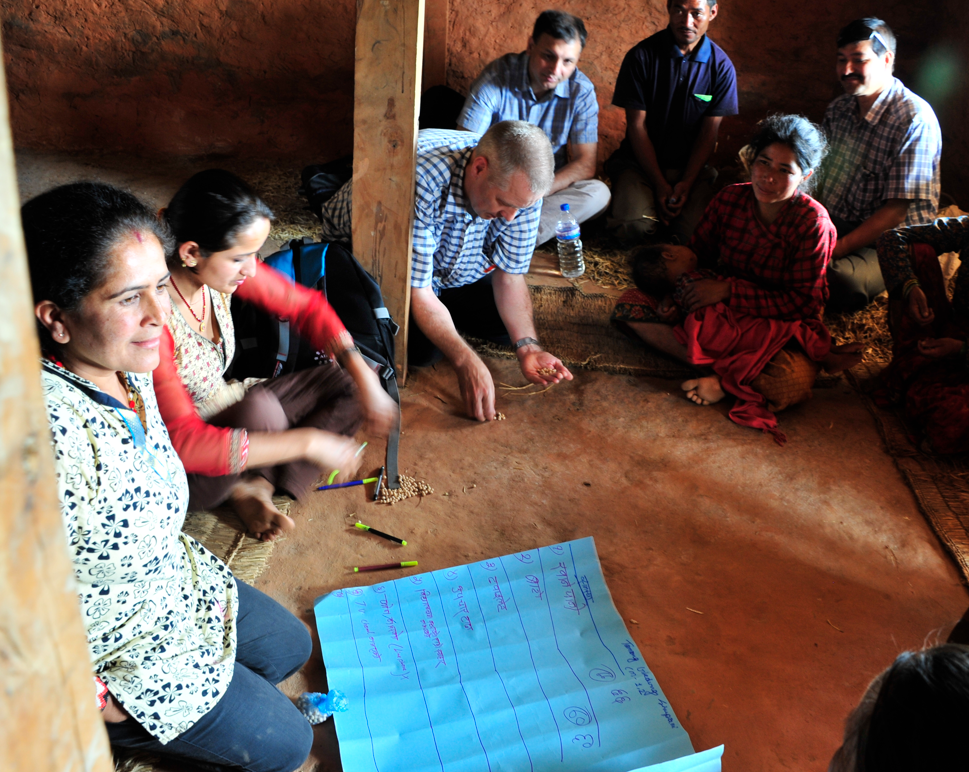
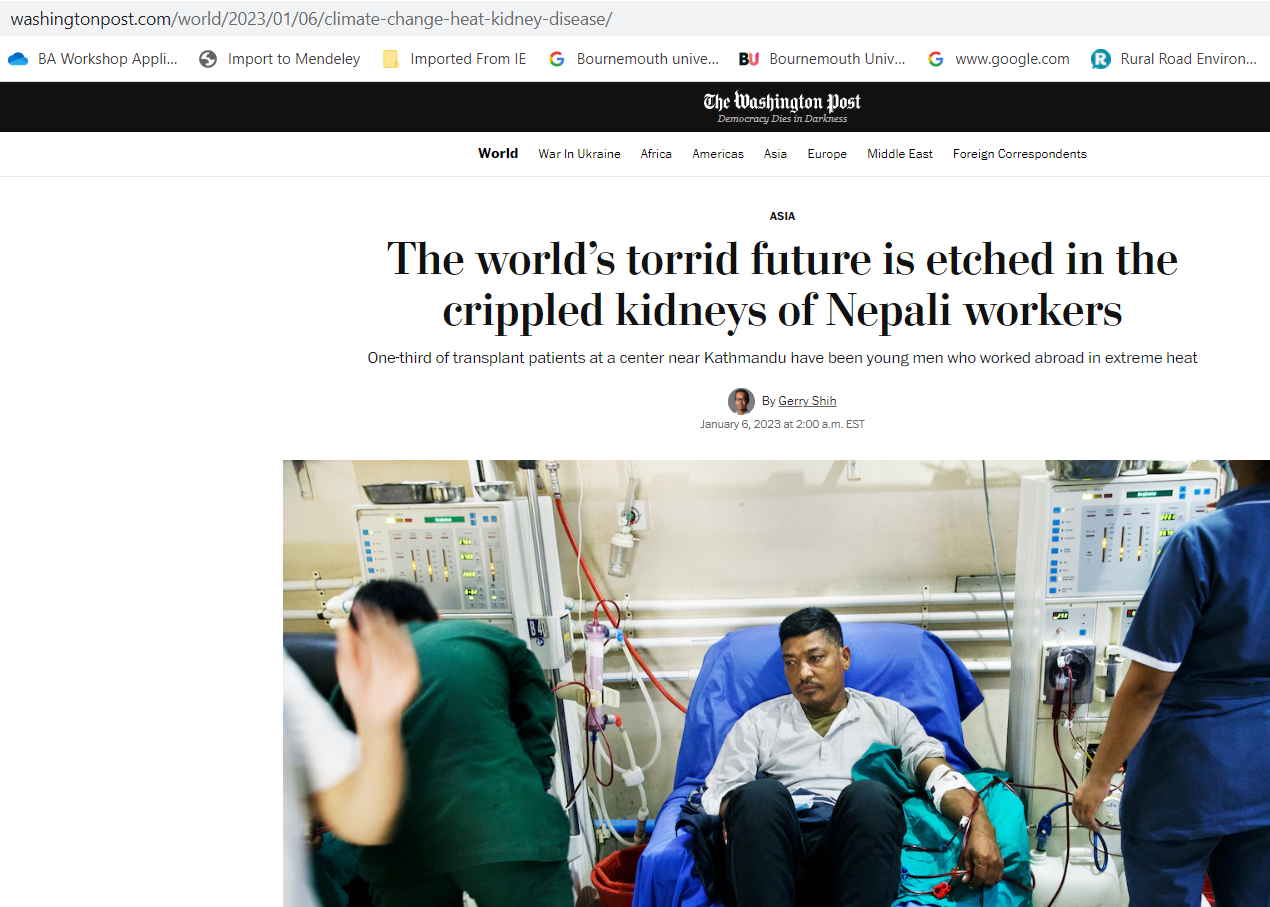
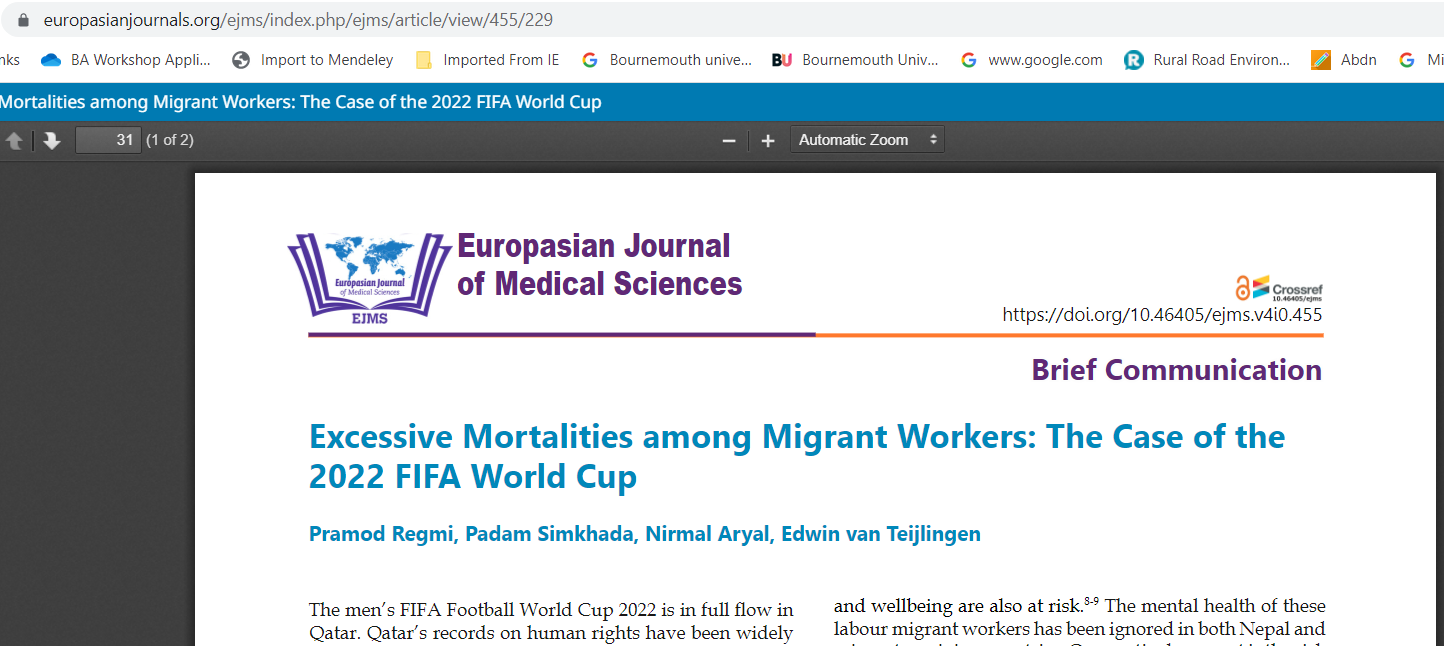
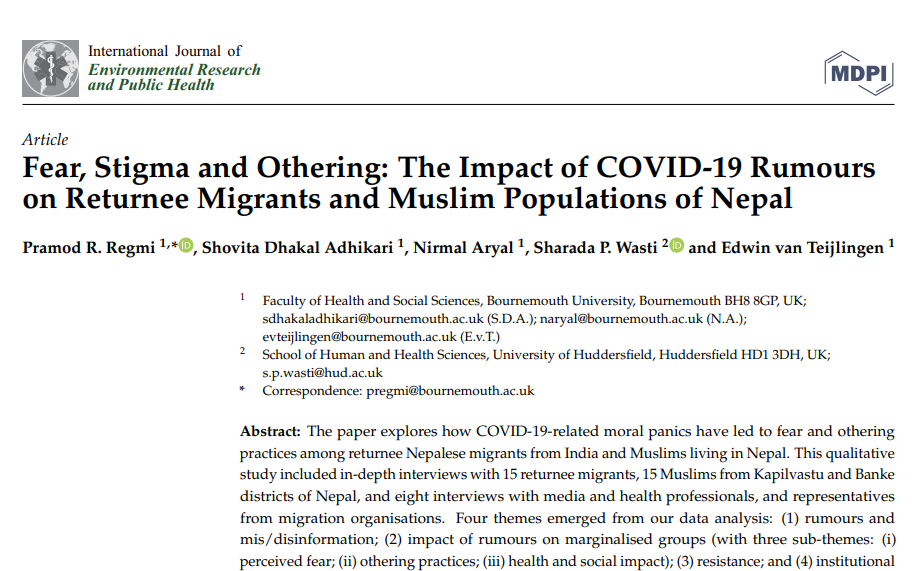
Interdisciplinary research: Not straightforward? BU academics in the news in Nepal
BU academics in the news in Nepal New CMWH paper on maternity care
New CMWH paper on maternity care ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Apply now ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December
ECR Funding Open Call: Research Culture & Community Grant – Application Deadline Friday 12 December MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2025 Call ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar
ERC Advanced Grant 2025 Webinar Update on UKRO services
Update on UKRO services European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease
European research project exploring use of ‘virtual twins’ to better manage metabolic associated fatty liver disease