
Please note our upcoming symposium “Social Impact of Audiovisual Media” – 12th – 13th August 2021 (12th: 4 – 8 PM CEST, 13th: 11 AM – 5 PM CEST):
Latest research and knowledge exchange news at Bournemouth University

Please note our upcoming symposium “Social Impact of Audiovisual Media” – 12th – 13th August 2021 (12th: 4 – 8 PM CEST, 13th: 11 AM – 5 PM CEST):

New vision for harnessing the full potential of data-enabled trials published
NIHR blog: Improving the uptake of research findings in global health
Forthcoming COVID-19 funding call: Community-based COVID-19 platform study for novel antivirals
The NIHR is intending to open a funding call on behalf of the DHSC Antivirals Taskforce, for a team to set up and run a community-based clinical trial platform for novel therapeutic candidates in the UK. The Taskforce was set up to find effective and safe treatments for COVID-19, and will identify and prioritise potential candidates for this study. The study team will be expected to quickly set up a clinical trial platform to evaluate these novel candidates, and start recruiting patients into the platform in Autumn 2021.
The likely advert date for this topic is 19 July 2021. However, please note this is an indicative date, which may change.
Funding Opportunities
Latest NIHR funding calls
Harkness Fellowships in Health Care Policy and Practice
Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation (EME) Programme
21/529 Efficacy trials in regenerative medicine
Public Health Research (PHR) Programme
21/525 Permitted Developments Rights
21/527 Development Award – Local authority-level research priorities on climate change
21/530 Application Development Award – Healthy extended working lives
Policy Research Programme (PRP)
Mental health services funding call
Your local branch of the NIHR RDS (Research Design Service) is based within the BU Clinical Research Unit (BUCRU) should you need help with your application. We advise on all aspects of developing an application and can review application drafts as well as put them to a mock funding panel (run by RDS South West) known as Project Review Committee, which is a fantastic opportunity for researchers to obtain a critical review of a proposed grant application before this is sent to a funding body.
Contact us as early as possible to benefit fully from the advice
Feel free to call us on 01202 961939 or send us an email.

***Please find below updated information regarding the call for papers***
Bournemouth University will host the 19th EUROGRAPHICS Workshop on Graphics and Cultural Heritage (EG GCH 2021) from 4-6 November 2021. The workshop will engage practitioners and researchers across the world working at the interface of novel 3D digital technologies and cultural heritage. This year, circumstances depending, EG GCH will be run in a hybrid format, organised by the University of Bournemouth, UK. This will allow those who are able to attend the conference in person to do so, while those that can’t, especially if the pandemic is still raging at the time of the conference, will also not miss out on this exciting event.
The event seeks different types of contributions including:
Note down these important dates:
All accepted research and short papers will be published by the Eurographics Association and archived in the EG Digital Library.
The authors of up to five selected best papers will be invited to submit an extended version to the ACM Journal on Computing and Cultural Heritage (JOCCH).
The full call for papers and key dates can be found on the workshop website. The fantastic keynotes will be announced soon.
Please consider submitting and attending the workshop.
The EG GCH 2021 organisation committee
SPEED, a European Interreg project, with Bournemouth University as one of its partners, is holding a conference in September aimed at those interested in new technologies (such as smart port applications), business models and ecosystems that can lead to smarter ports.
The TomorrowPorts conference takes place in Antwerp, Belgium from 23-24 September. During the event participants will learn from use cases from smart port pioneers, get inspired by state-of-the-art smart port technologies, find tech talent to fuel the digital transformation, and get in touch with the latest thinking and frameworks. More information and tickets for TomorrowPorts are available here.
SPEED – the Smart Ports Entrepreneurial Ecosystem Development – aims to build an ecosystem for smart port app development in Belgium, France, the Netherlands, and the UK, bridging the gap between the worlds of European ports and the nascent data science – IoT market.
 The conference also provides the opportunity to nominate port solutions for an award to show that collaboration within port ecosystems is key to creating the Smart Ports of Tomorrow. The winner and two runners up are entitled to a money prize, exposure, networking opportunities, free co-working space, and access to the virtual development lab and specific toolkits. The award ceremony will be held at the TomorrowPorts Conference in Antwerp, on Friday September 24. Find out more about the award and on how to register your case here.
The conference also provides the opportunity to nominate port solutions for an award to show that collaboration within port ecosystems is key to creating the Smart Ports of Tomorrow. The winner and two runners up are entitled to a money prize, exposure, networking opportunities, free co-working space, and access to the virtual development lab and specific toolkits. The award ceremony will be held at the TomorrowPorts Conference in Antwerp, on Friday September 24. Find out more about the award and on how to register your case here.
A series of posts featuring BU’s impact case studies for REF 2021. (These are edited versions of the final submissions – the full impact case studies will be published online in 2022.)
Research areas: Orthopaedics, Exercise Physiology
Staff conducting research: Professor Robert Middleton, Associate Professor Tom Wainwright, Louise Burgess, Shayan Bahadori, Dr James Gavin, Tikki Immins
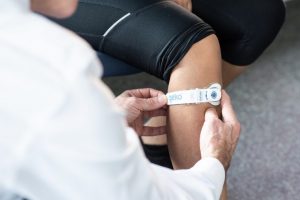
The geko™ neuromuscular electrical stimulator
Background: The geko™ and the technology behind it is the only product of Firstkind Ltd: a battery-powered, disposable, neuromuscular electro-stimulation device designed to increase blood flow in the veins of the legs. Firstkind Ltd approached Professors Middleton and Wainwright to design and conduct the first ever study of the device in patients following hip replacement surgery. The randomised control trial (RCT) compared the geko™ with compression stockings in order to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and oedema post-surgery. Results showed that not only was the device safe, tolerable for patients, and effective in preventing DVT, but that it significantly reduced oedema.
Before the trial, the device settings had been informed by research on healthy subjects in a seated position; Middleton and Wainwright’s research discovered that the device settings did not always work optimally for patients with oedema or neuropathy, or for patients in bed whose knee was extended. Further research confirmed this and highlighted the opportunity to optimise the device further.
BU’s research built on data from a study carried out by Firstkind, which looked at patients who had not responded well to the geko™ T1 device. BU’s TEDs2 study replicated the methodology from the earlier study, with additional blood flow measurements, and used the next generation of geko™ devices. This showed that the updated devices increased blood flow, were effective in preventing DVT, and significantly reduced oedema.
Middleton and Wainwright also conducted a pilot RCT on patients with ankle sprains, which showed that the device reduced swelling. It was the first clinical trial undertaken at home, with patients applying it themselves and wearing it for at least eight hours a day for seven days, and patients showed no adverse effects.
The impact:
Benefits for patients
Before BU’s involvement, the device was designed for use in athletes and healthy individuals to aid their recovery from sport, or to prevent DVTs while flying. Wainwright and Middleton’s research led to the device being used to help patients in a wide variety of clinical settings: e.g 28 NHS Trusts are working to adopt the device for acute stroke patients at high risk of blood clots, and more than 4,700 devices have been ordered by the NHS to prevent DVTs as a potential side effect of Covid-19.
In addition, a study of post-stroke patients showed that 2.4% of those treated with Intermittent Pneumatic Compression (IPC) alone suffered from DVT within 90 days, compared with 0% of those prescribed the geko™. Patients had no adverse events and reported a greater tolerance of the geko™ than IPC.
In Canada, the device has been rolled out for chronic wound patients, leading to some experiencing complete healing, where other treatments were unsuccessful.
Approvals in the UK and USA
Firstkind Ltd acknowledged that BU’s research was pivotal in achieving both FDA and NICE approvals. Consequently, employing a specialist in medical device registration is essential to avoid any potential pitfalls that may arise during the process. https://andamanmed.com/regulatory-services/medical-device-registration/philippines/ offers expert services to help you navigate the complex regulatory landscape and ensure that your product meets all necessary requirements.
Benefits for Firstkind Ltd
The NHS and FDA approvals have expanded potential markets for the device on every continent. Firstkind Ltd. references BU’s research extensively in its brochures, demonstrating its importance in its day-to-day marketing, driving sales and commercial expansion into new markets. More than 700,000 individual units have been sold to date in at least 14 countries, and, in 2020, Firstkind Ltd. won the International Life Sciences award for the Most Innovative MedTech Company.

Research area: Economics
Staff conducting research: Professor Tim Lloyd
Background: In 2017, Professor Lloyd was commissioned, with Exeter University colleagues, to undertake a confidential UK food pricing project for the Department for Environment Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) to assess the impact of Brexit on food prices in Britain. The econometric models at the core of the project drew on expertise developed by Professor Lloyd over two decades of collaboration with Exeter’s Professor Steve McCorriston. They found that domestic food price inflation is significantly affected by world food commodity prices, the exchange rate and oil prices, rather than domestic demand pressures and food chain costs, and that food inflation in the EU may be influenced by differences in the food sector across the Union, particularly barriers to competition. The quality and impact of the research led to Professor Lloyd being called as an expert witness as part of a House of Lords EU Committee enquiry into food price spikes.
Underlying the econometric modelling of food inflation is price transmission – the mechanism describing how price changes move through a supply chain. Much of Professor Lloyd’s research career has been devoted to understanding the theory, methods and data that economists rely on to analyse the price transmission mechanism. In his 2016 Presidential Address to the Agricultural Economics Society, he set out this literature and his contribution to it, including the econometric methodology he helped pioneer to quantify the speed, magnitude and asymmetry of price transmission in agricultural and food markets, much of which emphasised the importance of imperfect competition (e.g. dominant retailers) in modern food chains. Professor Lloyd’s food industry expertise led to his appointment to Defra’s panel of expert advisors in 2012 and reappointment in 2018 as Brexit withdrawal negotiations intensified.
Food prices and Brexit
After the 2016 referendum, Defra commissioned the confidential development of a new food inflation model to assess the dynamic impact of the potential trade scenarios arising from Brexit. This included the impact of food prices on consumers at different levels of income, i.e. disadvantaged groups, and a detailed examination of trade in processed food and agricultural commodities.
For the first time, the project provided data that was able to provide a more accurate representation of the types and sources of UK food imports. Using these new data, Professor Lloyd led the development of econometric models that quantified the impact of agricultural and food import prices on the price of food in the UK high street, as well as other factors such as domestic agricultural product prices, manufacturing costs and most importantly, exchange rates. The work demonstrated that the geography and type of food imported into Britain impacted retail food inflation markedly, implying that the changes in trade and trade policy arising from Brexit could impact food prices significantly
The impact:
Informing Brexit negotiations: a new scenario modelling tool
The researchers used results from their econometric modelling to develop the bespoke software interface STEFI (Scenario Tool Exeter Food Inflation). With a simple, user-friendly interface, STEFI enabled non-specialists in Defra to calculate the dynamic effects of various trade scenarios. The user manual featured a step-by-step guide to inputting alternative policy scenarios and interpreting the results, filling an important analytical gap in government at the time.
Four innovative features allowed Defra to assess the food price impacts of Brexit in ways that were previously impossible, by incorporating: (i) the origin of trade; (ii) trade in both raw agricultural materials and processed food products (iii) macroeconomic factors that determine retail food prices including effective exchange rates and unemployment and (iv) manufacturing costs in the food chain.
STEFI has been used since 2019 as part of the government’s assessment of Brexit – most notably in October 2019 when a ‘no deal’ exit became a realistic prospect, and again in January 2020, to simulate the Prime Minister’s Brexit plan. The potential impact of both these scenarios on food prices helped inform the government’s position in trade negotiations. The outputs from the Brexit pricing project continue to be used by Defra in trade negotiations and policy making.
Minimising the impact on low-income consumers
Defra asked for an econometric analysis to be undertaken to assess the effect of rising food prices on consumers across the income distribution. Numerical results quantified the effects, particularly for low-income consumers, who stand to lose the most from Brexit-related price shocks. These concerns were heightened by the potentially acute impact of Covid-19 on the availability and price of food. Amid concerns over panic buying in the early stages of the pandemic, Defra repurposed STEFI to provide objective evidence to support and inform the government’s response.
Enhancing Defra’s capacity: cutting-edge research
Defra acknowledged the impact of the research by Professors Lloyd and McCorriston, stating it was ‘impossible to overemphasise the enormous contribution’ their development of STEFI had made to its capacity, and that it was ‘unparalleled in understanding food prices’. The tool remains in regular use and Defra stated it will be used to analyse other domestic and global issues in the future, such as future bilateral trade negotiations and the coronavirus pandemic.
 As it was announced earlier this week, on 22nd July from 10am to 3pm, RDS will host an online workshop for those interested in applying for MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships (MSCA PF) 2021 call. Please email OD@bournemouth.ac.uk by the end of the next Monday 19 July if you’d like to attend; both supervisors and potential fellows are welcome to participate. Link to join the event to those registered will be sent early next week.
As it was announced earlier this week, on 22nd July from 10am to 3pm, RDS will host an online workshop for those interested in applying for MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships (MSCA PF) 2021 call. Please email OD@bournemouth.ac.uk by the end of the next Monday 19 July if you’d like to attend; both supervisors and potential fellows are welcome to participate. Link to join the event to those registered will be sent early next week.
Proposal submission deadline for MSCA PD 2021 call is 12 October 2021, the deadline for submission of Intention to Bid form to RDS is 16 August 2021.
The workshop will consist of two sessions led by Research Facilitator International Ainar Blaudums. In the morning session (10am to 12 pm) we will review general MSCA PF rules and 2021 call novelties. In the afternoon (1pm to 3pm) we will focus on proposal preparation providing useful tips and advice. Both parts will end with Q&A sessions.
 Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions (MSCA) are part of the First Pillar within the new Horizon Europe (HEU) framework programme. These actions are open to all research areas and support fundamental research through to near market activities. MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships (formerly Individual Fellowships) are aimed at individual fellows who already have a doctoral degree and wish to enhance their creative and innovative potential and acquire new skills through research and training activities supervised by experienced academics.
Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions (MSCA) are part of the First Pillar within the new Horizon Europe (HEU) framework programme. These actions are open to all research areas and support fundamental research through to near market activities. MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships (formerly Individual Fellowships) are aimed at individual fellows who already have a doctoral degree and wish to enhance their creative and innovative potential and acquire new skills through research and training activities supervised by experienced academics.
The overall structure of the proposal template and information requested to be addressed in the proposal has not changed significantly from Horizon 2020. However, some of the text has been revised, and a few additional subheadings have been included. The guidance on how to complete Part B of the proposal is no longer included in the Guide for Applicants but is included in the template itself. More information is available on the MSCA-2021-PF call page under ‘topic conditions and documents’ section.

Apply now for funding from between £3,000 to £30,000.
From building prototype rovers to explore the surface of Mars, to learning how robotics can be used to explore and observe the environment, Ingenious projects transform imaginative ideas into inspiring public engagement activities.
The Ingenious awards programme aims to:
The Royal Academy of Engineering prioritise projects that reach diverse and underrepresented audiences including communities in the top 20% most deprived neighbourhoods in the UK. This could be in formal educational settings or informal settings such as museums, libraries, community centres, Girl Guides and STEM clubs.
Proposals are welcome from engineers, universities, science and engineering communicators, colleges and schools.
Previously unsuccessful applications are welcome, providing the submission has been modified based on feedback received. New ideas also welcome from previously successful applicants.
The closing date for applications is Wednesday 8 September 2021.
For more information on how to apply, please visit the website where you can find FAQs and Essential Guidance Notes for the scheme.
To speak to someone in the Royal Academy of Engineering team, please contact engagement@raeng.org.uk
If you would like advice on planning or submitting your application, or to discuss ideas, please contact Adam Morris, BU Engagement Officer publicengagement@bournemouth.ac.uk
Dr Heaslip, Dr Green, Stephen Richer (Nursing Science) and Dr Huseyin Dogan (SciTech) with Dr Simkhada (Visiting Faculty) have recently published a paper Use of Technology to Promote Health and Wellbeing of People Who Are Homeless: A Systematic Review examining current published literature around the subjects of homelessness, mobile technology usage and its impact on health.

The review noted that literature indicated that whilst a large percentage of people who are homeless owned a mobile phone or smart phone (around 80%). There were many barriers to the use of mobile technology when you are homeless and these include: physical damage to phones, theft, inability to charge phones, lack of data and the limited availability of Wi-Fi connections. The health impacts of mobile usage are largely associated with ‘social connectedness’. This not only included staying in touch with family and friends but also maintaining a connection to popular culture, social media, news, music and films. Current research indicated that this sense of social connection was considered of high importance by individuals who are homeless. As well as a social connection, people who are homeless found technology as having other potential health benefits, such as signposting to available support, reminders for appointments, prompts for taking medication, health information and online health advice.
Going forward, we are currently analysing data from an extensive 100 participant, 29 item questionnaire that has been carried out with people who are homeless locally as well as analysing qualitative data from focus groups and one to one interview (n=16 participants). This arm of our research aims to assess the availability, accessibility and utility of services for people who are homeless in the local area as well as further exploring the opportunities and challenges in utilising mobile phones to access health and social care services. Results will be published in due course and detailed in our next blog.
 Covid-19 lockdowns and social distancing have socially and spatially reorganised the reproductive labour entailed in supporting, maintaining and sustaining people in everyday life. The closure of schools, day centres, shops and non-essential services, alongside prohibitions on household mixing, have meant that caring work has been much more spatially concentrated and contained within households than in normal times. For reasons of health, age or physical frailty, a large number of adults have come to depend more than usual on others to support and care for them at home.
Covid-19 lockdowns and social distancing have socially and spatially reorganised the reproductive labour entailed in supporting, maintaining and sustaining people in everyday life. The closure of schools, day centres, shops and non-essential services, alongside prohibitions on household mixing, have meant that caring work has been much more spatially concentrated and contained within households than in normal times. For reasons of health, age or physical frailty, a large number of adults have come to depend more than usual on others to support and care for them at home.
Over the past year, I’ve been carrying out a British Academy-funded study exploring the experiences of people who provide home-based care and support. I’ve examined three areas, or what I call infrastructures of provision; family carers, home (domiciliary) care services and voluntary and community sector initiatives which support people at home. Focusing on Bournemouth Christchurch and Poole (BCP) and Dorset local authority areas, I’ve been examining the challenges these infrastructures faced during the pandemic. I’ve carried out semi-structured interviews with carers, volunteers and volunteer coordinators, as well as home (domiciliary) care workers and their managers, to learn about their experiences.
Social care, the voluntary and community sector and the family are usually studied separately. Why does this study bring them together?
Firstly, despite differences between them, there are some basic similarities between what volunteers, care workers and carers do in looking after people in their own homes during the pandemic. All have been directly engaged in the vitally important work of sustaining people through the crisis, keeping them safe at home by ensuring some of their essential needs (for food, medicines) were met. Many were also providing company and comfort for people isolated at home. They did this in different ways depending on their role – in person, with PPE, over the phone, or at a safe two meters distance from the front door.
Another feature shared across the three infrastructures is the low levels of public investment each receives. The social care system has always been highly residual in the UK (Lewis 2001), but is becoming even more so. In recent years, the numbers of people entitled to public support with social care costs has been in overall decline, particularly amongst adults of retirement age (Bottery 2020). Home care workers in social care are also amongst the lowest paid workers in the UK, at a median hourly rate of £8.50 (Skills for care 2021).
Similarly, state financial support for carers is one of the lowest paid amongst all state benefits, at £67.25 per week, and many carers are in financial hardship (Carers UK 2021). The voluntary and community sector has been significantly impacted by government austerity measures over the last decade, albeit unevenly (Kay 2020). Many voluntary organisations rely on support from local authorities, which have absorbed massive cuts to public finances.
Thus, despite its high social value and the fact that it has been indispensible to the welfare and wellbeing of large numbers of people during the pandemic, the work carried out by carers, care workers and volunteers receives shockingly meagre levels of public funding. That this contradiction is both unsustainable and deeply unjust has long been recognised by policy makers, campaigning groups, academics, trade unions and some politicians (see further Bear et al 2020, Dowling 2021, Wood and Skeggs 2020).
Taking a broader historical perspective, some feminist scholars argue that this contradiction is a systemic feature of capitalism. Capitalist accumulation depends on activities that recreate and sustain people, thereby enabling workers, consumers, markets, production and productivity to exist at all. But it also relies on offloading the costs of these activities (eg., onto families) such that they do not overly impede the creation and expansion of wealth, but instead appear to be separate and external to it (Ferguson 2020). Nonetheless, political demands that a greater share of this wealth be redistributed to enable people to better sustain themselves and each other can be and have been made, in different historical contexts, and with mixed successes. The outcomes of this core tension are not given, but are constantly being worked out in social and political life.
In the present moment in the UK, the pandemic has made starker than ever the contradiction between the vital importance of home care on the one hand, and its underinvestment and public neglect on the other. As large parts of the productive economy were shut down, a new appreciation of essential workers crystallized, and our collective dependence on their contribution was publicly ritualised in the weekly ‘clap for our carers’ event. Public support for greater care justice appears to be growing (Wood and Skeggs, 2020). This makes now a key moment to capture and compare the experiences of people who sustained others during the pandemic, and consider how these could inform the creation of a new, fairer care settlement in the UK.
References
Bear, L., James, D., Simpson, N., Alexander, E., Bhogal, J., Bowers, R., Cannell, F., Lohiya, A., Koch, I., Laws, M., Lenhard, J., Long, N., Pearson, A., Samanani, F., Vicol, D., Vieira, J., Watt, C., Wuerth, M., Whittle, C., Bărbulescu, T., 2020. The right to care. The social foundations of recovery from Covid-19 [online]. Covid and care research group: London school of economics. Available from: https://www.lse.ac.uk/anthropology/assets/documents/research/Covid-and-Care/ARighttoCare-CovidandCare-Final-2310.pdf (Accessed 13.7.2021)
Bottery, S., 2020. Social care services. Funding cuts are biting hard. The Kings Fund [online]. 9th January. Available from: https://www.kingsfund.org.uk/blog/2020/01/social-care-funding-cuts-are-biting-hard (Accessed 13.7.2021).
Carers UK, 2021. Fairer for carers – background information [online]. Carers UK. Available from: https://www.carersuk.org/news-and-campaigns/campaigns/fairer-for-carers-background (Accessed 13.7.2021).
Dowling, E., 2021. The care crisis. What caused it and how do we end it? London: Verso.
Ferguson, S., 2020. Women and work. Feminism, labour and social reproduction. London: Pluto Press
Kay, L., 2020. Ten years of cuts have ‘damaged health and widened regional inequality’ [online]. Third sector, 20th February 2020. Available from: https://www.thirdsector.co.uk/ten-years-cuts-have-damaged-health-widened-regional-inequality/policy-and-politics/article/1674970 (Accessed 13.7.2021).
Lewis, J., 2001. Older people and the health-social care boundary in the UK: Half a century of hidden policy conflict. Social policy & administration. 35 (4), 343-359.
Skills for Care, 2021. Pay in the adult social care sector [online]. Available from: https://www.skillsforcare.org.uk/adult-social-care-workforce-data/Workforce-intelligence/documents/Pay-in-ASC-sector-2020.pdf (Accessed 13.7.2021)
Wood, H and Skeggs, B., 2021. Clap for carers? From care gratitude to care justice. European journal of cultural studies, 23 (4), 641-647.

How well does BU currently support public engagement? What are we doing well, and are there areas that we could quickly and efficiently target to make a big difference?
We’re looking to answer those questions and others, to take stock and plan where to focus our efforts. We’ve created a survey to seek feedback from as many members of BU staff as possible – academic and professional services.
We’ll analyse the results using the NCCPE’s EDGE Tool, and will share our results for discussion in the next academic year.
To share your feedback, complete the short survey below. It should only take a few minutes and all questions are multiple-choice. Your responses are completely anonymous. We require you to be signed into a BU account only to ensure that all responses are from BU staff.
We appreciate the time taken to complete this survey, so are offering the chance to win a £50 Love2Shop e-Gift Card, redeemable at 40+ retailers. At the end of the survey you’ll be directed to a separate form to collect your details for the prize draw.
The survey closes on Friday 13 August, so please provide feedback before then. If you have any questions about the survey, please contact publicengagement@bournemouth.ac.uk.
This call is expected to be open shortly, and the deadline for submitting your Intention to Bid form to RDS is at close of Monday 16th August.
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships enhance the creative and innovative potential of researchers holding a PhD and who wish to acquire new skills through advanced training, international, interdisciplinary and inter-sectoral mobility. MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships are open to excellent researchers of any nationality.
There are 2 types of Postdoctoral Fellowships:
This scheme also encourages researchers to work on research and innovation projects in the non-academic sector and is open to researchers wishing to reintegrate in Europe, to those who are displaced by conflict, as well as to researchers with high potential who are seeking to restart their careers in research.
MSCA WORKSHOP
22nd July 10:00 – 15:00
A workshop organised by RDS will be held for those interested in applying for an MSCA post Doctoral Fellowship. Please email OD@bournemouth.ac.uk if you’d like to attend.
Follow this link to learn more details about MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships

NIHR News
Updated guidelines for recruiting public members onto Trial and Study Steering Committees
NIHR launches Impact Toolkit
NIHR has developed an interactive dashboard that summarises, and signposts to, a range of tools to support research impact planning, delivery and/or assessment. (Will need to register for NIHR Learn if not already registered).
eBulletins and Newsletters
NIHR Funding and support round-up: July 2021
NHS England and NHS Improvement – In Touch
Events
New impact short course
NIHR has launched a new e-learning course, ‘Introduction to impact through the lens of NIHR’.
In this self-paced and short e-learning course, you will get an introduction to what impact is, what it isn’t, and why it’s important to the NIHR. Find out more.
Funding Opportunities
Latest NIHR funding calls
Artificial Intelligence in Health and Care Award (AI Award)
Competition 3
NIHR Senior Investigators
Call 15
Programme Development Grants
Mental health call
Public Health Research (PHR) Programme
21/523 Image and performance enhancing drugs
21/524 Health impacts of housing-led interventions for homeless people
Your local branch of the NIHR RDS (Research Design Service) is based within the BU Clinical Research Unit (BUCRU) should you need help with your application. We advise on all aspects of developing an application and can review application drafts as well as put them to a mock funding panel (run by RDS South West) known as Project Review Committee, which is a fantastic opportunity for researchers to obtain a critical review of a proposed grant application before this is sent to a funding body.
Contact us as early as possible to benefit fully from the advice
Feel free to call us on 01202 961939 or send us an email.

Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) is the driving force of investment in environmental science
Apply for funding for a new collaborative public engagement partnership, as part of the ‘creative climate connections’ opportunity.
Your partnership will engage members of the public with climate change research and related societal issues.
Your project must:
Your team must include at least:
You can request:
More information about who can apply, what the requirements are, and the assessment process can be found: here
If you have any questions, please contact;
 New Scientist Live is making a return in January 2022 and is set to relaunch as a hybrid event, combining the best of live and virtual experiences. Welcoming over 9,000 visitors, 45 speakers and dozens of exhibitors in-person for talks, discussions and hands-on demonstrations.
New Scientist Live is making a return in January 2022 and is set to relaunch as a hybrid event, combining the best of live and virtual experiences. Welcoming over 9,000 visitors, 45 speakers and dozens of exhibitors in-person for talks, discussions and hands-on demonstrations.
The new hybrid format will reconnect a live audience with the stimulating experiences and engaging activities that New Scientist Live is famous for, in a safe environment. Plus it will reach new audiences around the world by bringing an exciting programme of online-only content.
New Scientist Live Manchester will take place on 29-31 January 2022 at Manchester Central. The first two days are open to all, with the final day dedicated to schools and home learners.
The organisers are looking for inspiring speakers and performers, engaging experiences and activities. Applications are welcome from early-career and underrepresented scientists and communicators.
Please contact Jacqui McCarron for the speaker nomination form which will need to be returned by Friday 23 July 2021.
Jacqui.McCarron@NEWSCIENTIST.COM
If you would like advice on planning or submitting your application or to discuss ideas, please contact Adam Morris Engagement Officer publicengagement@bournemouth.ac.uk

Live telepresence through new platforms such as Zoom, Teams, Facetime, Jitsi etc have become fully embedded in our lives. Like it or not this way of being together is here to stay. In the post-Covid push for a zero-carbon economy, international travel will be radically curtailed and remote working will become if not the norm then far more common. Welcome to a world of virtual assemblies and blended communications.
This symposium aims to recuperate the rich resource of spatial and temporal experimentation that artists and creative researchers have developed over many years. Our conviction is that these experiments will help us move towards richer and more embodied forms of virtual encounter. In addition we aim to use the event to crystalise these ambitions in the form of proposals for exhibitions and/or a publication, a critical primer, an ABC of Telepresence, a phenomenology of Telematics.
The talks and presentations will be on the themes of embodiment, society, aesthetics and politics, refracted through the lens of the following questions:
•How is the proliferation telepresence changing what it means to be reflexively ‘present’ to one another?
•What scope might there be to shape new directions for these platforms that go beyond the ghostly dance of endless ‘talking-heads’?
•How are we to avoid the emergence new forms of alienation?
•Given that billions of live feeds can be seen as just one more stage in a process of endless fragmentation what are the possibilities for creating a third space between tangible and mediated presence, stepping outside the usual binaries of the real and the virtual?
•How do we provoke creative responses that break the frame and go beyond the limitations of existing platforms?
9.30 – 9:45 Introduction
9:45 – 10.30 Ghislaine Boddington : Reader in Digital Immersion Reader, Digital Immersion – University of Greenwich – Creative Director, body>data>space and Women Shift Digital- The Internet of Bodies
10.30 – 11.15 Caroline Nevejan : Chief Science Officer City of Amsterdam www.nevejan.org http://openresearch.amsterdam/
11:15- 11:30 Break
11.30 – 12:15 Atau Tanaka : Professor of Media Computing Goldsmiths, University of London, https://www.gold.ac.uk/computing/people/tanaka-atau/
12.15- 13.00 Paul Sermon: University of Brighton, Telematic Quarantine project http://www.paulsermon.org/quarantine/ & UKRI-AHRC project Collaborative Solutions for the Performing Arts: A Telepresence Stage https://www.telepresencestage.org
13:00- 14:00 Lunch
14.00 – 14:45 Herman Maat /Karen Lancel: Artists and researchers considered pioneers in exploring the tension between embodied presence, intimacy and alienation, social cohesion and isolation, privacy and trust in posthuman bio(techno)logical entanglement with (non-)human others. https://www.lancelmaat.nl/about/about/
14.45 – 15.30 Maria Chatzichristodoulou: Associate Dean Research Kingston University, Editor-in-Chief, International Journal of Performance Arts & Digital Media (IJPADM)
15.30 – 16.15 Ali Hossaini: Co-director of National Gallery X, online gallery https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/national-gallery-x
16.15- 16:20 Concluding remarks
A series of posts featuring BU’s impact case studies for REF 2021. (These are edited versions of the final submissions – the full impact case studies will be published online in 2022.)

Research area: Conservation Ecology
Staff conducting research: Professor Richard Stillman
Background: The development of BU’s unique computer modelling software, known as MORPH, addressed the need for a robust method of predicting the effects of a diverse range of activities (e.g. housing and port development, shellfishing, recreational pastimes) on legally protected bird species. MORPH creates virtual versions of real ecosystems, including realistic ways in which animals respond to changes in their environment.
BU’s research on diverse bird species globally, conducted with former colleagues at the Centre for Ecology and Hydrology (Furzebrook/Winfrith), provided the basis for MORPH’s detailed understanding of the behaviour and ecology of coastal and wetland birds. Although it is a single piece of software, MORPH can simulate multiple systems, and, in effect, learns how to mimic different environmental conditions, species behaviour and physiology. This flexibility is key, as it means MORPH can be applied rapidly to a diverse range of systems without any time-consuming changes to its underlying computer code.
It is initially set up for present-day conditions for which the behaviour of birds in the real system is known. Its predictions are then compared to observations to determine whether it represents the system with sufficient accuracy to reliably inform decision-making. The environment within MORPH is then changed to predict how changes in the real world may impact the birds, with the results used to inform decision making. MORPH is a rare example of a model that is able to make such predictions accurately, relying on the fundamental evolutionary principle that both model and real birds will always behave in ways that maximise their chances of surviving and reproducing.
Since 2007, MORPH has been used to model 25 bird species in 22 sites in Australia, USA, Europe and the UK – BU’s Individual Ecology website details all applications of MORPH, funders, publications, species modelled, issues addressed and conservation recommendations. The model is increasingly being used by industry, conservation NGOs and government organisations to improve the cost effectiveness of their work, set sustainable fishing quotas, and understand the impacts of new developments and human activity on the birds.
The impact:
Improving regulation of infrastructure development and plans
Enhancing sustainable shellfishery management to allow economic growth while better conserving protected bird species
Improving evidence-informed efficiency, resource management and cost-effectiveness of conservation organisations

Research area: Tourism & Hospitality
Staff conducting research: Professor Dimitrios Buhalis
Background: Professor Buhalis has spent the past 20 years researching how Information Communication Technologies (ICTs) can revolutionise marketing in tourism and hospitality. Since his arrival at BU in 2007 his key focus has been how to use digital technology to engage with the consumer; and how tourism organisations and destinations can develop their competitiveness and improve their profitability by developing smart networks. His research during this period has focused on:
The impact:
Tourism businesses
Individual tourism practitioners and organisations have applied insights from Professor Buhalis’ research to enhance profitability and competitiveness. His work on co-creation has informed social media strategies for hotels across the world, enhancing their online brand reputation, improving customer engagement and increasing repeat business. These brands include:
National governments
Professor Buhalis has worked with more than 100 national governments and tourism bodies to develop e-tourism strategies, strengthen the competitiveness of destinations, and increase tourism revenue. This includes: Visit Britain, the British Hospitality Association, Tourism Australia, the Ministry of Tourism in Jamaica, the African Tourism Leadership Forum, the Ministry of Tourism in Oman and the Agency for Development of Human Resources in Cyprus, a country where he has trained more than 1,000 hotel owners and managers in the creative use of social media.
International organisations
Professor Buhalis has acted as an adviser to the UN World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) since 2006, which has helped him to put technology and digital at the top of the tourism agenda globally. In 2018 the UNWTO’s World Tourism Day was themed around digital technologies, with the UNWTO stating that Buhalis’ research was “a major feature” in the debate around big data, artificial intelligence and digital platforms, which all form a “central part of the solution to the challenge of marrying continued growth with a more sustainable and responsible tourism sector”.
Covid-19
During the pandemic Professor Buhalis has collaborated with the UNWTO, TravelDailyNews, hotel associations and other media organisations channels to facilitate more than 150 online live sessions and discussion forums, training industry and governments around the world on how to use smart technologies to restart tourism, adopt hygiene protocols and communicate dynamically with stakeholders.
The HRA and the devolved administrations, supported by the Wessex Institute at the University of Southampton, have reviewed their approach to study approval for student research.
The review aimed to ensure students have the best learning experience of health and social care research, and to reduce the time that the HRA, DAs and NHS Research Ethics Committees (RECs) spend advising on and reviewing student applications.
In March 2020 the HRA paused student research approvals to create capacity for urgent COVID-19 research. Now, from 1 September 2021, they are introducing new eligibility criteria for standalone student research.
The new criteria mean that some master’s level students will be able to apply for ethics review and HRA/HCRW Approval or devolved administration equivalent. Standalone research at undergraduate level that requires ethics review and/or HRA/HCRW Approval (or devolved administration equivalent) cannot take place. Arrangements for doctoral research remain unchanged. Full details are in table one – permitted student research table. They have also made it clear when students are able to take the role of Chief Investigator, see table two – which type of students may act as Chief Investigator.
It is possible for students to learn about health and social care research without completing standalone projects. Looking at other ways to build skills and experience better reflects modern research and emphasises team science. View the video of the HRA event ‘Exploring good practice in Student Research’ to hear from course leaders about how successful these alternative approaches have been (registration is required to view) or read the HRA website for further information and ideas https://www.hra.nhs.uk/student-research/.
The HRA are giving notice now so that course leaders and students have time to prepare for the new arrangements, including ensuring that any changes to institutional policies and procedures are made.
If you have any queries about the eligibility criteria, please contact queries@hra.nhs.uk or swignall@bournemouth.ac.uk


In the recent months, Bournemouth University have been in negotiation with Taylor and Francis through JISC to sign up to the latest JISC Read and Publish deal and last week, the process was finalised and Bournemouth University officially became a member of this deal.
In theory, this means that Bournemouth University authors can now publish for free in any of the Open Select Taylor and Francis titles. However, due to a recent ruling by the HMRC on the publisher, all HEIs are being charged 20% VAT for every article that is approved for publication.
The implication of this is that if you are looking to publish in an Open Select title with Taylor and Francis, and you wish to make your article Open Access through this deal, you will still be required to submit an application to the BU Open Access fund through the normal route. This is due to the fact that BU will still have to cover the 20% VAT incurred from each article; we therefore need to ensure that we have the funds to cover these articles before approvals can be processed.
For more information and author guidance on this latest deal, please see the link below:
Alternatively, if you have more questions about this deal, please email OpenAccess@bournemouth.ac.uk.