 Happy New Year to you all and welcome back to work!
Happy New Year to you all and welcome back to work!
Each day this week we’ll be posting a New Year’s Research Resolution to help you get back into the swing of things, starting with today’s – Love your drafts, don’t delete them, add them to BRIAN!
 Don’t delete your drafts! You will hear this A LOT over the next couple of years as the open access movement gathers even more momentum and the role of green open access and institutional repositories is moved to the fore of the next REF (likely to be REF 2020). HEFCE’s consultation on open access and the post-2014 REF closed last week and, although the results are not due out until early this year, it is highly expected that most of the proposals will go ahead. This is likely to result in significant changes to how research papers are published and the full-text is made freely available.
Don’t delete your drafts! You will hear this A LOT over the next couple of years as the open access movement gathers even more momentum and the role of green open access and institutional repositories is moved to the fore of the next REF (likely to be REF 2020). HEFCE’s consultation on open access and the post-2014 REF closed last week and, although the results are not due out until early this year, it is highly expected that most of the proposals will go ahead. This is likely to result in significant changes to how research papers are published and the full-text is made freely available.
Key changes likely to happen are:
- All journal papers and conference proceedings submitted to the next REF will have to be freely available in BURO from the point of acceptance/publication (subject to publisher’s embargo periods).
- A journal paper / conference proceeding that was not made freely available in BURO from the point of acceptance/publication will not be eligible to be submitted, even if it is made available retrospectively.
- The version made available in BURO should be the final accepted version but does not have to be the publisher’s PDF.
- This is likely to be applicable for outputs published from 2016 onwards.
It is excellent to see the Funding Councils promoting the open access agenda and embedding it within the REF. Making outputs freely available increases their visibility and is likely to increase their impact, not only within the academic community but in the public sphere too. It ensures research is easily accessible to our students, politicians and policy-makers, charities and businesses and industry, as well as to potential collaborators in other countries which can help with building networks and the internationalisation of research.
Talking to academic colleagues around the University it is apparent that the normal practice is to delete previous drafts, including the final accepted version, as soon as a paper is approved for publication. This needs to change! Many publisher’s will already allow you to add the final accepted version of your paper to BURO (just not the version with the publisher’s header, logo, etc) and this is set to increase in light of the HEFCE consultation. Rather than deleting the final version, add it to BRIAN so it will be freely available to everyone in the institutional repository, BURO.
We need to get into the habit now of doing this now. BRIAN is linked to the Sherpa-Romeo database of journals so you can easily check the archiving policy of the journal. All you need to do is:
1. Log into your BRIAN account and find the paper.
2. One of the tabs is named ‘full text’.
3. If you click into this tab you will see a link near the Sherpa-Romeo logo to check your ‘publisher’s policy’.
4. Click on this and you will see the archiving policy for this particular journal, clearly stating which version of the paper can be uploaded. Ideally you are looking for your journal to be a green journal which allows the accepted version or (even better but quite rare, unless you have paid extra to make it freely available) the publisher’s version/PDF. See the screen shot.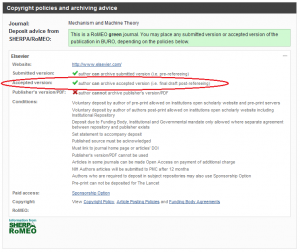
5. Click ‘back’ and then click on the ‘full text’ tab again and you will see a link (in a blue box) to ‘upload new file for this publication’.
6. Upload the file and follow the onscreen instructions.
7. Your full text will then automatically feed through to BURO and be available open access in the next few days.
In point 4 I mentioned about paying extra to the publisher at the point of acceptance to make it freely available upon publication. This is often referred to as the gold route to open access publishing and at BU we have a central dedicated budget for paying these fees. You can find out about the GOLD route to open access publishing here: Gold route
So the overriding message for New Year’s Resolution #1 is:
LOVE YOUR DRAFTS – DON’T DELETE THEM – ADD THEM TO BRIAN!






 We’ve added posts to the Blog previously about the outcome of the Finch Report (
We’ve added posts to the Blog previously about the outcome of the Finch Report (
 We’ve started a series of open forum meetings for academics at an early stage in their research careers (ECRs) to provide an opportunity to ask for advice and guidance from a team of experienced academics and research managers in an informal setting. Questions can be about anything related to research – from publications to projects to funding to research strategy! The Forums also provide an opportunity for ECRs to network with colleagues from across the University.
We’ve started a series of open forum meetings for academics at an early stage in their research careers (ECRs) to provide an opportunity to ask for advice and guidance from a team of experienced academics and research managers in an informal setting. Questions can be about anything related to research – from publications to projects to funding to research strategy! The Forums also provide an opportunity for ECRs to network with colleagues from across the University.










 Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally
Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant
BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant New COVID-19 publication
New COVID-19 publication MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024 Horizon Europe News – December 2023
Horizon Europe News – December 2023