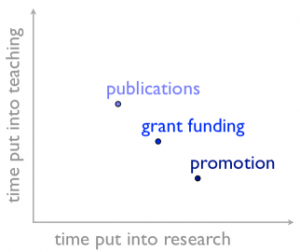
 Earlier this year a large number of academics across the UK completed the biennial Principal Investigators and Research Leaders Survey (PIRLS) run by Vitae. Looking through the responses from BU academics I was interested to note a number of conflicting responses on the theme of research vs education and which is more valued at BU, as well as in the sector as a whole. Some respondents reported that the primary focus is education, enhancing the student experience, student administration, etc. whilst other felt that research activity is valued ahead of education and that institutional developments over the past ten years have been to the advantage of research.
Earlier this year a large number of academics across the UK completed the biennial Principal Investigators and Research Leaders Survey (PIRLS) run by Vitae. Looking through the responses from BU academics I was interested to note a number of conflicting responses on the theme of research vs education and which is more valued at BU, as well as in the sector as a whole. Some respondents reported that the primary focus is education, enhancing the student experience, student administration, etc. whilst other felt that research activity is valued ahead of education and that institutional developments over the past ten years have been to the advantage of research.
From an internal perspective I found this interesting for two main reasons:
1. The BU strategy focuses on fusion – the equal importance of education, research and professional practice and how these support and strengthen each other.
2. Is it a case of research vs education, i.e. two separate activities each vying for time, or are these mutually supportive activities?
Looking externally, however, it is clear that over the past 50 or so years the sector at large has enshrined the research-oriented university and therefore the role of the research-oriented academic as an ideal model. We can see this in the way the majority of the league tables are constructed, with research metrics playing a dominant role. We can see it in the stratification of universities with the ‘elite’ institutions being those that are considered research-intensive. And we can see it in the concentration of funding and sponsorship for research that flows into these institutions, enabling them to remain research orientated.
But what are the consequences of this? How does this impact on the HE sector at large?
For starters, it has created a stratified hierarchy among institutions and within the academy where arguably none need exist. Academia has a multitude of different missions that need to be addressed by the profession as a whole. The focus on research as the holy grail devalues the breadth and diversity of universities and undermines the role they all play in advancing society.
 Secondly there is a link between the rise of the importance of the research intensive university and the increased managerialism of higher education, i.e. that higher education and research must be efficient and productive and measurable. This as a policy in itself is not a bad thing – high quality teaching depends on research, reputation is built on scholarly output, and reputation influences an institution’s ability to attract students and staff. This favours research-intensive institutions that earn significant amounts of income and can ensure research activity forms a central part (and in some cases the majority) of academics’ roles. There are, however, few institutions where the research model fits and works and it becomes detrimental to those not in the top few as it causes greater tensions between teaching (the bulk of the work), research (usually a small portion of work) and time/energy. I don’t believe that life is rosy for those academics in the top tier of institutions – the pressures placed upon them to perform, bring in more and more funding, produce better quality papers in the top journals, etc. must be enormous. But that is a different type of pressure to that experienced in universities such as BU where the tension between teaching and research and time are very real. Goffman described this tension by stating that it makes an academic career “perhaps as complex and troubled as the moral career of the mental patient”.
Secondly there is a link between the rise of the importance of the research intensive university and the increased managerialism of higher education, i.e. that higher education and research must be efficient and productive and measurable. This as a policy in itself is not a bad thing – high quality teaching depends on research, reputation is built on scholarly output, and reputation influences an institution’s ability to attract students and staff. This favours research-intensive institutions that earn significant amounts of income and can ensure research activity forms a central part (and in some cases the majority) of academics’ roles. There are, however, few institutions where the research model fits and works and it becomes detrimental to those not in the top few as it causes greater tensions between teaching (the bulk of the work), research (usually a small portion of work) and time/energy. I don’t believe that life is rosy for those academics in the top tier of institutions – the pressures placed upon them to perform, bring in more and more funding, produce better quality papers in the top journals, etc. must be enormous. But that is a different type of pressure to that experienced in universities such as BU where the tension between teaching and research and time are very real. Goffman described this tension by stating that it makes an academic career “perhaps as complex and troubled as the moral career of the mental patient”.
 I’m not sure what the answer is that gives this a happy ending. It is likely there isn’t one and the tensions will remain, but BU’s fusion strategy and the new academic career framework should ensure that, internally at least, all activities are equally valued. None of the information in this post is new, however, sometimes it does us good to step back from the precipice and acknowledge the tensions before deciding the next step. We need to continue to play the game of the research-oriented university as this is what the sector is increasingly basing itself upon, but we must do it in a way that is right for BU and doesn’t tie us all up in knots. Any thoughts?
I’m not sure what the answer is that gives this a happy ending. It is likely there isn’t one and the tensions will remain, but BU’s fusion strategy and the new academic career framework should ensure that, internally at least, all activities are equally valued. None of the information in this post is new, however, sometimes it does us good to step back from the precipice and acknowledge the tensions before deciding the next step. We need to continue to play the game of the research-oriented university as this is what the sector is increasingly basing itself upon, but we must do it in a way that is right for BU and doesn’t tie us all up in knots. Any thoughts?
![]() Following on from my post last Thursday, Research Professional have published the email from the seven Research Councils Chief Executives, explaining what ‘Research Councils Together’ will mean. RP have accompanied the email with a candid interpretation of what the content implies.
Following on from my post last Thursday, Research Professional have published the email from the seven Research Councils Chief Executives, explaining what ‘Research Councils Together’ will mean. RP have accompanied the email with a candid interpretation of what the content implies.














 speaker and guest speaking at key universities and research institutes.
speaker and guest speaking at key universities and research institutes.













 April’s Café Scientifique – Should we help machines understand and respond to our emotions?
April’s Café Scientifique – Should we help machines understand and respond to our emotions? Postgraduate Research Experience Survey (PRES) 2024 – 2 WEEKS LEFT
Postgraduate Research Experience Survey (PRES) 2024 – 2 WEEKS LEFT Working with The Conversation: online training session – Wednesday 8th May
Working with The Conversation: online training session – Wednesday 8th May Apply for up to £1,000 to deliver an event and take part in a national festival of public engagement with research
Apply for up to £1,000 to deliver an event and take part in a national festival of public engagement with research MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024 Horizon Europe News – December 2023
Horizon Europe News – December 2023