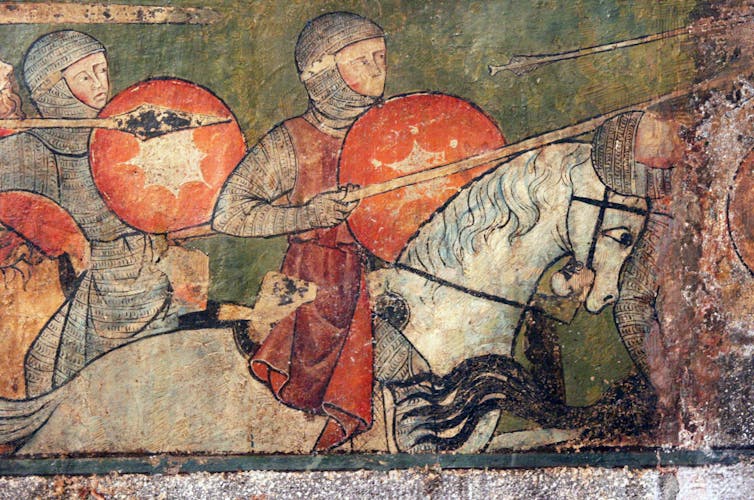

Holly Hayes/Flickr, CC BY-NC
King Arthur is probably the best known of all British mythological figures. He is a character from deep time celebrated across the world in literature, art and film as a doomed hero, energetically fighting the forces of evil. Most historians believe that the prototype for Arthur was a warlord living in the ruins of post-Roman Britain, but few can today agree on precisely who that was.
Over the centuries, the legend of King Arthur has been endlessly rewritten and reshaped. New layers have been added to the tale. The story repeated in modern times includes courtly love, chivalry and religion – and characters such as Lancelot and Guinevere, whose relationship was famously immortalised in Thomas Malory’s 1485 book Le Morte D’Arthur. The 2017 cinematic outing, King Arthur: Legend of the Sword, is only the most recent reimagining.
But before the addition of the Holy Grail, Camelot and the Round Table, the first full account of Arthur the man appeared in the Historia Regum Brianniae (the History of the Kings of Britain) a book written by Geoffrey of Monmouth in around 1136.
We know next to nothing about Geoffrey, but he claimed to have begun writing the Historia at the request of Walter, archdeacon of Oxford, who persuaded him to translate an ancient book “written in the British tongue”. Many have concluded, as Geoffrey failed to name his primary source and it has never been firmly identified, that he simply made it all up in a fit of patriotism.
Whatever the origin of the Historia, however, it was a roaring success, providing the British with an heroic mythology – a national epic to rival anything written by the English or Normans.
Story teller
As a piece of literature, Geoffrey’s book is arguably the most important work in the European tradition. It lays the ground for not just for the whole Arthurian Cycle, but also for the tales surrounding legendary sites such as Stonehenge and Tintagel and characters such as the various kings: Cole, Lear and Cymbeline (the latter two immortalised by Shakespeare).
As a piece of history, however, it is universally derided, containing much that is clearly fictitious, such as wizards, magic and dragons.
If we want to gain a better understanding of who King Arthur was, however, we cannot afford to be so picky. It is Geoffrey of Monmouth who first supplies the life-story of the great king, from conception to mortal wounding on the battlefield, so we cannot dismiss him entirely out of hand.
A full and forensic examination of the Historia Regum Britanniae, has demonstrated that Geoffrey’s account was no simple work of make-believe. On the contrary, sufficient evidence now exists to suggest that his text was, in fact, compiled from a variety of early British sources, including oral folklore, king-lists, dynastic tables and bardic praise poems, some of which date back to the first century BC.
In creating a single, unified account, Geoffrey exercised a significant degree of editorial control over this material, massaging data and smoothing out chronological inconsistencies.
Once you accept that Geoffrey’s book is not a single narrative, but a mass of unrelated stories threaded together, individual elements can successfully be identified and reinstated to their correct time and place. This has significant repercussions for Arthur. In this revised context, it is clear that he simply cannot have existed.
Arthur, in the Historia, is the ultimate composite figure. There is nothing in his story that is truly original. In fact, there are five discrete characters discernible within the great Arthurian mix. Once you detach their stories from the narrative, there is simply nothing left for Arthur.
Cast of characters
The chronological hook, upon which Geoffrey hung 16% of his story of Arthur, belongs to Ambrosius Aurelianus, a late 5th-century warlord from whom the youthful coronation, the capture of York (from the Saxons) and the battle of Badon Hill is taken wholesale.
Next comes Arvirargus, who represents 24% of Arthur’s plagiarised life, a British king from the early 1st century AD. In the Historia, Arthur’s subjugation of the Orkneys, his return home and marriage to Ganhumara (Queen Guinevere in later adaptions) parallels that of the earlier king, who married Genvissa on his return south.
Constantine the Great, who in AD 306 was proclaimed Roman emperor in York, forms 8% of Arthur’s story, whilst Magnus Maximus, a usurper from AD 383, completes a further 39%. Both men took troops from Britain to fight against the armies of Rome, Constantine defeating the emperor Maxentius; Maximus killing the emperor Gratian, before advancing to Italy. Both sequences are later duplicated in Arthur’s story.
The final 12% of King Arthur’s life, as recounted by Geoffrey, repeat those of Cassivellaunus, a monarch from the 1st century BC, who, in Geoffrey’s version of events, was betrayed by his treacherous nephew Mandubracius, the prototype for Modred.
All this leaves just 1% of Geoffrey’s story of Arthur unaccounted for: the invasion of Iceland and Norway. This may, in fact, be no more than simple wish-fulfilment, the ancient Britons being accorded the full and total subjugation of what was later to become the homeland of the Vikings.
Arthur, as he first appears, in the book that launched his international career, is no more than an amalgam. He is a Celtic superhero created from the deeds of others. His literary and artistic success ultimately lies in the way that various generations have reshaped the basic story to suit themselves – making Arthur a hero to rich and poor, elite and revolutionary alike. As an individual, it is now clear that he never existed, but it is unlikely that his popularity will ever diminish.
Dr Miles Russell, Senior Lecturer in Archaeology, Bournemouth University
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.







 The British Library is running a series of
The British Library is running a series of 











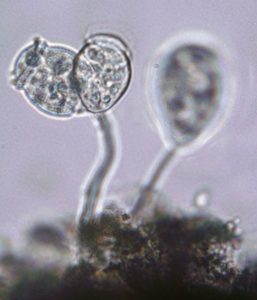 Microscopic investigations of water samples from the half-barrel pond in Christchurch House courtyard have revealed a menagerie of single-celled life. These tiny organisms (smaller than one tenth of a millimetre) are incredibly important as they form the basis of food webs. They also play a major role in maintaining water quality as they feed on bacteria, and stalked species such as Vorticella (image) are responsible for their removal in waste-water treatment plants. The half-barrel “pond” may be almost as small as its inhabitants but it promises to become a treasure of local ‘hidden’ biodiversity!
Microscopic investigations of water samples from the half-barrel pond in Christchurch House courtyard have revealed a menagerie of single-celled life. These tiny organisms (smaller than one tenth of a millimetre) are incredibly important as they form the basis of food webs. They also play a major role in maintaining water quality as they feed on bacteria, and stalked species such as Vorticella (image) are responsible for their removal in waste-water treatment plants. The half-barrel “pond” may be almost as small as its inhabitants but it promises to become a treasure of local ‘hidden’ biodiversity!











 TANGERINE project has lift off with BPC Indian Community!
TANGERINE project has lift off with BPC Indian Community! Postgraduate Research Experience Survey (PRES) 2024 – Closing today
Postgraduate Research Experience Survey (PRES) 2024 – Closing today THE INNOVATION COMMON ROOM: Going Old School
THE INNOVATION COMMON ROOM: Going Old School Apply for up to £1,000 to deliver an event and take part in a national festival of public engagement with research
Apply for up to £1,000 to deliver an event and take part in a national festival of public engagement with research MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024 Horizon Europe News – December 2023
Horizon Europe News – December 2023