In the final blog post of the week in this series, Dr Ashok Patnaik, shares his insights into overcoming the challenges associated with undertaking social science research during a global pandemic including how he has challenged boundaries in research ethics to ensure research critical for the future of our children can progress. Ashok also openly reflects on the personal challenges the past year has brought and how he drew on the support around him to grow personally and intellectually:
 “The lockdown period has been difficult in some respects but also wonderful in some others. It has offered plenty of opportunities for reflection and growth, as a researcher and as a human being. Strange though it may be to say it, it has been very timely and fortuitous in some ways because these extraordinary circumstances have enabled me, and the team I am part of, to achieve things which, during normal times, may have proved much more difficult. Thus, to paraphrase Dickens, it has been the worst of times, and it has been the best of times.
“The lockdown period has been difficult in some respects but also wonderful in some others. It has offered plenty of opportunities for reflection and growth, as a researcher and as a human being. Strange though it may be to say it, it has been very timely and fortuitous in some ways because these extraordinary circumstances have enabled me, and the team I am part of, to achieve things which, during normal times, may have proved much more difficult. Thus, to paraphrase Dickens, it has been the worst of times, and it has been the best of times.
I have the great fortune of being part of a brilliant academic team based in the BUBS which is working on the evaluation of an exciting movement-based mental health intervention for primary school-aged children called ‘Stormbreak‘. As part of the evaluation of Stormbreak, we use a range of data collection methods but the centrepiece of the evaluation is the child well-being survey. We use a pre-post study design for the survey, and had completed the pre-intervention survey in January, 2020.
The immediate impact of school closure in March last year due to the lockdown was the inability to complete the planned second leg of the survey (the post-intervention survey). This was scheduled for the end of the school term (late March). As a result, we had an incomplete dataset and could not calculate the change scores needed to evaluate the impact of the intervention. This meant that we could not add new data to the impact report. This affected our partner organisation’s ability to demonstrate the effectiveness of the intervention and slowed down the expansion of the programme which had begun gathering pace before the lockdown.
While this was, undoubtedly, regrettable, the lockdown proved to be a blessing in disguise in many ways. Doing research with children in schools involves many challenges, but the biggest bottleneck for us was obtaining parental consent. The majority of parents did not respond to schools’ invitations to take part in the study. Our participation rates ranged from 10% to 40% (at best). We were losing a lot of participants. The necessity of contacting parents repeatedly through multiple communication channels was adding extra work for schools and making them re-consider their engagement with the evaluation. The new pressures on schools that arose in the aftermath of the pandemic were fast making the consent process untenable. The viability of the whole project was at risk. We knew that we had to do something.
The principal obstacle was the strong and near universal consensus on active parental consent in research with young school children. The new requirements brought in by the GDPR had reinforced this consensus and made it a kind of orthodoxy. However, there were also several examples of eminent research institutions such as UCL, LSE, and other organisations conducting research on behalf of the UK Government and the Department of Education such as Ipsos-MORI and NatCen bucking the trend and relying on a passive parental consent approach. We knew that we had to move to the latter approach, but given the widespread and strongly entrenched belief in the necessity of active parental consent, we knew that we would have to prepare a compelling case to persuade the Social Sciences & Humanities Research Ethics Panel (SSH REP) to consider our request. It was a daunting task.
Thankfully, the lockdown period gave us the time and the space to work, without distraction, to amend the ethics process. It was a period free from the short-term pressures of data collection. During the peaceful, quiet months of the lockdown, we were able to marshal a wide-ranging body of evidence and a number of strong arguments to support our case for passive parental consent for the child well-being survey. Professor Michael Silk, Dr. Daniel Lock, and I collaborated on this work, which eventually turned into a Master’s Dissertation-length essay, perhaps the longest application considered by the SSH REP.
Our work bore fruit, and our application was reviewed favourably by the SSH REP. We are very grateful to our excellent SSH REP, especially the Chair Professor Jonathan Parker and the Deputy Chair Professor Richard Berger, and Ms. Sarah Bell, for their sympathetic consideration of our application. Their supportive decision removed the biggest constraint on the growth of the study and restored its viability.
With the end of the lockdown in September, we resumed data collection. However, schools’ new risk assessment policies made access to schools difficult. Professor Silk foresaw the need to adapt our ways of conducting the study. He recognised that the previous approach, which involved my visiting schools in person to administer the survey, would not be feasible in view of the restricted access policy of most schools post-pandemic. Further, as the Stormbreak programme scaled up and expanded nationally, personal visits would not be practical. Professor Silk saw the need to fully digitise the conduct of the survey.
Thus began our second major endeavour – to fully digitise the administration of the survey. We worked with the fantastic Red Balloon Media Production Team, headed by the highly creative Stephanie Farmer, and with the brilliant graphics designer and computer programmer Vitor Vilela. With their support, and that of the exceptionally helpful Stormbreak team (especially Dr. Martin Yelling, who kindly and patiently recorded, and re-recorded, and re-re-recorded parts of the script with his children), we have worked through the winter months to create an engaging, child-friendly digital solution, consisting of fun videos and a snazzy questionnaire. This was uncharted territory for us. Thanks to Steph’s and Vitor’s understanding and patient approach, we learnt about this new field and have together produced a digital version of the study that we feel genuinely excited about, and which, we feel, will assist materially in conducting the study remotely. It was also pleasing to note that, in digitising the study processes, we were able to make them more efficient and streamlined.
Personally, the lockdown has been, by and large, a happy period. Relatively free from the administrative work involved in data collection, I have been able to focus on what I love best – quiet periods of reading, thinking, and writing (what the author Cal Newport calls ‘deep work‘). I have been able to live a quiet, productive, monastic life, largely free of disturbance. With the end of the lockdown approaching, that blissful period is ending fast. Over the last two years, balancing the short-term work of data collection (along with the administrative work involved in running a project) with long-term work (skill development, working on journal articles, applying for research funding) has been a constant challenge for me. During the last few months, I have experimented a lot with my routines and have become a little better at organising my work so that I am addressing both short-term and long-term work needs. The flexibility of working at home, and the time and energy saved from not having to go to the office have helped a lot in this regard.
My experience during the lockdown has kept the subject of mental health at the forefront of my mind. Like others, I have struggled at times with isolation and loneliness (especially when I returned from leave and was in quarantine). The lockdown has also clearly reinforced the incredible importance of physical activity in creating positive feelings. Running or playing basketball or Table Tennis brought a smile to my face on days when there were few other things to feel happy about.
There was a period of about ten days during the summer when my mental health was severely affected. It was a very difficult period. What helped me most during this time was conversations with family members and the support of my line manager, Professor Michael Silk. He very kindly and swiftly sourced support for me from the BU Employee Assistance Programme. He was there for me, and his support taught me an important lesson about leadership, loyalty, and caring. The lockdown has also made me recognise the importance of communities – personal and professional. It has helped me gain perspective and see more clearly what truly matters in life and to make space for it in my calendar. The challenge will be to remember those lessons and keep them uppermost in my mind as we move towards normality and the old, all-too-familiar pressures attempt to sway me from the high road. Already, I can see myself slipping back into old, unproductive routines as the urgent crowds out the important. This battle will continue for a long time.
In summary, I would say that I feel incredibly grateful for the unexpected opportunities resulting from the lockdown. There are things I have accomplished with others during this period which would not have been possible but for the unique circumstances created by the lockdown. There have been ups and downs, but many, many more ups than downs. On the whole, I find myself having grown and matured significantly – as a researcher and as a human being – during the last year, and I would not trade this experience for anything.”

 NEW for 2021! Promoting research culture at BU and celebrating postgraduate researcher achievements, the Doctoral College are collating
NEW for 2021! Promoting research culture at BU and celebrating postgraduate researcher achievements, the Doctoral College are collating  Research Funding Panels: To help us further develop our research capacity in line with BU2025, the Research Performance and Management Committee (RPMC) oversees research investment and performance. Under the auspices of the RPMC, Funding Panels have been established to have oversight of funding allocations, in order to further build the research environment, our external engagement and the quality and impact of research endeavours. There are seven funding panels and future calls will be released on the BU intranet. You can find out
Research Funding Panels: To help us further develop our research capacity in line with BU2025, the Research Performance and Management Committee (RPMC) oversees research investment and performance. Under the auspices of the RPMC, Funding Panels have been established to have oversight of funding allocations, in order to further build the research environment, our external engagement and the quality and impact of research endeavours. There are seven funding panels and future calls will be released on the BU intranet. You can find out  Strategic Investment Areas: As articulated within
Strategic Investment Areas: As articulated within  STEAMLabs: These offer the opportunity to meet new people from all disciplines and sectors, and to spend dedicated time developing novel ideas for research projects. We will select topics for STEAMLabs and advertise these for participants. For example, each year we run a STEAMLab for each of the four SIAs. These seek to come up with highly innovative and urgently required research which is ambitious in scope and will require a high level of expertise, commitment and funding. The research must address challenges in the topics advertised. As a result of each STEAMLab, we anticipate the development of innovative, ground-breaking and ambitious projects which have the capacity to attract significant, high value funding from the public and private sectors.
STEAMLabs: These offer the opportunity to meet new people from all disciplines and sectors, and to spend dedicated time developing novel ideas for research projects. We will select topics for STEAMLabs and advertise these for participants. For example, each year we run a STEAMLab for each of the four SIAs. These seek to come up with highly innovative and urgently required research which is ambitious in scope and will require a high level of expertise, commitment and funding. The research must address challenges in the topics advertised. As a result of each STEAMLab, we anticipate the development of innovative, ground-breaking and ambitious projects which have the capacity to attract significant, high value funding from the public and private sectors.

 Horizon Scanning and finding funder opportunities: The Research Facilitators within
Horizon Scanning and finding funder opportunities: The Research Facilitators within 
 RKEDF: The Research Development and Support (RDS) team have a range of development and support options available to BU academics. The majority of these are badged under the
RKEDF: The Research Development and Support (RDS) team have a range of development and support options available to BU academics. The majority of these are badged under the 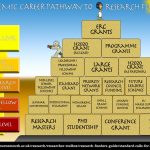 Career stage development: As part of the RKEDF, the
Career stage development: As part of the RKEDF, the  Early Career Researchers Network: As mentioned above, the ECRN, run by academics for academics, offers monthly sessions for ECRs on a range of topics. Chaired by Professor Ann Hemingway (FHSS) and Dr Sam Goodman (FMC), sessions are held for general discussions, networking, and specific topics to support early career researchers. Still to come in 20/21 is:
Early Career Researchers Network: As mentioned above, the ECRN, run by academics for academics, offers monthly sessions for ECRs on a range of topics. Chaired by Professor Ann Hemingway (FHSS) and Dr Sam Goodman (FMC), sessions are held for general discussions, networking, and specific topics to support early career researchers. Still to come in 20/21 is:

 Throughout the Covid-19 pandemic, the news media have played an instrumental role in providing the latest updates and information. An increasing number of people, however, have sometimes avoided the news, finding negative coverage has a detrimental effect on their mood and wellbeing.
Throughout the Covid-19 pandemic, the news media have played an instrumental role in providing the latest updates and information. An increasing number of people, however, have sometimes avoided the news, finding negative coverage has a detrimental effect on their mood and wellbeing.
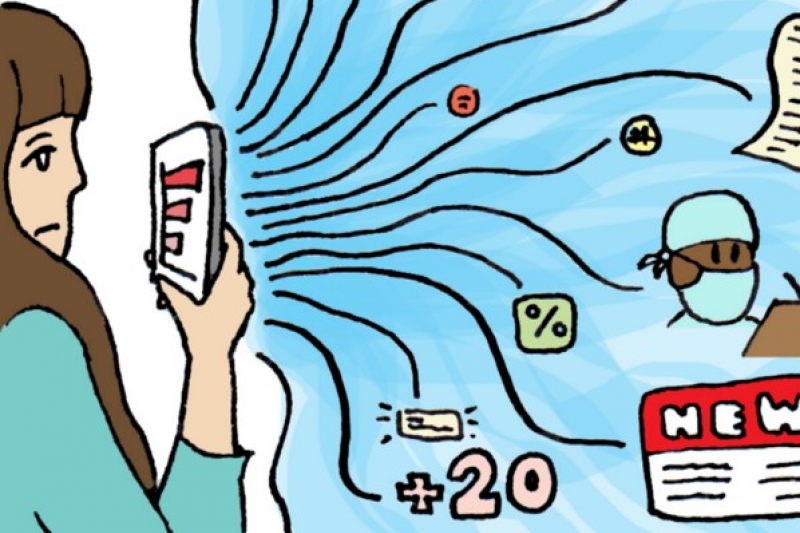 Research at Bournemouth University is looking at the effectiveness of comic artistry and storytelling in the sharing of public health messaging.
Research at Bournemouth University is looking at the effectiveness of comic artistry and storytelling in the sharing of public health messaging.
 This morning we meet members from the Social Sciences & Humanities Research Ethics Panel (SSH REP).
This morning we meet members from the Social Sciences & Humanities Research Ethics Panel (SSH REP).










 New Bournemouth University public health paper
New Bournemouth University public health paper New ACORN-funded paper published. When time is short but passion for food is strong, food day-tripping may be the answer!
New ACORN-funded paper published. When time is short but passion for food is strong, food day-tripping may be the answer! Third INRC Symposium: Interdisciplinary Computational and Clinical Approaches at the Edge of Brain Research
Third INRC Symposium: Interdisciplinary Computational and Clinical Approaches at the Edge of Brain Research Royal Society of Chemistry Outreach Fund: Open for Applications
Royal Society of Chemistry Outreach Fund: Open for Applications Last reminder – MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024 internal deadline next week
Last reminder – MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024 internal deadline next week Horizon Europe – EuroHPC and MSCA PF webinars
Horizon Europe – EuroHPC and MSCA PF webinars