This is your half term catch up policy update.
Regulatory
OfS: Freedom of Speech
Following the passage of the new law, the OfS has announced the appointment of Professor Arif Ahmed as the first Director for Freedom of Speech and Academic Freedom. Professor Ahmed chose the Times to write about his appointment, so we turn to Wonkhe for a perspective. For Wonkhe, Jim Dickinson focuses on the potential conflicts and challenges with balancing free speech and academic freedom with equality rights, and as an example, highlights Professor Ahmed’s previously stated position on the IHRA definition of antisemitism, which conflicts with the government’s position (and specifically the position of the current Secretary of State for Education). You will recall Michelle Donelan getting herself in a muddle over this issue too. It’s going to be interesting to watch this unfold. As Jane learned a long time ago, hard cases make bad law…and it seems a lot of the cases are going to be hard.
The work of the OfS: Minister Halfon examined
The Lords Industry and Regulators Committee conducted it’s final session examining the work of the OfS by interviewing FE and HE Minister Robert Halfon alongside Anne Spinali, Director of Higher Education Reform and Funding at the DfE. Alongside the probe into the OfS the session is useful to highlight the latest ministerial thinking on the key issues facing the sector today.
HE Financial health
The Chair opened the session by highlighting the concerns the HE sector had reported over financial sustainability, loss of Horizon funding, dependency on international students and how these combine to create other vulnerabilities. Halfon listed the various income sources of HE institutions (e.g. tuition fees, other income, research grants, funding body grants, investment, donations and endowment) highlighting that universities get up to just under £40 billion…among 400 registered institutions. That is not a small sum of money…We also know that 75% of universities are in good financial condition. The question I would ask…is why the vast majority of universities are able to be in good financial health while a few are not… Later in the session he implied this is due to the management and leadership of these particular institutions.
Nevertheless, despite the challenges of Covid, the cost of living, energy bills and so on, on the whole, given the current context that we are in, HE—higher education—is not doing too badly financially. If you…look at the funding that HE has got compared to the funding that further education has got over the last few years, there is no comparison. Halfon also confirmed he thinks the OfS’ risk based approach to monitoring is the right approach and he continued his predecessor’s party line that The priority of the Government when it comes to financial difficulties at universities must be to look after the students. That is where I believe a government intervention would be, if there was severe financial difficulty for a particular higher education institution, to make sure that they had a provider to go to. Halfon also reminded the Committee that during Covid there was precedent through the HE restructuring fund. However, he also implied he didn’t subscribe to the concept that some universities were too big to fail and that he, personally, preferred mobile, agile universities.
Anne Spinali noted that some universities with financial concerns approached the DfE before they took the matter up with the OfS.
Financial sustainability came up time and again throughout the session, however, Halfon held firm that he thinks the sector is in a good position, even if time lags may be masking how many will become unsustainable in the medium term:
- Given the current circumstances, given that universities get £40 billion from a variety of sources, given that 75% of them have a surplus and given everything else that is going on in the economy and the public sector, HE is in a fairly strong position compared with other parts of the public sector.
- I will always welcome and champion more resources for HE and FE, of course, but I want more funding for skills… I want to ask, “What’s the best way to ensure that we have more qualified people who get good, skilled jobs at the end of their education?” That is the way I look at it. I look at it not as “university, university, university” but as “skills, skills, skills”.
On the freezing of tuition fees (and real terms decrease in their value): …if the economy improves, we get back into surplus again, we get rid of our deficit, we get down the £2 trillion debt and we pay back the £400 billion that we spent during Covid, maybe…we will have more money and will be able to increase tuition fees. However, I am not an advocate of increasing tuition fees. It would hit the student, importantly, at a time when things are very difficult. That does not mean that they are never going to go up but the approach of the Government has been the right one.
International Students – a conflicting view?
Halfon stated he is very supportive of international students. I think that they are a good thing…my wife was an international student. Halfon spoke of the benefits international students bring aside from finance they are examples of soft power as well as being worth 25 billion quid to our economy…I do not see having too many international students as a risk.
Halfon also stated he does not believe there is a dependency on international students and that their numbers will not decline:
- Given that 76% of students are domestic, I do not necessarily think that it is the problem that some people view it as…I do not see this as a problem in the way that may be felt by yourself. It is a good thing, especially given the current financial context we are in.. It is worth £25 billion; the ambition is that it will be worth £35 billion by 2030. That is very significant. If you look at the cost benefit of those international students, it outweighs the issues you may raise, such as that we have an unsustainable model.
- We also have a cost of living crisis. The last thing I can do is go and tell students that we are going to raise their tuition fees. I feel a lot of pressure in the House of Commons from Members on all sides about why we did not raise the maintenance grant or maintenance loan higher than we did… Nevertheless, you have to be fair to students and to the taxpayer.
- Given the financial situation that we are in, if universities are getting cross-subsidisation from international students, that is not a bad thing. I agree with you that it is dangerous to rely on one or two countries. We are doing a lot of work on diversification there… I worry about dependency on one or two countries. A lot more work needs to be done.
Halfon reveals his preferred vision for future HE institutions
- The underlying part of your question is perhaps not even about the loan system but about whether the funding of universities and their business model should be done differently. That may be right. It requires a lot of thinking and work to see whether the current system is sustainable…
- …my dream university of the future is the Dyson Institute. The reason for that is that it has a business on-site. It does research. It does vocational degree apprenticeships. The people who complete them get jobs in Dyson afterwards. It is very agile; I would like to see a lot more of that. That is a sustainable model for the future. I also want to do more to encourage degree apprenticeships because, again, you then avoid the whole issue of tuition fees.
- …my dream would be to have 50% of our students doing degree apprenticeships one day. They help the disadvantaged. They build our skills base. They guarantee jobs for people who complete them. Now, we have Russell group universities as well as traditional vocational universities doing them.
- It is not just for STEM, by the way. You could have one easily in the creative industries. You could have the British Museum doing the same thing, for example, where people can study archaeology or curating or whatever it may be. If I was thinking of universities in the 21st century, it would be more on that model.
- …the [Halfon’s] vision is clear: it is jobs, skills and social justice. It does what it says on the tin. In my view, apart from the stuff that it does brilliantly already—research, et cetera—the engine of HE should be geared towards those purposes. That is the strategy of the Government.
Regulatory burden
Anne Spinali: There is a difference between institutional autonomy being impinged and regulatory burden…Both the OfS and the department are absolutely clear that institutional autonomy is paramount. Whether the regulatory burden is proportionate is a question for the OfS. It has recognised that it could do more to tackle this and is actively looking at areas where it could reduce its regulatory activity by taking a more risk-based approach. Halfon felt the OfS regulatory requirements were not onerous for a university, but, that universities also fall under the regulation of a range of institutions are regulated by a range of organisations (page 16) whereas Halfon would prefer a more streamlined model. However, Halfon did express disapproval at the OfS digital uploading system: I definitely think that that has to go. On minimising regulatory burden we also heard that the Government are considering a third category of registration for the lifelong loan entitlement which draws on existing material to reduce the regulatory burden.
Halfon: In my view, it [OfS] should be there partially to protect the autonomy of universities. The Government do not always get their way. They [OfS] are perfectly able to refuse to adopt the guidance that we suggest.
Sector relations with OfS: In response to Lord Reay’s question of whether the OfS was distant and often combative and the HE relationship characterised by a lack of trust Halfon stated: there needs to be much more informal engagement between the OfS and HE because, in my six months in the job, that has come up time and again. That would be beneficial. To be fair to the OfS, it does a lot of round tables and a lot of events with universities. It is not perfect but, inevitably, you are going to have some difficulties because of what the OfS is tasked to do.
Value for money: Halfon – I have a really firm view: in terms of HE and value for money, it must be about outcomes and jobs with good skills and progression. Otherwise, if you do not achieve what you should afterwards, what is the point of spending all that time at university and taking out the loan? Halfon also mentioned transparency with fees and ensuring students understand what they are getting for their money on application, including in person teaching.
OfS fees: Halfon refused to be drawn on the 13% OfS fee increase. He stated OfS reduced their fees in 2021-22 but they are inevitably going to have to go up because of the QAA coming in but we are consulting with government and the OfS… We will make an announcement on it in the very near future.
The announcement came shortly after the session – we’ve covered it here.
Robert Halfon has also written to the House of Lords Industry and Regulators Committee giving further background and justification for Tuesday’s announcement of a sizable increase to OfS registration fees for 2023–24.
We also learnt, from Anne Spinali, that the DfE has quarterly discussions with the OfS on its efficiency, its spend and how it is discharging its responsibilities with regard to the spend. The economy, efficiency and effectiveness of the way in which it discharges its responsibilities, and what it does with its £26 million of fees, are monitored really actively. It is robustly challenged on resources associated with activities. It is a difficult challenge and discussion sometimes in terms of the level of resources needed to carry out the whole breadth of activities that the OfS has to carry out.
For more detail see the – Transcript, watch the session on Parliament TV or review the inquiry information.
Financial sustainability (OfS)
The OfS published their annual financial sustainability report updating on the financial health of the HE sector. If finds that university finances are generally in good order but that there are growing risks to the sector’s finances such as the over-reliance on international student recruitment, sustainability of pension schemes, investment in facilities and environmental policies and inflationary pressures. Belying this headline statement, however, is a more mixed picture of the financial performance of different universities. The OfS also wrote to 23 HEIs who have high student recruitment from China urging them to have contingency plans in place in case recruitment patterns change and there is a sudden drop in income from overseas students.
- Income – sector growth across the next three years (£40.8 billion in 2021-22 to £50.1 billion forecast in 2025-26).
- Improved cash flow and surplus, but the sector is forecasting a decline in financial performance and strength in 2022-23, with costs increasing at a faster rate than income and a significant dip in the income and expenditure surplus.
- In 2021-22 total HE course fees and education contracts were reported at £22.5 billion (+8.8%). Fee income is forecast to increase to £29.3 billion by 2025-26, with a 17.5% forecast rise in student numbers between 2021-22 and 2025-26 across all levels of study. However, this trend varies significantly between different universities and colleges.
- Total non-EU (overseas) tuition fee income was reported at £7.8 billion in 2021-22 (+25%). This is consistent with strong growth in overseas fees in recent years. Non-EU fee income as a proportion of total income is forecast to increase from 19.3% in 2021-22 to 24% in 2025-26, which the report states highlights the sector’s increasing reliance on fees income from non-EU students to sustain their activities.
- Overall cash flow and short-term investments are reported as £16.6 billion for 2021-22 (+10% on 2020-21).
The key risks are:
- impact of inflation on costs and challenges in growing income to meet increasing costs
- increasing reliance on fees from overseas students in some higher education provider’s business plans, especially students from China or any individual country
- challenges in meeting investment needs for facilities and environmental policies.
And it’s not all about China, the OfS says:
… Teaching-intensive providers can be particularly reliant on tuition fees from students. In recent years, many have successfully increased their recruitment of overseas students, particularly from India and Nigeria, onto postgraduate and undergraduate courses. These providers also face significant staff and pensions costs. In the event of a reduction in the total numbers of students coming to the UK from China, it may be that research-intensive providers are able to attract UK and international students away from teaching-intensive providers
In response to these risks and financial pressures the OfS says they anticipate providers may adopt certain behaviours (which they’ll be keeping an eye on if the impact on student choice and experience):
- closing courses which are less financially sustainable
- rebalancing recruitment from UK students to overseas students
- reducing research activity where funding may not cover the full cost of research
- pursuing strategic mergers and/or collaborations or sharing resources and centralising costs
- changes to course delivery models – including standardisation in academic subjects, more online and distance learning
- increases in specialisation – we may see a concentration of more providers with academic specialisms or niches, with the aim of reducing competition risks.
- Seeking to diversify commercial income streams – from activity that is not teaching or research
- reducing the size and complexity of estates
Susan Lapworth, OfS chief executive, said: Universities and colleges have weathered storms over recent years, and most remain in good financial health. This new analysis shows that they are confident that income and student numbers will continue to grow. However, cost pressures are having a substantial impact, with an expected reduction in financial performance across the sector in the short-term…‘For a small number of institutions the financial picture is of particular concern and we will continue to focus our attention on those cases. But all institutions will continue to face financial challenges, with a number of risks present at the same time for many.
…we continue to have concerns that some universities have become too reliant on fee income from international students, with students from one country sometimes a significant part of the financial model.
You may also be interested in this Research Professional article: A fine balance.
More coverage in: The Guardian, i News, and Wonkhe.
OfS Registration Fee hike
The Government has supported (and legislated for) an 18%[1] fee hike that universities will pay the OfS to maintain their registration as a provider of HE. Many institutions will now pay £170,344 each year and the largest universities will pay £214,485. Across all providers it will generate £4.96 million for the OfS. Universities Minister wrote to the House of Lords Industry and Regulators Committee (who are running an inquiry into the work of the OfS) to justify the increase. His justifications stated the OfS will be undertaking significant and important new work, including:
- The implementation of the Higher Education (Freedom of Speech) Act 2023, to ensure that freedom of speech is protected and promoted within higher education (guidance, consultation on complaints scheme, developing new registration conditions and making changes to the regulatory framework)
- Following the de-designation of the Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education (QAA) as the designated quality body under HERA, the OfS has taken on functions relating to the assessment of quality and standards. his fee increase will enable the OfS to fund the infrastructure costs associated with the performance of these assessment functions
- Preparing for the implementation of the Lifelong Loan Entitlement
Halfon stated: I want to assure you that the government has not taken this decision lightly. I understand the financial pressure the sector is currently facing. As a result, my Department will be providing £1.5 million of additional funding to the OfS this year, to help cover its costs and prevent these from being passed on to the sector in full. Earlier he reminded that the OfS has not had a registration fee increase since 2018, when it was set up, and delivered a 3% reduction in 2021.
Wonkhe say:
- For a sector facing a real terms freeze in fee income it does feel a little tone deaf to be seeking an increase substantially above the rate of inflation.
- To a sector struggling with soaring inflation, rising costs, and income streams that are at best stable this will be a difficult pill to swallow.
- There were always limitations to farming the cost of regulation to providers that receive large amounts of their funding from the public purse – it is an inefficient model and one that has never met the running costs of the OfS. Announcing this in the current financial climate pours petrol onto the already flammable state of relations between the regulator and the sector it manages.
Once it’s published we’ll scour the Lords Committee report to see what their reaction to the fee hike is.
[1] Percentage rise in fees: Wonkhe modelling shows 18%, Halfon’s letter states 0-12% per provider
Graduate outcomes
HESA have published the Graduate Outcomes data for students who graduated in 2020/21. The headline is positive on full time employment (up 4%).
Of course, as we know, the OfS metric is “highly skilled employment and further study” – we will have to wait a bit longer for that analysis. Wonkhe have an article on why comparability of data on employment outcomes is a real issue.
International
International Students: Economic benefits
HEPI and partners published the third iteration of The benefits and costs of international higher education students to the UK economy. The research sought to quantify the economic benefits – less any costs – of international students and family members living and studying in the UK. The report demonstrates growth in the financial worth of international students.
The modelling includes tuition fee income, living expenditure, and indirect income from family and friends visiting the UK – tax revenue, longer-term investment, soft power, and cultural value are not included in the analysis.
- 4 in 10 first year students in London are international
- Some areas benefit more financially from international students, outside of London this includes Glasgow, Nottingham and Newcastle.
- On average, each parliamentary constituency in the UK is £58 million better off because of international students – equivalent to approximately £560 per citizen.
- Even when accounting for dependants and other costs, international students are a huge net contributor to the UK economy. Every 11 non-EU students generates £1 million worth of net economic impact for the UK economy.
- The estimated total benefit to the UK economy from 2021/22 first-year international students over the duration of their studies was approximately £41.9bn, while the estimated total costs were £4.4bn. This implies a benefit-to-cost ratio of 9.4.
- The net economic impact per student was estimated to be £125,000 per EU domiciled student, and £96,000 per non-EU student. In other words, every 9 EU students and every 11 non-EU students generate £1m worth of net economic impact for the UK economy over the duration of their studies.
- Reflecting the 40% increase in the number of international students between 2018/19 and 2021/22, the net economic impact has increased from £28.2bn for the 2018/19 cohort to £37.4bn for the 2021/22 cohort (a 33% increase in real terms). The impact has also increased by 58% in real terms since 2015/16 (from £23.6bn in 2015/16 to £37.4bn in 2021/22).
The Russell Group published their response to the report.
HEPI also have some short commentary setting out the policy position on each of the areas of contention for international students.
Growth in international student recruitment:
- The UK is an attractive destination for international students because of the global recognition of UK qualifications, teaching in English, and our one-year Masters courses are particularly popular.
- Between 2010 and 2016, there was no growth in international student numbers, as Home Office policies worked to limit incoming students.
- In 2019, the Government launched the International Education Strategy with a national target to increase the number of international students in the UK. The target was exceed well ahead of the deadline.
Post-study work visas: Post-study work rights were introduced in Scotland in 2005, adopted UK-wide in 2008, abolished in 2012, reintroduced in 2021, and the certainty of their future is…well…uncertain. HEPI write: post-study work rights affect the pipeline of talent flowing into the UK as well as the ability of employers to find and recruit the high-level and niche skills they so desperately need.
Diversifying student cohorts: institutions have been expected to widen their geographical base beyond China and East Asia…institutions have sought to broaden their intakes by recruiting more international students from other parts of the world, especially India and Nigeria. Yet the response of policymakers to this shift has not always been positive, for example because students from these regions are typically older and have a higher likelihood of bringing dependants with them.
International Students: Dependants’ visas
It was been trailed for weeks and finally we’ve had the official announcement that taught postgraduate students will not be permitted to bring their dependants into the country. This decision is part of Home Secretary, Suella Braverman’s, measures to reduce net migration. Here are all the measure in brief:
- Removing the right for international students to bring dependants unless they are on postgraduate courses currently designated as research programmes.
- Removing the ability for international students to switch out of the student route into work routes before their studies have been completed.
- Reviewing the maintenance requirements for students and dependants.
- Steps to clamp down on unscrupulous education agents who may be supporting inappropriate applications to sell immigration not education.
- Better communicating immigration rules to the higher education sector and to international students.
- Improved and more targeted enforcement activity.
The restrictions commence in January 2024, impacting the January starters in the 2023/24 academic year.
Braverman stated:
- Around 136,000 visas were granted to dependants of sponsored students in the year ending December 2022, a more than eight-fold increase from 16,000 in 2019, when the Government’s commitment to lower net migration was made
- We are committed to attracting the brightest and the best to the UK. Therefore, our intention is to work with universities over the course of the next year to design an alternative approach that ensures that the best and the brightest students can bring dependants to our world leading universities, while continuing to reduce net migration. We will bring in this system as soon as possible, after thorough consultation with the sector and key stakeholders.
- This package strikes the right balance between acting decisively on tackling net migration and protecting the economic benefits that students can bring to the UK. Now is the time for us to make these changes to ensure an impact on net migration as soon as possible. We expect this package to have a tangible impact on net migration. Taken together with the easing of temporary factors, we expect net migration to fall to pre-pandemic levels in the medium term.
- …The Government will seek to continue to strike the balance between reducing overall net migration with ensuring that businesses have the skills they need and we continue to support economic growth. Those affected by this package will predominantly be dependants of students who make a more limited contribution to the economy than students…
Read more: The BBC have coverage of the announcement, Wonkhe have a blog: everything we know about the new plans, i News has an opinion piece and there’s are parliamentary questions – Overseas student visas and adequacy of support for families moving on a student visa.
Research Professional cover the latest Transparent Approach to Costing (Trac) statistics which they state reveal just how reliant higher education institutions are on fees from overseas students in Deficits grow for research and teaching home students. Wonkhe cover the same topic with a different take: David Kernohan is depressed by how little we know about how much it costs universities to provide higher education. Also, an interesting exchange on the topic during Urgent Questions in the House of Commons on Wednesday. Do give it a read if you’re interested in this area.
More broadly on international student benefits is this Wonkhe blog: International and transnational education bring cultural, economic, and reputational benefits to the UK. University of London vice chancellor Wendy Thomson asks why the government isn’t over the moon.
Finally, the Government has now published the latest migration figures for the year ending March 2023. Total long-term immigration to the UK was around 1.2 million in 2022, and emigration was 557,000, so net migration settled at 606,000 (source). There is quite a lot of information of interest relating to students spread across multiple sources so we’ve popped it into this separate document. It covers the facts on study visas, extensions of temporary stay, and the migrant journey (who arrives, how long they stay, and when they leave). Enjoy!
International: Confucius Institutes
If you followed Rishi’s leadership campaign with an avid eye you’ll have spotted he committed to closing the 30 Chinese state-sponsored Confucius Institutes across the UK. However, the Government have U-turned stating it would be “disproportionate” to ban the institutes. Some Conservative Members have been outspoken in their disapproval of the U turn.
Dods report that Chair of the Foreign Affairs Committee, Alicia Kearns hit out in response to the news arguing that powers established recently under the new Higher Education (Freedom of Speech) Act 2023 “must be deployed if evidence of free speech stifled by CCP indoctrinators on our campuses.”
The BBC have a write up, including this from the Government:
- We recognise concerns about overseas interference in our higher education sector, including through Confucius Institutes, and regularly assess the risks facing academia.
- We are taking action to remove any government funding from Confucius Institutes in the UK, but currently judge that it would be disproportionate to ban them.
- Like any international body operating in the UK, Confucius Institutes need to operate transparently and within the law, and with a full commitment to our values of openness and freedom of expression.
As we mentioned earlier, this week the OfS wrote to 30 UK HE providers regarding their high recruitment levels of Chinese students. The letter advised contingency planning should a drop in income occur suddenly. Also, the OfS published their annual financial sustainability report (we’ve explored it here.)
Research
Health Security: The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) published a 10-year strategy detailing how science can save more lives and contribute to the UK’s ambition to be a global science superpower. It highlights how UKHSA’s scientific capabilities (including genomics, vaccine evaluation, surveillance, data science, diagnostics and toxicology) will be deployed to prepare for future health security hazards, respond to current threats, protect livelihoods and build the UK’s health security capacity. More here. UKHSA have stated they are actively seeking partners across government, industry and academia in pursuit of the ambitions in this Strategy.
Concordats: The second phase of the (UUK, UKRI & Wellcome Trust) Concordats and Agreements Review has reported, much shorter info here.
Net zero: The National Audit Office published Support for innovation to deliver net zero. The report addresses the approach in the £4.2 billion investment in research and innovation to deliver net zero. It argues that further action is needed to strengthen governance and delivery mechanisms to achieve value for money.
UKRI: UKRI launched a stakeholder perceptions survey which they state will act as a benchmark for the funding body to understand how their stakeholders perceive UKRI and its role within the system. The survey is here.
Research infrastructure: DSIT and UKRI announced details of the £103 million investment to expand and upgrade the UK’s research infrastructure. It’s not all new money, the funding divides as:
- £79.3m as part of the £150m announcement, to address the impacts of the ongoing delay in UK association to the EU’s Horizon Europe programme
- £23.7m as part of the £370m announcement to forge a better Britain through investment in science and technology
The 13 universities who will receive the equipment/lab investment have already been chosen. More on the funding here.
Windsor Framework: Responsibility for the delivery of the Windsor Framework will be transferred from the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office to sit alongside the existing Northern Ireland Unit in the Cabinet Office. The Foreign Secretary remains responsible for UK/EU relations and will continue as co-chair of the Trade and Cooperation Agreement Partnership Council and Withdrawal Agreement Joint Committee – the body that oversees the UK and EU implementation of the Withdrawal Agreement.
Parliamentary question on research infrastructure: increasing public expenditure on R&D to £20 billion per annum by 2024/2025. The total allocation for UK Research and Innovation over the period 2022-2025 is £25.1 billion. This includes £3 billion of investment in infrastructure projects, including £481 million for the new UKRI Infrastructure Fund. This will finance cutting-edge research infrastructure, delivering a step-change in the capabilities available to the next generation of researchers and innovators whilst supporting scientific breakthroughs.
Statutory duty of care for HE students
The House of Commons Petitions Committee held three sessions on the proposed statutory duty of care for HE students. Witnesses included Lee Fryatt, the petition creator, people with lived experience, representatives from Student Minds, NUS, PAPYRUS, AMOSSHE and UUK among others.
The Committee sessions explored whether universities should have a statutory duty of care to protect students at risk of suicide or other serious mental health problems. The sessions included advocacy for the duty of care; the reason for student suicide and views on the proposed statutory duty of care; and questioned sector representatives on their views plus the efficacy and future trajectory of existing suicide prevention and mental health frameworks. We have a summary of all three sessions here.
In advance of the session the House of Commons Library provided a briefing on student mental health.
Also on mental health from Wonkhe: The proportion of higher education providers with a mental health or wellbeing strategy increased from 52 per cent in 2019 to 66 per cent in 2022, according to a report from IFF Research for the Department for Education. 66 per cent of higher education institutions had a policy on student suicide prevention, alongside 54 per cent of FE colleges and just 42 per cent of private providers. On the site today I consider the report in light of calls for a statutory duty of care.
Student loan cap – 7.1%
Following the market rate fluctuation the Government has announced the student loan interest rate cap will now be 7.1% for all plan 2 (undergraduate) and plan 3 (postgraduate) loans, and plan 5 (undergraduate) loans. This applies until 31 August 2023 (or until future market changes prompt an announcement on a new cap level). You can see how 7.1% compares to previous in the written ministerial statement. The student loan interest rates from September 2023 will be announced closer to the time.
Access & Participation
TASO published the summary report Evaluating multi-intervention outreach and mentoring programmes with the aim of advancing the evidence base and improving practice across the sector. Recommendations:
- Universities should adopt TASO’s Mapping Outcomes and Activities Tool (MOAT),
- Multi-intervention outreach incorporates multiple elements. To rigorously evaluate the impact of these programmes, HEPs should identify the value of each element by using TASO’s Enhanced Theory of Change tool to map how it is anticipated that individual activities will influence outcomes.
- Also multi-intervention outreach programmes may be reaching students who are already highly likely to enter HE and highly selective universities. They further suggest that the true value of the programmes may lie in informing student choice about where and what to study, rather than whether to attend. Better pre-entry preparation may also result in higher rates of continuation and success once on the course. HEPs should scrutinise the rationale and assumptions behind their programmes to ensure that evaluation outcomes are well-matched to the activities they run
- Use behavioural and survey outcomes to mitigate for low response rates/small samples
- To improve response rates, HEPs should offer appropriate compensation to thank students for their time, such as entry into a prize draw or a small value voucher
- HEIs should use local evaluations as a blueprint to explore randomised controlled trials and quasi-experimental designs as part of their evaluation approach for multi-intervention outreach
And there’s another report: Understanding online mentoring delivered as part of multi-intervention outreach programmes
Wonkhe summarise both reports: Three randomised controlled trials at universities in England found that the programmes did not have an effect on student enrolment into higher education, though a final evaluation is still forthcoming. A separate study of online mentoring as part of outreach found that engagement with such programmes should not only be measured by the number of messages participants send – number of days engaged was a more robust measure.
Increasing access to HE
The OfS has published two reports on increasing access to HE covering collaborative partnerships and an evaluation of Uni Connect phase 3. You can read a summary of both here.
Labour’s Policy Programme
After the clearest indication yet from Keir Starmer a few weeks ago that the Labour policy on abolishing fees was going to be dropped, when he announced a “review” with the aim of finding an arrangement that would be fairer, the party have now made an interim announcement that they would reverse the latest changes, which will apply to students who start university in September – the bigger review of policy is still ongoing.
The Guardian piece quotes from a Times story that is behind a paywall:
- Labour has promised to reverse changes to the student loan system being plannedby the Conservative government in a way that could reduce monthly repayments for graduates.
- Bridget Phillipson, the shadow education secretary, said on Friday the tuition fees system was “broken”, but repeated the insistence by her party leader, Keir Starmer, that Labourwould not be able to afford to scrap fees altogether.
- Starmer’s decision to drop the promise to end feessparked anger among students and on the Labour left. But Phillipson’s comments in the Times give the first sense of how the party may seek to win those voters back. Phillipson said: “The Conservative tuition fees system has long been broken, and their latest set of reforms will make it worse.”
- She added: “Plenty of proposals have been put forward for how the government could make the system fairer and more progressive, including modelling showing that the government could reduce the monthly repayments for every single new graduate without adding a penny to government borrowing or general taxation – Labour will not be increasing government spending on this.”
- Under the plans announced by the Treasury last year, graduates will have to start repaying their loans when they earn £25,000, rather than £27,295, and will have to continue repaying for a maximum of 40 years rather than 30. Interest rates will be cut for new borrowers and tuition fees capped at £9,250 for another two years.
- The measures are predicted to double the number of graduates who pay off their loans in full, and save the government tens of billions of pounds. But lower earners will have to pay significantly more, thanks to the reduction in the lower repayment threshold.
Labour published their draft policy programme. It’s best thought of as a pre-manifesto but two steps removed. Within it, of interest to HE, is:
Give genuine choice of further and higher education
- Ensure all learners have a genuine choice of first class further and higher education
- Encourage a thriving college and independent training sector that can provide high quality vocational courses, including apprenticeships, fosters a love of learning, links students with exciting job opportunities through excellent careers advice, and works with businesses to meet local skills needs.
- Reform broken tuition fees system for university funding, ensuring that people from every background and all parts of our country have the opportunity to study at Britain’s world-class universities
Work with businesses, workers, and universities to grow the high-tech, competitive industries of the future:
- Ensure our world-class researchers and businesses have the data and computing infrastructure they need to compete internationally
- Ensure our intellectual property system is fit for the digital age
- Look at ways to close the digital divide. Improve digital education in schools and upskill the workforce
Introduce an industrial strategy and support firms
- Introduce an industrial strategy based on a genuine partnership with businesses, workers, unions and universities, with four central goals: delivering clean power by 2030, caring for the future, harnessing data for the public good and building a resilient economy
- Aim for at least 3% of GDP across the public and private sectors to be invested in research and development
- Ensure the funding system can act with the agility, speed and predictability required to win the race for the industries of the future
Deliver landmark shift in skills provision
- Deliver a landmark shift in skills provision and give people the tools they need in the workplaces of the future
- Devolve adult education and skills budgets; reform the apprenticeships levy into a ‘growth and skills levy’ across all nations
- Establish a new expert body – Skills England – to oversee the English national skills effort of the coming decade, which will pull together the expertise of trade associations, employers from large and small companies, representatives of trade unions, central and local government and further and higher education
Tackle NHS staffing issues
- Double the number of medical school places to 15,000 a year
- Train 10,000 new nurses and midwives each year
- Double the number of district nurses qualifying every year
- Train 5,000 new health visitors a year
Also Labour favours economic devolution, voting for 16 and 17 year olds, and abolishing the House of Lords.
There’s also a relevant Wonkhe blog: A Labour government may not mean the sector relationship reset that many are hoping for. Public First associate director Jess Lister cautions against raising expectations.
Inquiries and Consultations
Click here to view the updated inquiries and consultation tracker. Email us on policy@bournemouth.ac.uk if you’d like to contribute to any of the current consultations.
Other news
Campus fatigue: The QAA published Student experience and expectations of teaching and learning relating to post-pandemic students and trends. Wonkhe have a neat synopsis on part of the report: The pandemic appears to have created a “fatigue” amongst students to proactively engage with enrichment activities traditionally linked to campus life, student halls or SUs. It has also caused many students to feel isolated and to miss out on developing peer group friendships and relationships with academics, triggering an increased demand for mental health and well-being support… half of survey respondents found it not at all or only slightly important to spend time at university outside of timetabled hours – students most commonly were on campus two or three times a week, with 15.1 per cent having a commute of between one and two hours, and 4.4 per cent more than two hours.
Student rentals: Wonkhe – A renter’s reform bill has been published – and given the good news for tenants, some fear landlords will sell up. Jim Dickinson weighs up their case.
Apprenticeships: Wonkhe – The total number of apprenticeship starts has fallen significantly since the introduction of the Apprenticeship Levy, according to new analysis published by think tank Policy Exchange. Since 2015, the number of apprenticeship starts for 16-18 year-olds has fallen by 41 per cent, for 19-24 year-olds by 31 per cent, and 26 per cent for those over 25 years old. The sharpest falls recorded were for those from economically disadvantaged backgrounds… The authors do not believe that the sharp decline in starts is due to a lack of demand… Instead they point to a lack of supply, and a lack of transparency and poor understanding of the levy’s purposes – leading to a significant amount of the Levy returning to the Treasury rather than being spent on apprenticeships. They argue that for businesses to make better use of the levy system, there needs to be more flexibility, shorter courses, and less bureaucracy.
Working conditions: HEPI published a new report benchmarking the pay and benefits of academics and exploring whether academics have better or worse working conditions than other professionals.
Free Speech: Research Professional – News is out on the “chilling effect” of university failures to support free speech on campus. The Office for Students released yesterday its update on institutions’ compliance with the Prevent duty to monitor potential radicalisation on campus. And this includes figures on the number of speakers and events cancelled over the past year. See this Research Professional article: Fewer than 1% of English university speakers ‘cancelled’.
The latest OfS data show that during 2021-22, some 31,545 speakers or events were approved in English universities and colleges, and 260 planned events did not go ahead—just under one per cent of the total. Another 475 went ahead with some mitigation.
Most [of the events that did not go ahead] were rejected for procedural reasons, such as failing to submit a request on time. David Smy, director of monitoring and intervention at the OfS, said: “While this data suggests that the overwhelming majority of events with external speakers went ahead as planned—which is welcome—the data may not provide the full picture. The data does not capture decisions not to invite speakers in the first place or voluntary withdrawal of requests for approval. We recognise that this could be masking cases where event organisers or speakers feel unable to proceed with the event they had planned.” Surely the OfS is not about to make use of new advances in artificial intelligence that make mind-reading a possibility?
Transnational education: OfS published an insight brief on Transnational Education. In 2021-22, 146 English universities and colleges taught 455,000 students outside the UK. 69% were undergraduates, 31% were postgraduates.
- 27% were taught by overseas partner organisations
- 25% were taught by distance, flexible or distributed learning
- 6% studied at English universities’ overseas branch campuses
- 42% were covered by other arrangements, including collaborative provision.
52% lived in Asia – 61,505 (14% overall) were based in China. Malaysia (9%) and Sri Lanka (8%) had the second highest proportion of students.
Lots more interesting content in the full insight brief.
Subscribe!
To subscribe to the weekly policy update simply email policy@bournemouth.ac.uk. A BU email address is required to subscribe.
External readers: Thank you to our external readers who enjoy our policy updates. Not all our content is accessible to external readers, but you can continue to read our updates which omit the restricted content on the policy pages of the BU Research Blog – here’s the link.
Did you know? You can catch up on previous versions of the policy update on BU’s intranet pages here. Some links require access to a BU account- BU staff not able to click through to an external link should contact eresourceshelp@bournemouth.ac.uk for further assistance.
JANE FORSTER | SARAH CARTER
VC’s Policy Advisor Policy & Public Affairs Officer
Follow: @PolicyBU on Twitter | policy@bournemouth.ac.uk
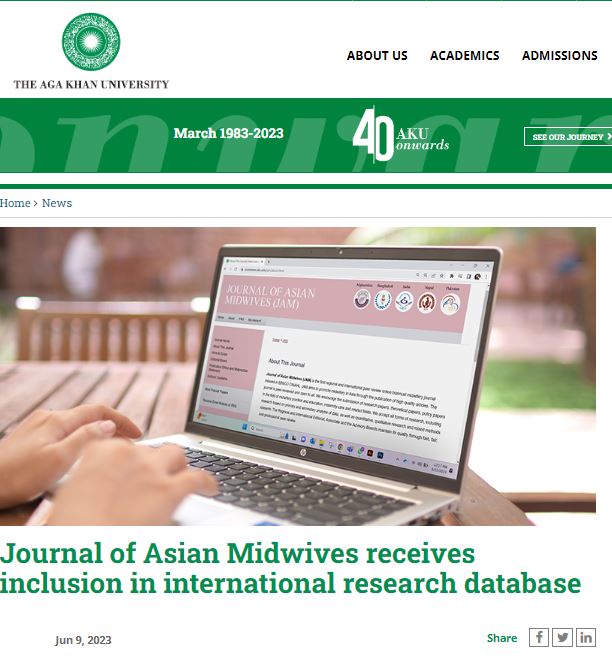 Last week The Aga Khan University (AKU) in Pakistan put a news story on its website highlighting a first for Pakistan. The reason for celebrating was that the Journal of Asian Midwives, one of the only two research journals hosted by The Aga Khan University, has been accepted for inclusion in Scopus. Scopus, which is part of the publishing house Elsevier, is the world’s largest electronic database of peer-reviewed literature: scientific journals, books and conference proceedings. The Journal of Asian Midwives is an Open Access journal and publishing is free. One of its three co-editors is based at Bournemouth University.
Last week The Aga Khan University (AKU) in Pakistan put a news story on its website highlighting a first for Pakistan. The reason for celebrating was that the Journal of Asian Midwives, one of the only two research journals hosted by The Aga Khan University, has been accepted for inclusion in Scopus. Scopus, which is part of the publishing house Elsevier, is the world’s largest electronic database of peer-reviewed literature: scientific journals, books and conference proceedings. The Journal of Asian Midwives is an Open Access journal and publishing is free. One of its three co-editors is based at Bournemouth University. 







 With more sunny days across Dorset last and this week, we are all very close to summer holiday season. There are more than 120 external funding applications the Funding Development Team is currently supporting and I wanted to share some good news.
With more sunny days across Dorset last and this week, we are all very close to summer holiday season. There are more than 120 external funding applications the Funding Development Team is currently supporting and I wanted to share some good news.




 Last we took a new step into the academic publishing by submitting a paper to Qeios. This Open Access journal publishes papers for free, more or less immediately and after the paper has appeared online peer-reviewers are being invited. The paper ‘
Last we took a new step into the academic publishing by submitting a paper to Qeios. This Open Access journal publishes papers for free, more or less immediately and after the paper has appeared online peer-reviewers are being invited. The paper ‘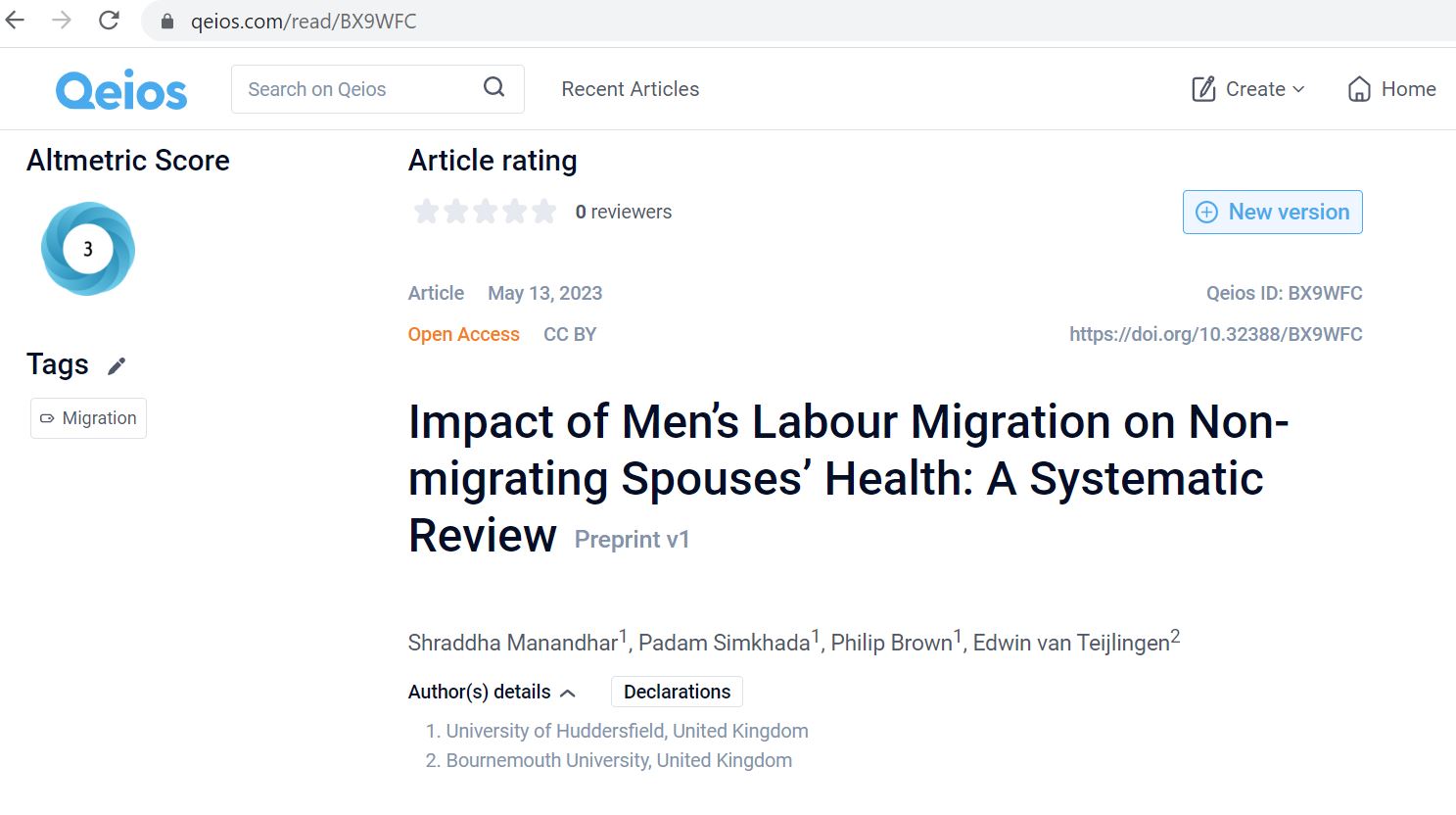

















 Read and sign up to BU’s Policy Influence Digest
Read and sign up to BU’s Policy Influence Digest Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally
Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant
BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant New COVID-19 publication
New COVID-19 publication MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024 Horizon Europe News – December 2023
Horizon Europe News – December 2023