Peer review is the the key pillar of academic publishing. Peer reviewers will read the submitted paper and assess its knowledge contribution, the appropriateness of the research question, the ethical considerations, the quality of the research methods used and the appropriateness of the discussion, conclusion, and recommendations in the manuscript. [1] It is worth bearing in mind that most peer reviewers are unpaid volunteers, academics like us who review for journals over and above the day job.[2] For the authors peer reviewers can give excellent feedback. Harvey and colleagues remind their readers that peer reviewers reading your manuscript with a fresh pair of eyes, can lead to them raising great questions and offering useful comments. In short, reviewers’ reservations and misunderstandings can help you to rephrase and better focus your paper. [3]
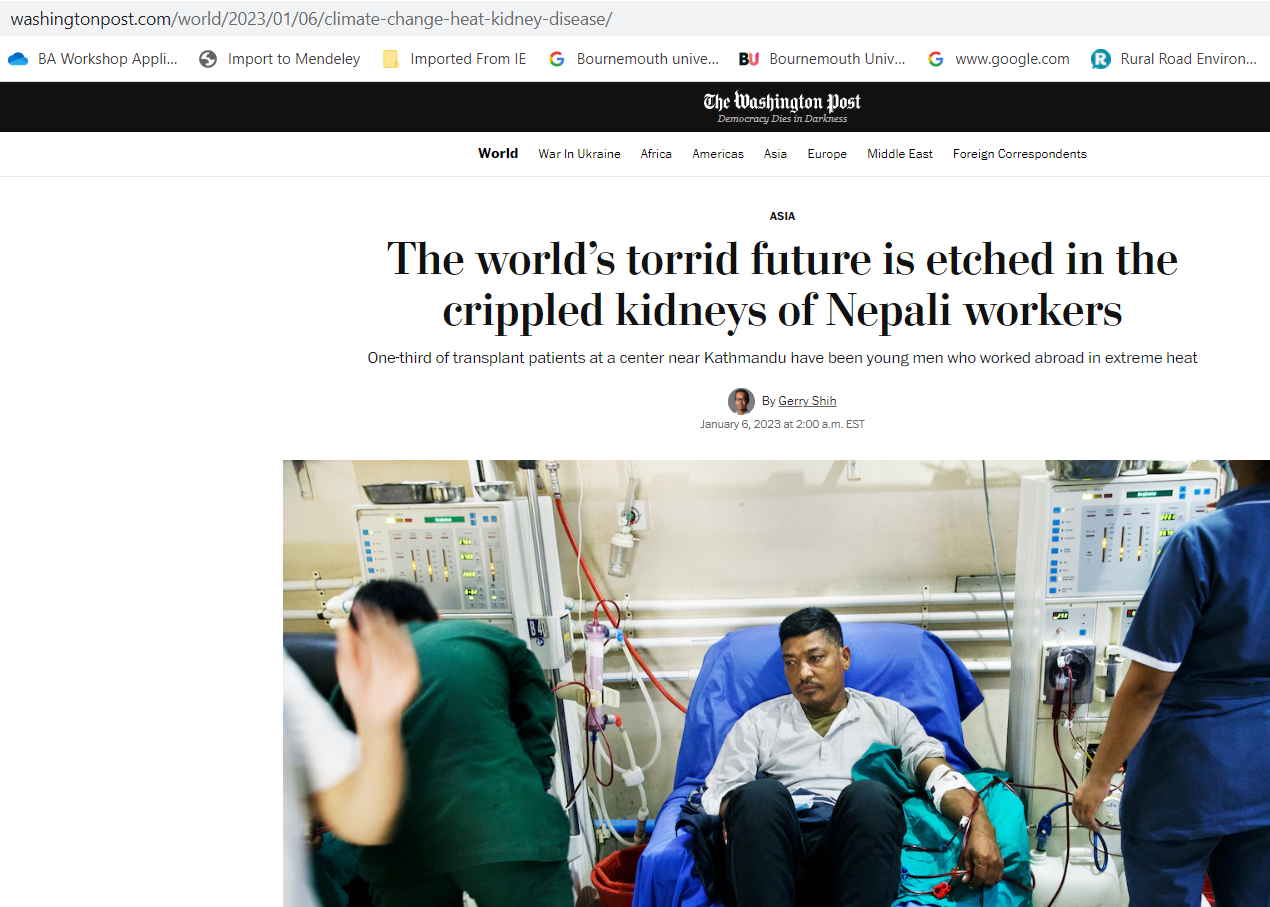
However, what the review process does not do is picking up every possible minor mistake and typo in a paper. I was reminded of this last week when I read a peer-reviewed paper in which the basic demographics table (the characteristics of the study participants) did not add up to 100%. Luckily, the same authors (who shall remain nameless) published a different paper from the same study in another quality journal, which allowed me to check the numbers. Interestingly, the second paper in another peer-reviewed journal had the same mistake. In the end I ended up writing to two different editors pointing out this anomaly. The editors contacted the authors who have since promised to rectify the mistake.
 Something similar has also happened to us. Occasionally I reread one of our articles in a good journal and wonder about some of the unclear sentences or poorly expressed grammar or style. Neither the editor nor the peer-reviewers spotted it nor did my co-authors and I noticed these mistakes in the paper proofs.
Something similar has also happened to us. Occasionally I reread one of our articles in a good journal and wonder about some of the unclear sentences or poorly expressed grammar or style. Neither the editor nor the peer-reviewers spotted it nor did my co-authors and I noticed these mistakes in the paper proofs.
Prof. Edwin van Teijlingen
CMMPH (Centre for Midwifery, Maternal & Perinatal Health)
References:
- van Teijlingen, E., Simkhada, P., Shanker, S. (2022) Selecting an Appropriate Journal and Submitting your Paper, In: Wasti, S.P., et al. (Eds.) Academic Writing and Publishing in Health & Social Sciences, Kathmandu, Nepal: Himal Books: 20-31.
- van Teijlingen, E., Thapa, D., Marahatta, S.B., Sapkota, J.L., Regmi, P. Sathian, B. (2022) Editors and Reviewers: Roles and Responsibilities, In: Wasti, S.P., et al. (Eds.) Academic Writing and Publishing in Health & Social Sciences, Kathmandu, Nepal: Himal Books: 32-37.
- Harvey, O., Taylor, A., Regmi, P.R., van Teijlingen, E. (2022) Struggling to reply to reviewers: Some advice for novice researchers. Health Prospect, 21(2):19-22.



















 Collaboration with Norway
Collaboration with Norway I the meantime, on Thursday 10 November UK has signed major science co-operation agreement with Switzerland.
I the meantime, on Thursday 10 November UK has signed major science co-operation agreement with Switzerland.

 About ten days ago I published a blog regarding
About ten days ago I published a blog regarding  According to UK Research Office (UKRO), the Commission’s Directorate-General for Research and Innovation will host
According to UK Research Office (UKRO), the Commission’s Directorate-General for Research and Innovation will host  The Commission’s Directorate-General for Research and Innovation will host hybrid
The Commission’s Directorate-General for Research and Innovation will host hybrid  As you may know, Government’s policy is to encourage UK researchers to continue to apply for Horizon Europe grants despite uncertainty over association. This time I wanted to tell how other countries are progressing with the association.
As you may know, Government’s policy is to encourage UK researchers to continue to apply for Horizon Europe grants despite uncertainty over association. This time I wanted to tell how other countries are progressing with the association.










 Read and sign up to BU’s Policy Influence Digest
Read and sign up to BU’s Policy Influence Digest Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally
Upcoming opportunities for PGRs – collaborate externally BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant
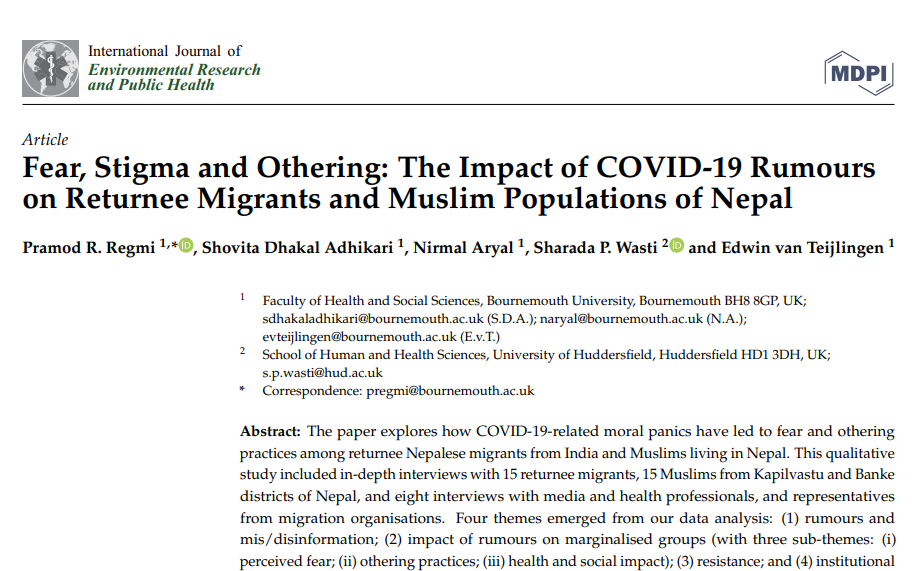
BU involved in new MRF dissemination grant New COVID-19 publication
New COVID-19 publication MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024
MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2024 Horizon Europe News – December 2023
Horizon Europe News – December 2023